
What are home remedies for skin cancer?
x-rays) to kill cancer cells in a part of the body. Radiation can be used to treat cancer that’s just on the skin or that has spread to other parts of the body. The most common side effects are skin changes and hair loss where the radiation is given. Your skin may become red, swollen, flaky, or darker. You may also feel very tired. Immunotherapy
How do you cure skin cancer?
Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis. Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells. Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color.
What are the early stages of skin cancer?
The 8 Types of Skin Cancer Treatments. Surgery. Radiation therapy (RT) Chemotherapy. Photodynamic therapy. Immunotherapy. Targeted therapy. Cryotherapy. Laser treatment.
How do you treat skin cancer?
Jul 01, 2020 · Depending on the type and stage of skin cancer, the team has several treatment options available, including surgical excision, immunotherapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapy individualized to that patient’s case.
What are 3 types of treatments used for skin cancers?
Simple excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, curettage and electrodesiccation, and cryosurgery are used to treat basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Laser surgery is rarely used to treat basal cell carcinoma.Aug 27, 2021
What is the most common treatment for skin cancer?
Surgery is the primary treatment for most skin cancers. For patients with basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas, a dermatologist or other qualified doctor may perform an outpatient procedure using a local anesthetic.Mar 17, 2022
What treatment is there for skin cancer?
Surgery is the main treatment for non-melanoma skin cancer, although it may depend on your individual circumstances. Non-surgical treatments, such as freezing (cryotherapy), anti-cancer creams, photodynamic therapy (PDT), radiotherapy and electrochemotherapy, are also used in certain circumstances.
Which type of skin cancer is the most treatable?
Melanoma is the most invasive skin cancer with the highest risk of death. While it's a serious skin cancer, it's highly curable if caught early.
What are the 4 types of skin cancer?
There are 4 main types of skin cancer:Basal cell carcinoma. Basal cells are the round cells found in the lower epidermis. ... Squamous cell carcinoma. Most of the epidermis is made up of flat, scale-like cells called squamous cells. ... Merkel cell cancer. ... Melanoma.
Can a dermatologist remove basal cell carcinoma?
How dermatologists treat basal cell carcinoma. When possible, BCC is treated with a procedure called “surgical removal.” If you have an early BCC, this can often be performed in your dermatologist's office while you remain awake.Oct 21, 2021
Are there any new treatments for skin cancer?
New research suggests a nonsurgical treatment called high dose rate brachytherapy may be an option for some people with skin cancer. Researchers said this radiation treatment could be a better option for older adults and other people who might have complications from surgery.Dec 3, 2019
Can skin cancer be treated with medication?
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells, usually by keeping the cancer cells from growing, dividing, and making more cells. In skin cancer treatment, these drugs are usually applied to the skin every day for several weeks. This is called topical treatment.
What does Stage 1 melanoma look like?
Stage 1A means the: melanoma is less than 1 mm thick. outer layer of skin (epidermis) covering the tumour may or may not look broken under the microscope (ulcerated or not ulcerated)
Which is worse basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma?
Though not as common as basal cell (about one million new cases a year), squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread (metastasize). Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%–5% of cases. After it has metastasized, it's very difficult to treat.May 1, 2006
Which is worse basal cell or melanoma?
While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage. Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
What are the 3 most common skin cancers?
