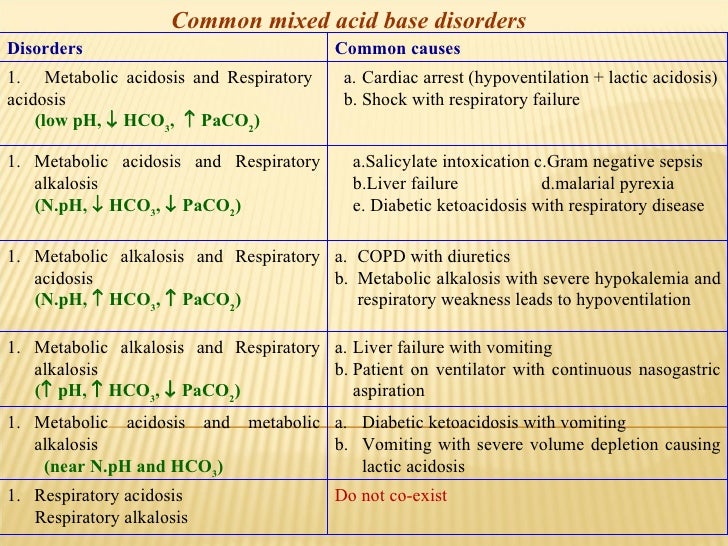
What are the different symptoms of alkalosis?
Symptoms of alkalosis can include any of the following:
- Confusion (can progress to stupor or coma)
- Hand tremor
- Lightheadedness
- Muscle twitching
- Nausea, vomiting
- Numbness or tingling in the face, hands, or feet
- Prolonged muscle spasms (tetany)
How can respiratory acidosis be prevented?
You can do the following to reduce your risk of respiratory acidosis:
- Take sedatives as prescribed and never mix them with alcohol.
- Stop smoking. Smoking can damage your lungs and make breathing less effective.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can make it harder for you to breathe.
How to assess and treat acute respiratory distress?
- Check if there is an illness, infection, or trauma
- Quit smoking and don’t become a passive smoker
- Stop drinking alcohol
- Pneumonia vaccination is necessary to avoid lung infection
How do you know if its respiratory or metabolic acidosis?
Respiratory Acidosis
- Respiratory Acidosis. One pathway to acidosis goes through the respiratory system, and we refer to this as respiratory acidosis.
- Metabolic Acidosis. The other pathway to acidosis involves the digestive and urinary systems. ...
- Acidosis Symptoms. ...
- Acidosis Treatment. ...
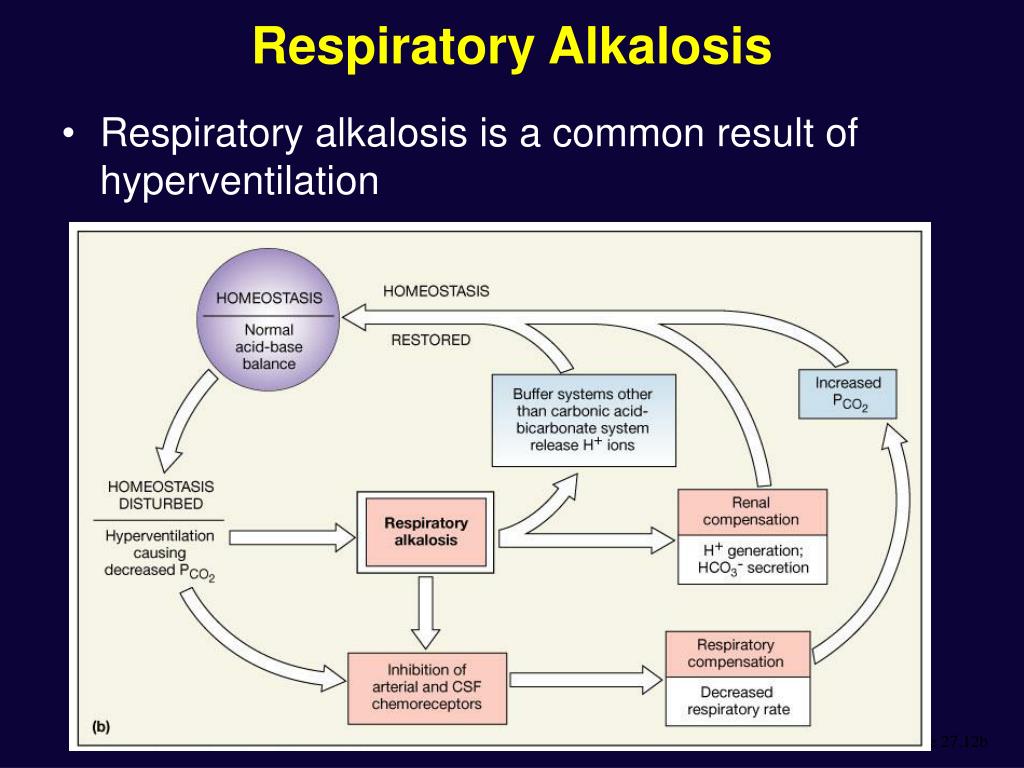
What is the compensatory mechanism for respiratory alkalosis?
