Symptoms
4 rows · Jun 01, 2011 · Surgical treatment. Mild bunion. Shaves the bony excess on the outside of the metatarsal head. ...
Causes
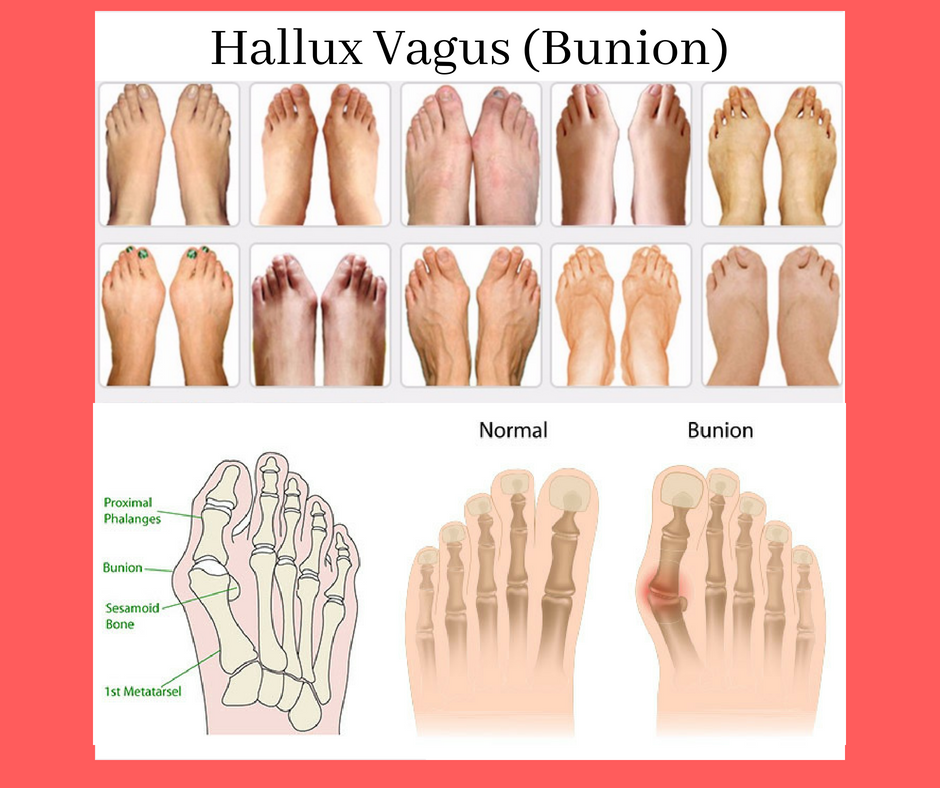
A bunion is a bump that forms on the outside of the big toe. This foot deformity occurs from years of pressure on the big toe joint (the metatarsophalangeal, or MTP, joint). Eventually, the toe joint gets out of alignment, and a bony bump forms. The medical term for bunions is hallux abducto valgus. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Prevention
What causes bunions? Bunions may develop due to a variety of biological or environmental factors, including arthritis, biomechanical factors, neuromuscular disorders, genetic disorders, and trauma. Arthritic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, typically cause inflammation of many joints in the body and may affect the MTP joint.
Complications
Sep 19, 2013 · The general idea behind natural bunion treatments is to address the underlying cause of the bunion; that is, footwear that forces the big toe into a deviated position. Using footwear that allows your toes to splay as nature intended is an essential part of an effective bunion treatment plan.
What is the difference between gout vs bunion?
A bunion, or hallux valgus, is a hard bump that develops on the outside of the joint where the big toe meets the ball of the foot. Bunions are usually a result of excess, prolonged pressure on the area, and eventually push the big toe toward the other toes. Bunions most frequently occur in adults, but some children can be born with congenital ...
When should I have surgery for my bunions?
A bunion can also be the result of heredity or arthritis. If you have developed a bunion, it is wise to consult with a podiatrist earlier rather than later. The podiatrist can examine the area and help you decide the correct measures to take. Treatment ranges from elastic bunion pads or shoe inserts in minor cases to surgery in the most severe.
Does my bunion need surgery?
Nov 17, 2020 · A bunion is a physical deformity in which the big toe moves and points toward the second toe. Initial treatment is normally conservative and focuses on relieving symptoms.
Why do bunions get worse over time?
Apr 12, 2022 · How our Sterling Heights, MI, podiatrists recommend treating a bunion will depend on the severity of the deformity. It’s important to recognize the early warning signs of a bunion so you can turn to us right away for care. In the beginning stages, our goal is to create a treatment plan that will slow the progress of the deformity.

How do you get a bunion to go away?
Wear wide shoes with a low heel and soft sole. In most cases, bunion pain is relieved by wearing wider shoes with adequate toe room and using other simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe.Try bunion pads. ... Hold an ice pack. ... Take paracetamol or ibuprofen. ... Try to lose weight.Nov 30, 2018
Do bunions need to be treated?
