
Medication
Options include:
- Aripiprazole (Abilify)
- Brexpiprazole ( Rexulti)
- Haloperidol ( Haldol)
- Olanzapine ( Zyprexa)
Self-care
Some research has found that Aricept can postpone the worsening of Alzheimer's symptoms for 6 to 12 months in about half of the people who take it. For many, the improvement is minimal, yet worthwhile. Anecdotal evidence suggests that a small percentage of people may benefit more dramatically from this drug.
See more
New Alzheimer's Treatment Could Reverse Brain Damage . A new drug that promises to slow cognitive decline is having great success in early clinical trials. Learn more about this drug, the studies that have been done to determine its success, and what will come next for the newest hope in Alzheimer's treatment.
What therapies are used to treat Alzheimer's disease?
Alzheimer's disease is complex, and it is unlikely that any one drug or other intervention will successfully treat it. Current approaches focus on helping people maintain mental function, manage behavioral symptoms, and slow down the symptoms of disease.
Is Aricept effective in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease?
Could new treatment reverse Alzheimer's?
Can we find cure for Alzheimer's disease?
See more
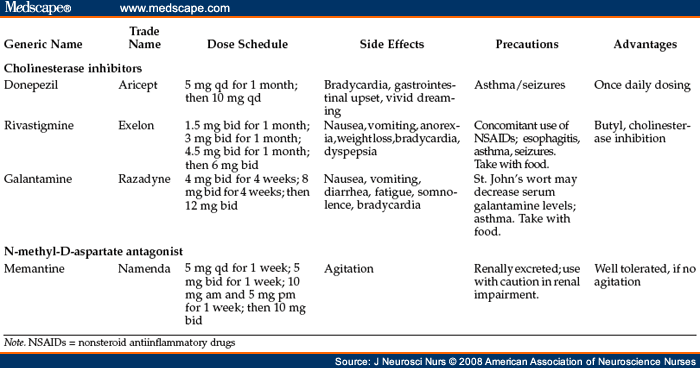
What are 3 treatments for Alzheimer's?
Three cholinesterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed:Donepezil (Aricept) is approved to treat all stages of the disease. It's taken once a day as a pill.Galantamine (Razadyne) is approved to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's. ... Rivastigmine (Exelon) is approved for mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease.
How is Alzheimer's treated or cured?
There's currently no cure for Alzheimer's disease. But there is medicine available that can temporarily reduce the symptoms. Support is also available to help someone with the condition, and their family, cope with everyday life.
What is the most promising treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
Aducanumab (Aduhelm™) has received accelerated approval as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This is the first FDA-approved therapy to address the underlying biology of Alzheimer's disease.
What treatments are available for dementia?
Medications. The following are used to temporarily improve dementia symptoms. Cholinesterase inhibitors. These medications — including donepezil (Aricept), rivastigmine (Exelon) and galantamine (Razadyne) — work by boosting levels of a chemical messenger involved in memory and judgment.
When is Alzheimer's cured?
With a growing understanding of how AD affects the neurons in the brain, finally, there has been an Alzheimer's cure breakthrough 2022. The majority of research has focused on the plaques in the brain of AD individuals.
How do you slow down Alzheimer's?
How to reduce your risk of Alzheimer's and other dementiasPhysical activity.Eating healthily.Don't smoke.Drink less alcohol.Stay mentally and socially active.Take control of your health.
Why is there no cure for Alzheimer's disease?
There is currently no "cure" for dementia. In fact, because dementia is caused by different diseases it is unlikely that there will be a single cure for dementia. Research is aimed at finding cures for dementia-causing diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies.
What's the difference between dementia and Alzheimer's?
While dementia is a general term, Alzheimer's disease is a specific brain disease. It is marked by symptoms of dementia that gradually get worse over time. Alzheimer's disease first affects the part of the brain associated with learning, so early symptoms often include changes in memory, thinking and reasoning skills.
How to help someone with Alzheimer's?
For someone with Alzheimer's, establishing and strengthening routine habits and minimizing memory-demanding tasks can make life much easier .
What are some ways to prevent Alzheimer's?
Alternative medicine. Various herbal remedies, vitamins and other supplements are widely promoted as preparations that may support cognitive health or prevent or delay Alzheimer's. Clinical trials have produced mixed results with little evidence to support them as effective treatments.
How to help someone with memory loss?
If you're worried about memory loss or related symptoms, ask a close relative or friend to go with you to a doctor's appointment. In addition to providing support, your partner can provide help in answering questions.