The initial compensating response to an acute respiratory alkalosis is a modest decline in ECF bicarbonate concentration as the result of cellular buffering. Subsequent renal responses result in decreased ECF bicarbonate concentration through reduced renal bicarbonate reabsorption.
What are the 2 ways to treat alkalosis?
Outlook of metabolic alkalosis These deficiencies can be treated with intravenous fluids or, in mild cases, with a diet adjustment. Some cases of alkalosis are caused by serious underlying heart, kidney, or liver conditions.
How do you fix a respiratory alkalosis on a ventilator?
To correct respiratory alkalosis in this situation, the clinician should decrease minute ventilation during volume-controlled ventilation by decreasing f and, if necessary, by decreasing VT. If pressure-controlled ventilation is used, the clinician should decrease f first and then decrease set pressure, if necessary.
Which of the following can be used for alkalosis treatment?
Metabolic alkalosis treatment uses an intravenous (IV) line to deliver fluid and other substances, such as:Saline infusion.Potassium replacement.Magnesium replacement.Chloride infusion.Hydrochloric acid infusion.Stopping the medications that caused the condition, for example high doses of diuretics.
Why does breathing too fast cause respiratory alkalosis?
Outlook. Breathing too fast can cause a person to go into respiratory alkalosis. This occurs when a person’s pH level is higher than 7.45. A person may breathe too fast due to anxiety, overdosing on certain medications, or using a ventilator. Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis may include muscle spasms, irritability, ...
What are the symptoms of respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis include anxiety and lightheadedness. At its simplest definition, respiratory alkalosis almost always means that a person is breathing so fast that they are getting rid of carbon dioxide in excess. Carbon dioxide is an acid. As a result of this carbon dioxide loss, the body’s pH becomes more alkaline, ...
What is the pH of alkaline blood?
A person with respiratory alkalosis will have a pH higher than 7.45 and a lower arterial carbon dioxide level because they are breathing off excess carbon dioxide.
Why do women breathe faster in the third trimester?
This is because a woman tends to breathe faster during the third trimester due to the metabolic demands of the growing fetus. 2. Accidentally induced. Sometimes, a person receiving breathing support via a ventilator may show signs of respiratory alkalosis. This means that the ventilator is providing too many breaths, or breaths that are too large, ...
Why is alkalosis not life threatening?
Because respiratory alkalosis is not usually life-threatening and the body often works to correct the imbalance, a doctor may not treat the higher-than-normal pH level aggressively. Instead, they will treat the underlying condition to help a person’s pH achieve a more normal value with time.
What causes alkalosis in the lungs?
Numerous medical conditions can cause respiratory alkalosis. Some of these include: 1 atrial flutter 2 panic disorder 3 liver disease 4 pneumothorax, which occurs when air in the pleural cavity causes a collapsed lung 5 pulmonary embolism 6 overdose of salicylate medications, such as aspirin
Why do doctors change ventilator settings?
If a person has a condition that causes acidosis, a doctor may make changes to their ventilator settings to try to help them breathe off excess carbon dioxide. This can help bring a person’s pH levels back to normal. An example of a time when a doctor may do this is after a head injury.
Why is respiratory alkalosis unsuccessful?
Because respiratory alkalosis usually occurs in response to some stimulus, treatment is usually unsuccessful unless the stimulus is controlled. If the PaCO 2 is corrected rapidly in patients with chronic respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis may develop due to the renal compensatory drop in serum bicarbonate.
Is respiratory alkalosis life threatening?
The treatment of respiratory alkalosis is primarily directed at correcting the underlying disorder. Respiratory alkalosis itself is rarely life threatening. Therefore, emergent treatment is usually not indicated unless the pH level is greater than 7.5. Because respiratory alkalosis usually occurs in response to some stimulus, treatment is usually unsuccessful unless the stimulus is controlled. If the PaCO 2 is corrected rapidly in patients with chronic respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis may develop due to the renal compensatory drop in serum bicarbonate.
Can mechanical ventilation cause respiratory alkalosis?
In mechanically ventilated patients who have respiratory alkalosis, the tidal volume and/or respiratory rate may need to be decreased. Inadequa te sedation and pain control may contribute to respiratory alkalosis in patients breathing over the set ventilator rate.
What is the mechanism of carpopedal spasm?
Mechanism is thought to be change in cerebral blood flow and pH. Tachypnea or hyperpnea is often the only sign; carpopedal spasm may occur in severe cases due to decreased levels of ionized calcium in the blood (driven inside cells in exchange for hydrogen ion [H + ]).
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a primary decrease in carbon dioxide partial pressure (P co2) with or without compensatory decrease in bicarbonate (HCO 3− ); pH may be high or near normal. Cause is an increase in respiratory rate or volume (hyperventilation) or both. Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
Why does ventilation increase?
