...
Medications to treat myocardial ischemia include:
- Aspirin. ...
- Nitrates. ...
- Beta blockers. ...
- Calcium channel blockers. ...
- Cholesterol-lowering medications. ...
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ...
- Ranolazine (Ranexa).
Medication
Treatment. The goal of myocardial ischemia treatment is to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. Depending on the severity of your condition, your doctor may recommend medications, surgery or both. Medications. Medications to treat myocardial ischemia include: Aspirin.
Procedures
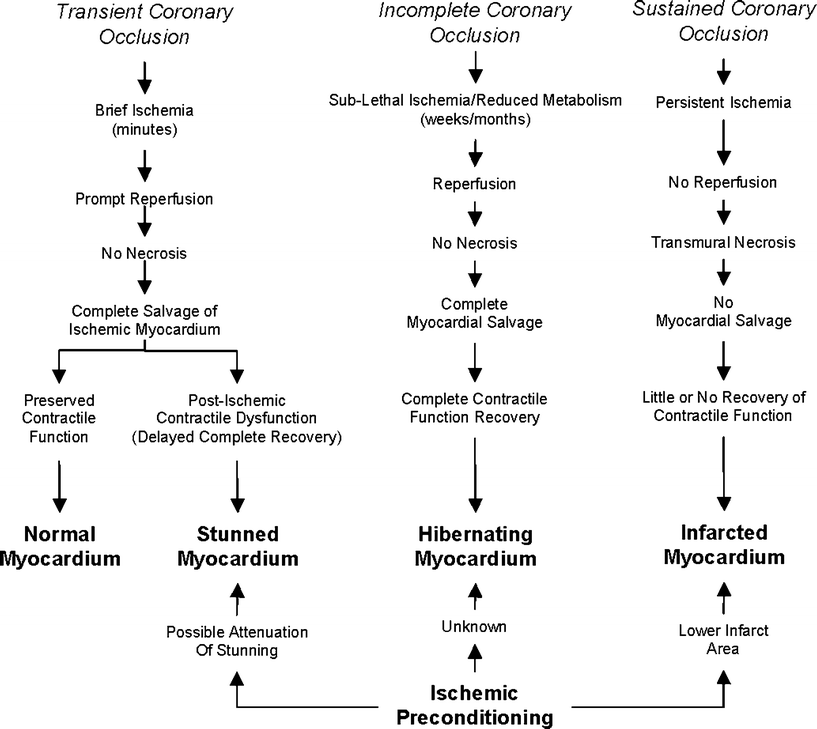
Ischemia denotes diminished volume of perfusion, while infarction is the cellular response to lack of perfusion. Some of the changes discussed here are the result of ischemia such as those involving myocardial substrate extraction.
Self-care
After that, your doctor might recommend:
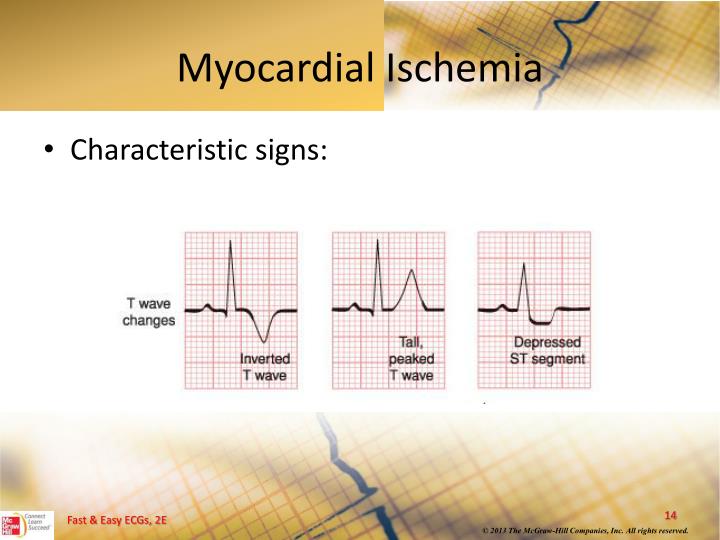
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). The electrical activity of your heart is recorded via electrodes attached to your skin. ...
- Echocardiogram. Sound waves directed at your heart from a wand-like device held to your chest produce video images of your heart. ...
- Nuclear scan. ...
- Coronary angiography. ...
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan. ...
- Cardiac CT scan. ...
- Stress test. ...
Nutrition
Myocardial ischemia, also called cardiac ischemia, reduces the heart muscle's ability to pump blood. A sudden, severe blockage of one of the heart's artery can lead to a heart attack. Myocardial ischemia might also cause serious abnormal heart rhythms.
What is the overall treatment for ischemia?
What is the difference between ischemia and infarction?
How do you treat cardiac ischemia?
What condition can myocardial ischemia lead to?