You may need bunion surgery if you have severe foot pain that happens even when walking or wearing flat, comfortable shoes. Surgery may also be needed when chronic big toe inflammation and swelling isn't relieved with rest or medicines.
Can bunions be treated at home?
Although bunions will not heal on their own, natural bunion treatment can help to alleviate the pain and pressure they cause. A person should talk with a doctor if their bunion is causing severe pain or other issues. People can use padding and wear comfortable shoes to help reduce pressure on the big toe.Feb 10, 2022
What is the main cause of bunions?
Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or make them worse. Bunions can also develop as a result of the shape of your foot, a foot deformity or a medical condition, such as arthritis. Smaller bunions (bunionettes) can develop on the joint of your little toe.Nov 6, 2021
How can I shrink my bunions naturally?
0:3410:10HOW TO SHRINK BUNIONS NATURALLY | Bunion ExercisesYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMake sure we're rolling off that mound of your big toe come up and then back down things you want toMoreMake sure we're rolling off that mound of your big toe come up and then back down things you want to be careful of is not gripping with your toes.
Can you push a bunion back in?
It's really quite simple: With the use of bunion splints or toe spacers (such as Correct Toes—McClanahan's own invention) toes can be gradually restored to a more natural position, thereby undoing the motion that pushes the bunion out. In other words, as your toes spread out, the bunion starts to recede.Feb 17, 2015
What cream helps bunions?
Use a topical pain-relief gel over the bunion Quality topical gels like biofreeze can reduce short term pain and inflammation. Since it's only temporary relief, you may grow tired of continually icing and applying gel over time and the cost will add up.
What are the five steps to fix a bunion?
1:1614:40How to Fix Bunions in 5 Steps - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlan to overcome these issues the first and probably the greatest cause of bunions is wearing shoesMorePlan to overcome these issues the first and probably the greatest cause of bunions is wearing shoes that have a narrow toe.
Painful Bunions Interfere With Walking and Exercising, but You Can Keep Them from Getting worse.
Many women have a bunion — a deformity of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint at the base of the big toe. A bunion develops when the first metatars...
Why Bunions Need Attention
The MTP joint helps us bear and distribute weight during a range of activities. A bunion at this critical junction of bones, tendons, and ligaments...
Outcomes and Complications of Bunion Surgery
Variations among toe-joint deformities and surgical techniques make it difficult to evaluate the results of bunion surgery. Some studies suggest th...
What is a bunion?
A bunion, or a hallux valgus, refers to a bulge at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP joint) of the big toe, also referred to as the base of the bi...
What causes bunions?
Bunions may develop due to a variety of biological or environmental factors, including arthritis, biomechanical factors, neuromuscular disorders, g...
Are bunions genetic?
Bunions are not necessarily genetic; however, some of the causes of bunions can be inherited, or passed down from a person’s parents. For example,...
What does a bunion look like?
A bunion typically presents as a red or swollen bulge at the base of the big toe. Over time, the phalanges of the big toe may gradually protrude fu...
What are the signs and symptoms of a bunion?
Signs and symptoms of a bunion vary depending on severity. Regardless, all bunions appear as a bulge at the base of the big toe. A dull, achy pain...
How is a bunion diagnosed?
A bunion is usually diagnosed through physical examination. During the physical exam, a clinician will typically ask about the severity of the symp...
How is a bunion treated?
Initial treatment for a bunion typically consists of conservative measures, like wearing supportive, well-fitting shoes with a wider toe box (i.e.,...
What are the most important facts to know about bunions?
Bunions, characterized by a bulge of the joint at the base of the big toe, where the metatarsal and phalangeal bones meet, are among the most commo...
How to treat a bunion?
Nonsurgical treatments that may relieve the pain and pressure of a bunion include: 1 Changing shoes. Wear roomy, comfortable shoes that provide plenty of space for your toes. 2 Padding. Over-the-counter, nonmedicated bunion pads or cushions may be helpful. They can act as a buffer between your foot and your shoe and ease your pain. 3 Medications. Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) can help you control the pain of a bunion. Cortisone injections also might help. 4 Shoe inserts. Padded shoe inserts can help distribute pressure evenly when you move your feet, reducing your symptoms and preventing your bunion from getting worse. Over-the-counter supports can provide relief for some people; others require prescription orthotic devices. 5 Applying ice. Icing your bunion after you've been on your feet too long or if it becomes inflamed can help relieve soreness and swelling. If you have reduced feeling or circulation problems with your feet, check with your doctor first before applying ice.
How long does it take to recover from a bunion?
It's possible that you'll be able to walk on your foot right after a bunion procedure. However, full recovery can take weeks to months. To prevent a recurrence, you'll need to wear proper shoes after recovery.
What to do if your toes hurt?
Padding. Over-the-counter, nonmedicated bunion pads or cushions may be helpful. They can act as a buffer between your foot and your shoe and ease your pain. Medications.
Can bunion surgery be done?
Surgery is not recommended for cosmetic reasons; only when a bunion causes you frequent pain or interferes with your daily activities. There are many surgical procedures for bunions, and no one technique is best for every problem. Surgical procedures for bunions can be done as single procedures or in combination.