Ventilation increase occurs most often as a physiologic response to hypoxia (eg, at high altitude), metabolic acidosis, and increased metabolic demands (eg, fever) and, as such, is present in many serious conditions. In addition, pain and anxiety and some central nervous system (CNS) disorders (eg, stroke, seizure [post-ictal]) ...
Is respiratory alkalosis asymptomatic?
Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic. The chronic form is asymptomatic, but the acute form causes light-headedness, confusion, paresthesias, cramps, and syncope. Signs include hyperpnea or tachypnea and carpopedal spasms. Diagnosis is clinical and with arterial blood gas (ABG) and serum electrolyte measurements.
Is alkalosis life threatening?
Treatment is directed at the underlying disorder. Respiratory alkalosis is not life threatening, so no interventions to lower pH are necessary. Increasing inspired carbon dioxide through rebreathing (such as from a paper bag) is common practice but may be dangerous in at least some patients with CNS disorders in whom the pH of cerebrospinal fluid may already be below normal.
Why is respiratory alkalosis a sign of urea cycle disorder?
Rarely, respiratory alkalosis may be the presenting sign of a urea cycle disorder during the first days of postnatal life because the rising ammonia level may initially stimulate the respiratory center in the brain.
What is the diagnostic approach to respiratory alkalosis?
The diagnostic approach to respiratory alkalosis begins by deciding on clinical grounds whether there is a disease process present that is associated with acute respiratory alkalosis; if not, the patient is presumed to have chronic respiratory alkalosis.
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is an extremely common and complicated problem affecting virtually every organ system in the body [producing as it does] multiple metabolic abnormalities, from changes in potassium, phosphate, and calcium, to the development of a mild lactic acidosis.
Why does my child breathe so much?
In a spontaneously breathing child, this can result from fever, sepsis, mild asthma, panic attack, or central nervous system disorders. In the intensive care unit, the most common cause is mechanical overventilation of an intubated child.
Can respiratory alkalosis occur with higher levels of CO2?
An element of respiratory alkalosis may still occur with higher levels of Pa co2 in patients with metabolic alkalosis, in whom a normal Pa co2 is inappropriately low for this primary metabolic disorder. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What is the mechanism of carpopedal spasm?
Mechanism is thought to be change in cerebral blood flow and pH. Tachypnea or hyperpnea is often the only sign; carpopedal spasm may occur in severe cases due to decreased levels of ionized calcium in the blood (driven inside cells in exchange for hydrogen ion [H + ]).
What causes cellular acidosis in the arterial blood?
Exhalation of large amounts of CO 2 causes respiratory alkalosis in arterial blood (hence on ABG measurements), but poor systemic perfusion and cellular ischemia cause cellular acidosis, leading to acidosis of venous blood.
Why does ventilation increase?
Ventilation increase occurs most often as a physiologic response to hypoxia (eg, at high altitude), metabolic acidosis , and increased metabolic demands (eg, fever) and, as such, is present in many serious conditions. In addition, pain and anxiety and some central nervous system (CNS) disorders (eg, stroke, seizure [post-ictal]) ...
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a primary decrease in carbon dioxide partial pressure (P co2) with or without compensatory decrease in bicarbonate (HCO 3− ); pH may be high or near normal. Cause is an increase in respiratory rate or volume (hyperventilation) or both. Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
What is Merck and Co?
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community. The legacy of this great resource continues as the Merck Manual in the US and Canada and the MSD Manual outside of North America. Learn more about our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
Is respiratory alkalosis asymptomatic?
Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic. The chronic form is asymptomatic, but the acute form causes light-headedness, confusion, paresthesias, cramps, and syncope. Signs include hyperpnea or tachypnea and carpopedal spasms. Diagnosis is clinical and with arterial blood gas (ABG) and serum electrolyte measurements.
When was the Merck Manual first published?
The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community. The legacy of this great resource continues as the Merck Manual in the US and Canada and the MSD Manual outside of North America. Learn more about our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge.
What Causes Respiratory Alkalosis?
The best way to describe Respiratory Alkalosis is breathing faster than normal. When an individual breathes exceedingly fast he tends to release more carbon dioxide than normal. This results in an imbalance in the pH scale of the body with more acid being lost due to breathing and the pH becoming alkaline.
What Are The Treatment Options For Respiratory Alkalosis?
The treatment for Respiratory Alkalosis depends on what exactly is causing this condition. If it is the ventilator that is causing the individual to hyperventilate then changing the settings to bring the breathing back to normal is the way to go. In such cases, once the breathing normalizes Respiratory Alkalosis clears off quickly. [2]
How to manage metabolic alkalosis?
Most cases of metabolic alkalosis can be managed with fluid and electrolyte therapy. When metabolic alkalosis needs to be resolved quickly or when conventional therapy cannot be tolerated, mineral acid administration should be instituted.
What is the role of buffering systems in the body?
Three buffering systems are used by the body to correct an arterial pH above 7.45--tissue, respiratory, and renal systems. The kidneys have the primary responsibility for correcting a severe metabolic alkalosis, but several conditions (e.g., severe volume contraction) can interfere with the renal mechanisms.