What is the treatment for myocardial ischemia?
Treatment for myocardial ischemia involves improving blood flow to the heart muscle. Treatment may include medications, a procedure to open blocked arteries (angioplasty) or bypass surgery.
Can heart ischemia be cured?
Lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery can successfully treat ischemic heart disease. You can reduce your risk of this disease by following heart-healthy practices.
Can myocardial ischemia be reversed?
Generally, if the patients received timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment, the ischemia can be reversed and a favorable prognosis could be expected. Otherwise, reversible myocardial ischemia may develop into myocardial infarction, which is irreversible and the prognosis may be poor.
How long can you live with myocardial ischemia?
About 68.4 per cent males and 89.8 per cent females still living have already lived 10 to 14 years or longer after their first infarction attack; 27.3 per cent males, 15 to 19 years; and 4.3 per cent, 20 years or longer; of the females, one is alive 15 years, one 23 years and one 25 years or longer.
Is myocardial ischemia the same as coronary artery disease?
Myocardial ischemia can develop slowly as arteries become blocked over time. Or it can occur quickly when an artery becomes blocked suddenly. Conditions that can cause myocardial ischemia include: Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis).
Can you exercise with ischemia?
It is generally accepted that exercise training intensity in patients with ischaemic heart disease (IHD) should correspond to a heart rate that remains 10 b.p.m. below the threshold for myocardial ischaemia (1 mm ST-segment depression).
Is myocardial ischemia the same as angina?
Myocardial ischemia is one of the more common causes of chest pain (also termed "chest discomfort") in adults. Angina pectoris, or angina for short, is the term used when chest discomfort is thought to be attributable to myocardial ischemia.
What are some of the symptoms someone with myocardial ischemia may experience?
Other myocardial ischemia symptoms can also include: Pain or discomfort in your upper body, including your arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw or stomach. Trouble breathing or feeling short of breath. Sweating or "cold sweat."
How to treat myocardial ischemia?
Your doctor will talk to you about the treatment that is best for you, which may include medications or procedures to improve blood flow to the heart muscle .
What is the most common symptom of myocardial ischemia?
The most common symptom of myocardial ischemia is angina (also called angina pectoris). Angina is chest pain that is also described as chest discomfort, heaviness, tightness, pressure, aching, burning, numbness, fullness, or squeezing. It can feel like indigestion or heartburn.
What causes supply problems in the heart?
The supply problem can be caused by coronary artery disease. This is a build-up of plaque and cholesterol inside the coronary arteries. The build-up narrows the artery so much that the oxygen-rich blood the heart needs can’t get through, and the heart muscle becomes starved for oxygen. This causes ischemia and angina. (need picture of obstructive CAD).
What are the symptoms of ischemia?
Nausea or vomiting. Feeling light-headed, dizzy, very weak or anxious. Fast or irregular heartbeat. If you have angina or any of the symptoms of ischemia listed above that last for more than 5 minutes, CALL 9-1-1 RIGHT AWAY! You may be having a heart attack or have a coronary artery that is completely blocked.
Why does my heart get ischemia?
Ischemia is most likely to happen when your heart needs more oxygen and nutrients than it is getting. It is simply a supply-demand imbalance that happens at times when there is more demand for blood, such as when you are active, eating, excited, stressed or in the cold, and your body can’t keep up with the need for more blood.
Can angina go away when you take medication?
Unstable angina can happen at any time, even when you are relaxed or sleeping. It may not go away when you take medication. Symptoms of myocardial ischemia can also include: Pain or discomfort in the upper body, including the arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw or stomach. Trouble breathing or feeling short of breath.
How to treat myocardial ischemia?
Treatment may include medications, a procedure to open blocked arteries (angioplasty) or bypass surgery.
What happens if myocardial ischemia is blocked?
If a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, the lack of blood and oxygen can lead to a heart attack that destroys part of the heart muscle. The damage can be serious and sometimes fatal. Irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
What are the factors that increase the risk of myocardial ischemia?
Factors that can increase your risk of developing myocardial ischemia include: Tobacco. Smoking and long-term exposure to secondhand smoke can damage the inside walls of arteries. The damage can allow deposits of cholesterol and other substances to collect and slow blood flow in the coronary arteries.
What side of the body does myocardial ischemia occur?
When they do occur, the most common is chest pressure or pain, typically on the left side of the body (angina pectoris).
Can myocardial ischemia develop slowly?
Myocardial ischemia can develop slowly as arteries become blocked over time. Or it can occur quickly when an artery becomes blocked suddenly.
Can a spasm in the heart cause myocardial ischemia?
This temporary tightening of the muscles in the artery wall can briefly decrease or even prevent blood flow to part of the heart muscle. Coronary artery spasm is an uncommon cause of myocardial ischemia. Chest pain associated with myocardial ischemia can be triggered by: Physical exertion. Emotional stress.
