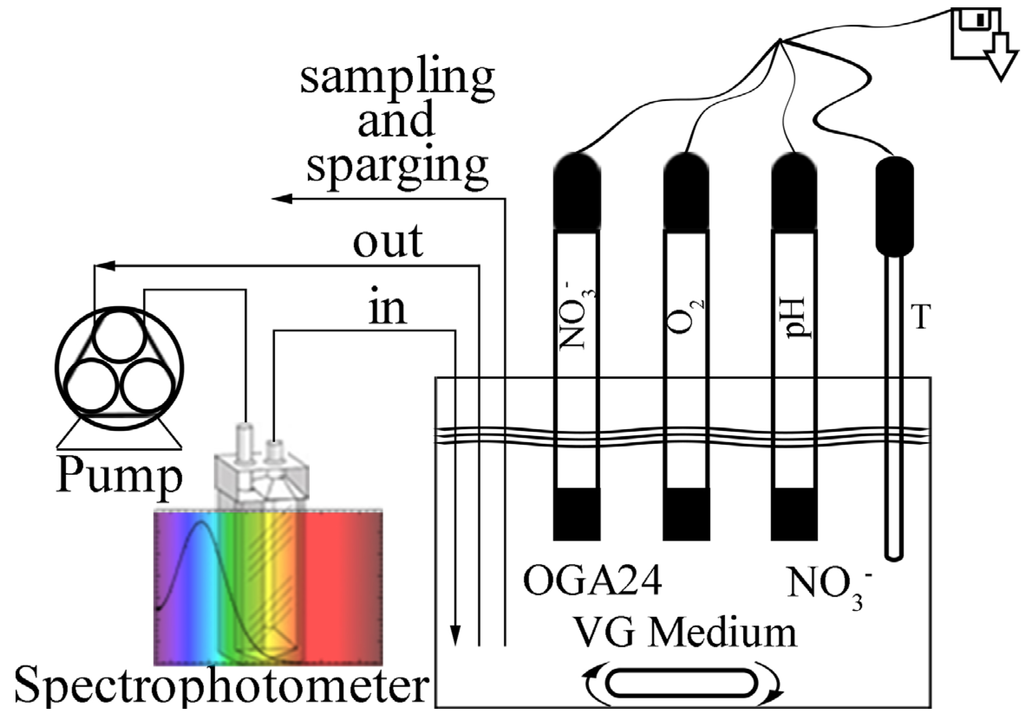
The pressure that is needed to press water through a membrane is called Trans Membrane Pressure (TMP). The TMP is defined as the pressure gradient of the membrane, or the average feed pressure minus the permeate pressure.
Full Answer
How is the initial TMP value set?
The treatment of biologically treated white water with laccase before microfiltration gave a large improvement in removal efficiency for all contaminants originating from the TMP but the material ...
What is the significance of the TMP of the filter?
· TMP = ((P feed + P retentate) / 2 – P permeate) as the module average transmembrane pressure. TCF = (viscosity of water at measured temperature)/(viscosity of water @ 25°C) as temperature correction factor (see Appendix).
What happens If tmp is too high?
Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) Filter Pressure Drop (∆ P Filter) USMP/MG120/19-0012 05/19 Access Pressure Access Pressure Access Pressure Pressure created by pulling blood from patient Can be negative or positive, depending on the blood source to which the access line is connected 1 Main determinants: 2
How much TMP should I run at for NWP?
· In addition, hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid are commonly used in this treatment process. I hope you can understand it. Working Principle of Water Treatment Chemicals. Speaking of water treatment chemical, we all know that it is a kind of water treatment chemical. In fact, there are many types of water treatment chemicals.
What is TMP in water?
The pressure that is needed to press water through a membrane is called Trans Membrane Pressure (TMP). The TMP is defined as the pressure gradient of the membrane, or the average feed pressure minus the permeate pressure.
What is TMP formula?
TMP = ((Pfeed + Pretentate) / 2 – Ppermeate) as the module average transmembrane pressure.
What is TMP in MBR?
Mechanisms of membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors (MBR). In operational terms, membrane fouling decreases the permeate flux when the MBR is operated at constant transmembrane pressure (TMP), and results in the increase of TMP when the MBR is operated at constant permeate flux.
How do you calculate transmembrane pressure?