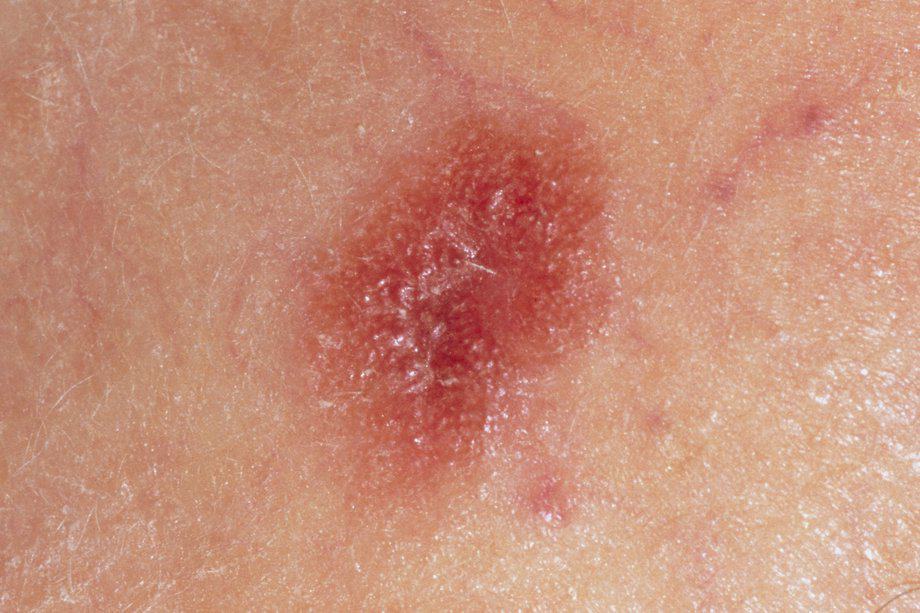
Skin cancer — the abnormal growth of skin cells — most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. But this common form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. There are three major types of skin cancer — basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.Dec 5, 2020
What is the treatment for skin cancer?
Systemic chemotherapy can be used to treat skin cancers that have spread to other parts of the body. Photodynamic therapy. This treatment destroys skin cancer cells with a combination of laser light and drugs that makes cancer cells sensitive to light. Biological therapy.
How to diagnose skin cancer?
To diagnose skin cancer, your doctor may: Examine your skin. Your doctor may look at your skin to determine whether your skin changes are likely to be skin cancer. Further testing may be needed to confirm that diagnosis. Remove a sample of suspicious skin for testing (skin biopsy). Your doctor may remove the suspicious-looking skin ...
What test is needed to determine the stage of skin cancer?
Because superficial skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma rarely spread, a biopsy that removes the entire growth often is the only test needed to determine the cancer stage. But if you have a large squamous cell ...
How to treat actinic keratoses?
Freezing. Your doctor may destroy actinic keratoses and some small, early skin cancers by freezing them with liquid nitrogen (cryosurgery). The dead tissue sloughs off when it thaws. Excisional surgery. This type of treatment may be appropriate for any type of skin cancer.
What does the IV mean in cancer?
Doctors use the Roman numerals I through IV to indicate a cancer's stage. Stage I cancers are small and limited to the area where they began. Stage IV indicates advanced cancer that has spread to other areas of the body. The skin cancer's stage helps determine which treatment options will be most effective.
What kind of doctor do you see for skin problems?
In some cases, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in skin diseases and conditions (dermatologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to be well-prepared.
How does Mohs surgery work?
During Mohs surgery, your doctor removes the skin growth layer by layer, examining each layer under the microscope, until no abnormal cells remain . This procedure allows cancerous cells to be removed without taking an excessive amount of surrounding healthy skin. Curettage and electrodesiccation or cryotherapy.
What is the best treatment for skin cancer?
Freezing, light therapy, or lasers may be used to treat some cancers. Other times, topical chemo or other drugs are used by rubbing them right on the skin. Local treatments are mostly used to treat basal and squamous cell skin cancers.
How does immunotherapy help with cancer?
Immunotherapy helps your immune system find and fight cancer. It may be given as a shot into a vein in your arm, or as pills or capsules that you take by mouth.
How does chemo work?
Chemo uses medicines to fight cancer. Most of the time, chemo is given as a shot into a vein in your arm. Or, chemo might be taken by mouth as a pill or capsule. Other times, it may be rubbed on the skin. When it’s given as a pill or into a vein, chemo travels to most parts of the body to treat cancer that has spread. When it’s put on the skin, it stays in the area where it’s rubbed in to treat cancer in that spot.
How does targeted therapy work?