How to relieve pressure on bunion?
The first step is to relieve the pressure by wearing the right kind of shoe. (It's also important to maintain a normal weight.) Shoes should have a wide, flexible sole to support the foot and enough room in the toe box (the part surrounding the front of the foot) to accommodate the bunion.
Why do bunions run in families?
Bunions run in families, because foot type (shape and structure) is hereditary, and some types are more prone to bunions than others. Low arches, flat feet, and loose joints and tendons all increase the risk.
Why do women have bunions?
Women can develop bunions and other foot problems during pregnancy because hormonal changes loosen the ligaments and flatten the feet. Bunions are also associated with arthritis, which damages the cartilage within the joint.
What is a bunion in women?
Many women have a bunion — a deformity of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint at the base of the big toe. A bunion develops when the first metatarsal bone of the foot turns outward and the big toe points inward (toward the other toes), causing the joint to jut out (see "Anatomy of a bunion"). The Latin name for the deformity is hallux valgus ( ...
How long does it take to recover from bunion surgery?
You won't necessarily get rid of all your symptoms, and you'll have to stay off your foot for many weeks. Complete recovery can take a year or more, depending on the procedure. As with any surgery, you'll want to make sure the surgeon is experienced in performing the particular operation you've decided to undergo. You may also want to talk to other patients who've had the operation.
How long does it take to heal a metatarsal bunion?
Shaves the bony excess on the outside of the metatarsal head. Realigns the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint. Recovery takes 3–4 weeks and usually involves wearing a postoperative shoe. May not correct the deformity that caused the bunion.
How to prevent bunions from getting worse?
Proper-fitting footwear is key to preventing bunions or keeping an existing bunion from getting worse. Your healthcare provider can offer tips on how to select appropriate shoes. In general, you should buy shoes with a wide toe box and soft soles.
How to prevent bunions in feet?
Avoid shoes that are narrow and pointed at the tip, and high heels that put pressure on the front of the foot. If you have flatfeet or another inherited structural foot problem, custom-fitted orthotics can help prevent, or slow the progression of, bunions.
What is a bunion on the outside of the big toe?
What is a bunion? A bunion is a bump that forms on the outside of the big toe. This foot deformity occurs from years of pressure on the big toe joint (the metatarsophalangeal, or MTP, joint). Eventually, the toe joint gets out of alignment, and a bony bump forms. The medical term for bunions is hallux abducto valgus.
How to stop bunion pain?
Your provider can recommend other treatment options, such as shoe gear modifications, physical therapy, medications and orthotics. Treatments can reduce pain and stop bunion symptoms from getting worse. If the pain becomes severe, surgery to remove the bunion and realign the big toe can help you get moving again.
What does a bunion look like?
A bunion resembles a turnip — red and swollen. In fact, some sources say the word bunion comes from the Greek word for turnip. Other symptoms include: Inability to bend the big toe, or pain and burning when you try to bend it.
How to diagnose a bunion?
A bunion is usually diagnosed through physical examination. During the physical exam, a clinician will typically ask about the severity of the symptoms, inspect the foot, and observe the person’s gait, or the way they walk.
What is a bunion in the foot?
What is a bunion? A bunion, or a hallux valgus, refers to a bulge at the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP joint) of the big toe, also referred to as the base of the big toe. The MTP joint is the link between the metatarsal bone (i.e., the long bone of the toe) and the proximal, or first, phalange (i.e., the short bone of the toe).
What is the most common foot problem?
Bunions are one of the most common foot problems, especially among older adults and individuals who frequently wear tight shoes or high heels. The foot is composed of several bones that form the ankle (i.e., tarsal bones) and the long bones that extend out to form the toes (i.e., metatarsal bones and phalanges ).
Can bunions be genetic?
Bunions are not necessarily genetic; however, some of the causes of bunions can be inherited, or passed down from a person’s parents. For example, the shape of an individual's foot is typically passed down through families. Additionally, some inherited genetic disorders can increase the likelihood of bunion formation in an individual.
What Are Bunions?
A bunion is a sometimes painful dislocation of the 1st or 5th metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. A bunion appears to be a bump or prominence located at the base of the big or, in the case of a tailor’s bunion, at the base of the little toe, or both.
What Causes Bunions?
Bunions are a problem only among shod, or shoe-wearing, populations. A bunion is caused by shoes that possess tapering toe boxes, or toe boxes that force your big and/or little toes toward your foot’s midline. Tapering toe boxes, especially when combined with rigid soles, hold your foot and toes in a bunion configuration.
What Are Some Natural Treatment Approaches?
Natural treatment approaches to bunions are simple, noninvasive, and effective. The general idea behind natural bunion treatments is to address the underlying cause of the bunion; that is, footwear that forces the big toe into a deviated position.
Conclusion
Bunions, though often painful, are not life threatening. They are, however, a sign of inappropriate footwear use. Bunions are almost non-existent in unshod or minimally-shod populations, such as indigenous groups in Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia.