Using your calculator, add the values for the feed pressure and the retentate pressure. Divide the sum by two and subtract the permeate pressure. The result is the transmembrane pressure.
What is normal transmembrane pressure?
TMPs will vary but will typically be in the range of 5 to 50 psid.
What is TMP in ultrafiltration?
Transmembrane pressure, usually abbreviated TMP, has a precise ADQI definition: Transmembrane pressure is the hydrostatic pressure gradient across the membrane. This is the driving force that causes ultrafiltration.
What is SBR in wastewater treatment plant?
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and- draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged.
What is MBR ETP?
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is a combination of membrane process like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, the activated sludge process. It is now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
What is fouling in RO membrane?
Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane foulants and fouling. Fouling is the accumulation of foreign materials from feed water in the active membrane surface and/or on the feed spacer to the point of causing operational problems.
What does TMP mean in dialysis?
The major driving force that determines the rate of ultrafiltration or convective flow is the difference in hydrostatic pressure between the blood compartment and the dialysate compartments across the dialysis membrane; this is called the transmembrane pressure (TMP).
How is TMP calculated in dialysis?
TMP = (BPA + BPV)/2 - (DPIN + DPOUT)/2.= (300 + 200)/2 - (260 + 240)/2.= (500)/2 – (500)/2 = 0 mmHg.
What is normal water permeability?
Normalized water permeability (NWP) is an established method for determining the cleanliness of a cassette after cleaning. This method involves measuring the passage of clean water through the membrane under standard pressure and temperature conditions (Figure 2).
What is the cutoff value of a membrane?
The cutoff of a specific membrane represents the molecular weight of the smallest solutes retained by the membrane; it depends on average membrane pore size and pore size distribution. The statistical cutoff value is defined as the molecular weight of the solute having an SC of 0.1.
What is the purpose of the NWP test?
The normalized water permeability (NWP) test is a recommended method to assess the effectiveness of the CIP process to restore process flux rates. NWP uses water permeability (LMH/psi) as a measure of membrane cleanliness:
What does ADH do to the nephron?
ADH Controls Distal Nephron Permeability. ADH increases the water permeability of the late distal tubule (or connecting duct) and all parts of the collecting duct. It also increases the urea permeability of the inner medullary collecting duct.
How does ADH affect kidneys?
ADH increases the water permeability of the late distal tubule (or connecting duct) and all parts of the collecting duct. It also increases the urea permeability of the inner medullary collecting duct. When the distal nephron permeability to water and urea is high, all of the mechanisms for concentrating the urine operate, and the kidneys excrete a small volume of highly concentrated urine. In the absence of ADH, the distal nephron is not permeable to either water or urea. Fluid that enters the distal tubule is hypoosmotic, about 100 mOsM. Low water permeability prevents water from leaving the hypoosmotic fluid to equilibrate with the interstitial fluid. Thus the tubular fluid stays hypoosmotic all the way through the collecting duct. Because the late distal tubule and collecting duct can pump out some Na +, the final concentration of the urine is actually lower than 100 mOsM. The kidneys can maximally dilute urine to about 70 mOsM. The low urea permeability in the absence of ADH shuts off the urea recycling, so that the concentration profile in the kidney interstitium is changed. Figure 7.5.11 shows approximate values for tubular fluid concentration along the nephron in the presence and absence of ADH.
Reasons for Adding Acid When Using Amino Trimethylene Phosphonic Acid
Among many kinds of water treatment agents, amino trimethylene phosphonic acid has the function of dispersing insoluble inorganic salts in water, preventing or interfering the precipitation and scaling of insoluble inorganic salts on metal surface.
Working Principle of Water Treatment Chemicals
Speaking of water treatment chemical, we all know that it is a kind of water treatment chemical. In fact, there are many types of water treatment chemicals. When these chemicals are used in sewage, the purpose of scale removal, separation, sterilization, flocculation and purification can be realized.
What is MF water treatment?
MF is used to remove turbidity and larger microorganisms. Water treatment in existing installations uses immersed membrane modules that are simply placed in water tanks where a vacuum at the permeate side drives the collection of purified water.
Why is water treatment important?
Water treatment is performed in order to improve water quality. The processes employed for water treatment depend on the quality of the water supply. In all cases, water has to be disinfected in order to deactivate any existing microorganisms present in water. So far, this technique was proved to be the most important for the protection ...
Why is water disinfected?