Can you get tested for Alzheimer's?
Genetic testing generally isn't recommended for a routine Alzheimer's disease evaluation. The exception is people who have a family history of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Meeting with a genetic counselor to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic testing is recommended before undergoing any tests.
Can Alzheimer's cause you to forget to eat?
People with Alzheimer's may forget to eat, lose interest in preparing meals or not eat a healthy combination of foods. They may also forget to drink enough, leading to dehydration and constipation.
When is Alzheimer's Awareness Month?
June is Alzheimer’s & Brain Awareness Month — the perfect time to join the fight to end Alzheimer’s. Help us provide compassionate care and support and advance critical research with a generous gift today.
Is there a cure for Alzheimer's?
There's no cure for Alzheimer’s, but one treatment may potentially delay decline from the disease, and there are drug and non-drug options that may help treat symptoms. Understanding available options can help individuals living with the disease and their caregivers to cope with symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is the drug used to treat Alzheimer's disease?
Researchers are studying ways to treat inflammatory processes at work in Alzheimer's disease. The drug sargramostim (Leukine) is currently in research. It's thought that the drug may stimulate the immune system to protect the brain from harmful proteins.
What are the plaques in Alzheimer's?
Plaques are a characteristic sign of Alzheimer's disease. Strategies aimed at beta-amyloid include: Recruiting the immune system. Several drugs — known as monoclonal antibodies — may prevent beta-amyloid from clumping ...
What is the best way to reduce beta-amyloid?
Production blockers. These therapies may reduce the amount of beta-amyloid formed in the brain. Research has shown that beta-amyloid is produced from a "parent protein" in two steps performed by different enzymes. Several experimental drugs aim to block the activity of these enzymes.
Does beta secretase slow cognitive decline?
They're known as beta- and gamma-secretase inhibitors. Recent studies showed that the beta-secretase inhibitors did not slow down cognitive decline and were associated with significant side effects in those with mild or moderate Alzheimer's, which has decreased enthusiasm for this mechanism of drug.
Does Alzheimer's disease stop memory loss?
These Alzheimer's treatments boost performance of chemicals in the brain that carry information from one brain cell to another. However, these treatments don't stop the underlying decline and death ...
Is dementia related to heart disease?
Growing evidence suggests that brain health is closely linked to heart and blood vessel health. The risk of developing dementia appears to increase as a result of many conditions that damage the heart or arteries. These include high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, diabetes and high cholesterol.
Alzheimer's Disease & Related Dementias
Current treatment approaches focus on helping people maintain mental function, manage behavioral symptoms, and slow or delay the symptoms of disease.
Next Steps After an Alzheimer's Diagnosis
Get information and resources about what to do and expect after a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
How Is Alzheimer's Disease Treated?
Learn about prescription drugs and other strategies to treat the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. Find out about medicines to avoid and take with caution.
What are the two classes of medications for Alzheimer's?
The first Alzheimer medications to be approved were cholinesterase (KOH luh NES ter ays) inhibitors. Three of these drugs are commonly prescribed: donepezil (Aricept ®), approved in 1996; rivastigmine (Exelon ®), approved in 2000 ; and galantamine (approved in 2001 under the trade name Reminyl ® and renamed Razadyne ® in 2005). Tacrine ( Cognex ® ), the first cholinesterase inhibitor, was approved in 1993 but is rarely prescribed today because of associated side effects, including possible liver damage.
Why is vitamin E important for Alzheimer's?
Vitamin E supplements are often prescribed as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease, because they may help brain cells defend themselves from "attacks". Normal cell functions create a byproduct a called free radical, a kind of oxygen molecule that can damage cell structures and genetic material. This damage, called oxidative stress, may play a role in Alzheimer's disease.
How does Alzheimer's disease affect the brain?
These symptoms worsen as brain cells die and the connections between cells are lost. Although current drugs cannot alter the progressive loss of cells, they may help minimize or stabilize symptoms. These medications may also delay the need for nursing home care.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Drugs
Current Alzheimer's medications can help for a time with memory symptoms and other cognitive changes. Two types of drugs are currently used to treat cognitive symptoms: 1. Cholinesterase inhibitors. These drugs work by boosting levels of cell-to-cell communication by preserving a ch… - Creating a safe and supportive environment
Adapting the living situation to the needs of a person with Alzheimer's disease is an important part of any treatment plan. For someone with Alzheimer's, establishing and strengthening routine habits and minimizing memory-demanding tasks can make life much easier. You can take thes…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.