What is myocardial ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia is a disorder that is usually caused by partial or complete blockage of your heart’s coronary arteries , which is also known as atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (coronary heart disease) (see Figures 1 and 2).
Why is it important to diagnose myocardial ischemia?
Diagnosing myocardial ischemia prior to a heart attack is important because ischemic heart disease is responsible for approximately 14% of all deaths worldwide. Approximately 1.5 million Americans will have a heart attack this year as a result of myocardial ischemia; about 500,000 of those will be fatal.
What is the difference between a heart attack and a myocardial infarction?
Myocardial ischemia vs myocardial infarction. Myocardial infarction (MI) is a medical term for a heart attack. Myocardial infarction (heart attack) is a serious medical emergency in which the supply of blood to the heart is suddenly blocked, usually by a blood clot. Without the blood coming in, the heart can’t get oxygen.
What side of the body does myocardial ischemia pain occur?
When signs and symptoms occur, the most common is chest pressure or pain, typically on the left side of the body (angina pectoris).
Can a spasm in the heart cause myocardial ischemia?
Coronary artery spasm. This temporary tightening of the muscles in the artery wall can briefly decrease or even prevent blood flow to part of the heart muscle. Coronary artery spasm is an uncommon cause of myocardial ischemia.
Can myocardial ischemia develop slowly?
Myocardial ischemia can develop slowly as arteries become blocked over time. Or it can occur quickly when an artery becomes blocked suddenly.
Is ECG monitoring an initial procedure?
Exercise with ECG monitoring alone is the initial procedure of choice in patients without baseline ST-segment abnormalities or in whom anatomic localization of ischemia is not a consideration. Note the following:
What is Myocardial Ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia is a condition that is characterized by inadequate blood flow in the coronary arteries (of the heart) owing to a partial or complete blockage of the arteries. The disease causes the heart muscles to lose their ability to pump blood and causes severe abnormal heart rhythms.
Signs & Symptoms
Patients may have myocardial ischemia and still not present any signs and symptoms. However, it typically causes pressure with pain in the chest and pain on the left side of the body. Some common symptoms of myocardial ischemia include:
Causes of Myocardial Ischemia
The disease myocardial ischemia occurs when the blood flow through one or more coronary arteries is impaired. The ischemic condition develops gradually as the arteries become blocked over time. The decrease in blood flow also reduces the amount of oxygen that your heart muscles receive. The conditions that cause myocardial ischemia are:
Risk Factors
Certain factors can enhance your risk of developing myocardial ischemia. Some of them are:
Diagnosis
Your cardiologist may recommend a few of the following tests depending on your illness to diagnose myocardial ischemia:
Complications
The chest pain occurring in myocardial ischemia is usually triggered by factors such as physical exertion, emotional stress, consumption of heavy meals, use of cocaine, and cold temperatures. Delays in the treatment can be deadly and also lead to permanent damage to the heart.
Treatment of Myocardial Infarction
Medications: Your doctor will prescribe medications or recommend surgery depending on the severity of the illness. Medications that improve the blood flow in the heart muscles may be used. These include the use of aspirin, nitrates, cholesterol-lowering medicines, blood pressure-lowering medications, and diuretics.
What is the best medication for ischemia?
We may prescribe a medication regimen for you to follow to reduce your symptoms and help prevent future attacks. Medications include: Organic nitrates, to relax muscles. Beta blockers, to reduce the amount of work your heart needs to do. Statins, to reduce cholesterol levels.
What is the procedure for ischemia?
Surgery for Ischemic Heart Disease. If your symptoms are severe or not responding to treatment, our doctors may recommend a cardiac catheterization procedure. During a cardiac catheterization, we can determine the extent of the disease. We may then decide to do a procedure that will open up blocked arteries:
What is the goal of ischemic heart disease?
The goal of treatment for ischemic heart disease is to prevent myocardial infarction ( heart attack ), reduce symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Our cardiologists are involved in refining current heart disease therapy and pioneering new treatment options, including
Is myocardial injury the same as MI?
Myocardial injury is similar but does not fulfill the clinical criteria for MI. There is uncertainty in terms of the clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of type 2 MI and myocardial injury in comparison with type 1 MI.
Is MI type 2 more likely to be treated than type 1?
Patients with type 2 MI and myocardial injury were less likely to receive medical therapy for CAD than those with type 1 MI. No differences in all-cause mortality among MI subtypes were observed. Additional studies to determine optimal medical therapy and risk stratification strategies for these hig …

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Complications
- Your doctor will start by asking questions about your medical history and with a physical exam. After that, your doctor might recommend: 1. Electrocardiogram (ECG).Electrodes attached to your skin record the electrical activity of your heart. Certain changes in your heart's electrical activity …
Prevention