In all cases, water has to be disinfected in order to deactivate any existing microorganisms present in water. So far, this technique was proved to be the most important for the protection of human life.
How to remove hardness from water?
Softening is another technique commonly used to remove hardness in case water is hard, which is performed by the addition of lime and subsequent precipitation of calcium as calcium carbonate and magnesium as magnesium hydroxide.
How to improve the taste of water?
1. Understand the treatment need: For many consumers, simply improving the taste of the water is their primary treatment need. For some, there may be health contaminants that must be treated. And others may have very hard water, causing issues with lime scale around fixtures and possibly damaging appliances. 2.
What is biological waste water treatment?
Biological waste water treatment is the primary method of preparing food-processing waste water flows for return to the environment. Increasing waste water loads on existing plants and more stringent government discharge requirements have put considerable pressure on the food-processing industry to refine and understand better the design and management of biological waste water treatment processes. Though activated sludge and other biological treatment processes are still frequently operated by general guidelines and ‘rules of thumb,’ facility design and operation must be guided by consideration of both the physical and biological aspects of waste water treatment. Various modifications and combinations of aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment processes are commonly used in the food-processing industry.
Do water treatment plants have clarification?
Conventional water treatment processes have clarification before filtration. Although direct filtration (filtering after the flocculation tank) and in-line filtration (filtering after the rapid mixing tank) are occasionally practiced, the design and operating restrictions have been applied for these applications primarily due to concerns of deterioration in the quality of the finished water. As membranes are less sensitive to chemical coagulation, a significant number of water purification plants are being designed to use direct or in-line filtration. Replacing the conventional water treatment processes with direct or in-line filtration has obvious advantages of having a smaller footprint for the plant and savings in capital costs for the clarification equipment. Two questions remain:
What is surface water treatment?
EPA has developed the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs) to improve your drinking water quality. The regulations provide protection from disease-causing pathogens, such as Giardia lamblia, Legionella, and Cryptosporidium. The regulations also protect against contaminants that can form during drinking water treatment.
What are the regulations for drinking water?
The regulations provide protection from disease-causing pathogens, such as Giardia lamblia, Legionella, and Cryptosporidium. The regulations also protect against contaminants that can form during drinking water treatment. Pathogens, such as Giardia , Cryptosporidium and Legionella, are often found in water.
What are the diseases that can be caused by drinking water?
Pathogens, such as Giardia , Cryptosporidium and Legionella, are often found in water. If consumed, these pathogens can cause gastrointestinal illness (e.g., diarrhea, vomiting, cramps) and other health risks. These illnesses may be severe and sometimes fatal for people with weakened immune systems.
What is TDS in water?
The term “TDS” is an acronym for Total Dissolved Solids when referring to water. This means the amount of ‘inorganic salts’ which can be found in water. Basically speaking, this is anything that contaminates the purity of the water. Some of these solids can cause a huge amount of health issues. TDS salts include calcium, potassium, chloride, ...
How to measure TDS?
Measuring TDS. TDS can be measured via a specially made meter. This should be submerged in the water you wish to measure and will provide a reading. For an accurate reading, do this multiple times from multiple samples which are taken from the same place.
Is water pure?
Water is rarely totally pure , and even natural processes can lead to minerals or other solids ending up in the water. Not all are harmful, but some certainly are. Many solids enter our water supply from human processes such as agriculture, water treatments and even wastewater getting into water supplies.
Is mineral water bad for you?
For instance, some mineral water has high levels of solids within and this is not seen as harmful, but that is because the actual solids are. These are usually calcium, magnesium or other substances which may not be bad for the body. A high TDS can also be caused by harmful items such as chlorine, sulfates and more.
What does high TDS mean?
High TDS can also mean ‘hard’ water, which is far more likely to cause limescale or other build-ups and deposits on pipes or appliances around the home, shortening their lifespan.
Can you reduce TDS?
With adequate filtration, it is possible to reduce the TDS level to ensure that whenever you are consuming water it is in the ‘excellent’ category. The benefits of this are not only to reduce risks to your health. Filtration for TDS usually takes place within a RO (Reverse Osmosis) filter. Deionisation and Distillation can also be used, ...
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis is a process by which water is forced through a membrane. This has tiny porous materials which allow only the tiniest of molecules (such as water) to pass through. This means that the ‘solids’ will be left behind in the membrane and in the process will have been removed from the water.