Targeted therapy finds and attacks cancer cells while causing less harm to normal cells. These medicines change the way cancer cells grow, divide, or repair themselves. They are given by mouth as pills or capsules or might be given as a shot into a vein in your arm.
What is the purpose of radiation?
Radiation can be used to treat cancer that’s just on the skin or that has spread to other parts of the body.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials test new medicines or treatments in people. They help doctors find better ways to treat cancer. If your doctor talks to you about a clinical trial, it’s up to you whether to take part. And if you do sign up for a clinical trial, you can stop at any time.
What is the purpose of skin cancer?
The skin is the body’s largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D.
What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. Different types of cancer start in the skin. Skin color and being exposed to sunlight can increase the risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, ...
How does chemotherapy stop cancer cells from growing?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing . Chemotherapy for basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis is usually topical (applied to the skin in a cream or lotion).
Where does basal cell carcinoma occur?
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin occur most often in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the nose, ears, lower lip, or top of the hands. Signs of actinic keratosis include the following: A rough, red, pink, or brown, scaly patch on the skin that may be flat or raised.
What are the layers of the skin?
The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer) and the dermis (lower or inner layer). Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells: Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
Where are abnormal cells found in the epidermis?
In stage 0, abnormal cells are found in the squamous cell or basal cell layer of the epidermis. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
What are the cells that make melanin?
Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken. Enlarge.
What are targeted therapies for skin cancer?
Genetic sequencing revealed mutations in some of the “drivers” of skin cancers, including BRAF (melanoma) and PTCH1 ( basal cell carcinoma), both of which have targeted therapies available.
What are the different types of skin cancer?
There are several types of skin cancer. The most common types are non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC), such as basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. The majority of skin cancers begin in the epidermis, which is predominantly made up of three kinds of cells: squamous cells, basal cells and melanocytes. The most serious forms of skin cancer are ...
What is the second most common skin cancer?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer. This type of skin cancer has a low but not negligible incidence of metastases, spreading in approximately 2% of cases. Usually, squamous cell carcinoma occurs on parts of the skin that are exposed to long periods of sunlight, such as the face, ears, lips, neck, ...
What is the Skin Cancer Team?
The Skin Cancer Team at the School of Medicine and Siteman Cancer Center consists of dermatologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, pathologists, nurses, councilors and caregivers and patients. Depending on the type and stage of skin cancer, the team has several treatment options available, including surgical excision, immunotherapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapy individualized to that patient’s case.
How does immunotherapy help cancer?
Immunotherapy aims to “take the brakes” off the immune system to fight cancer. If a skin cancer has spread, most therapies are given in a way that potentially affect the entire body.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma occur?
Usually, squamous cell carcinoma occurs on parts of the skin that are exposed to long periods of sunlight, such as the face, ears, lips, neck, arms and backs of hands. This cancer may appear as a firm red bump, a scaly red patch, an open sore, or a wart that may crust or bleed easily.
What doctor can evaluate a new lesion?
A board-certified dermatologist can evaluate a new lesion to determine whether or not it needs a biopsy. If you live in an area without a board-certified dermatologist , your primary care physician may be able to do the same. You can request a “full-body skin examination” to have your skin lesions checked—even ones on your back or the backs of your legs where you may not be able to typically see. If you have had a previous skin cancer, your doctor is likely to recommend that you repeat this several times a year.
Treatment options
Find out how your doctor decides which treatment you need and the types of treatment you might have.
Surgery
The type of surgery you have depends on where the cancer is, how big it is and how deep.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy uses high energy waves similar to x-rays to kill cancer cells.
Imiquimod cream (Aldara)
Imiquimod cream uses your body’s natural defences to help kill cancer cells. Find out how you have it and what the side effects are.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses a drug and a special type of light to destroy cancer cells. Find out when it's used.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses anti cancer (cytotoxic) drugs to destroy cancer cells. Find out how and when you might have chemotherapy for skin cancer.
Follow up
Find out about the follow up you'll need after treatment for skin cancer.
