...
Short course regimens include:
- Three months of once-weekly isoniazid plus rifapentine (3HP)
- Four months of daily rifampin (4R)
- Three months of daily isoniazid plus rifampin (3HR)
Who should be treated for latent TB?
1. Garlic...
2. Bananas...
3. Drumstick...
4. Indian Gooseberry...
5. Oranges...
6. Custard Apple...
7. Black Pepper...
8. Walnuts...
Learn More...Can you cure latent TB?
Treating latent TB If tests show that you have latent TB (see tuberculosis) and you are 65 or under, your TB team should offer you antibiotics to prevent this progressing to active TB disease. Treatment usually lasts 3 or 6 months. If you are 35–65, you should only be offered treatment if a doctor thinks there is little risk of liver damage.
Does latent TB have to be treated?
Treatment is the only way to remove the TB bacteria from your body. Latent TB treatment is often shorter than treatment for active TB, and it involves less medication. These are all good reasons to treat the latent TB bacteria while you are healthy and before they have a chance to wake up.
Why treat latent TB?
The size of the lump determines how significant this reaction is. If you have latent TB, you do need treatment to prevent the disease from becoming active, endangering your own health and that of others. The currently recommended treatment for latent TB is nine months of the drug isoniazid taken by mouth.

What is the best treatment for latent TB?
Isoniazid and Rifapentine (INH-RPT) are medicines used together to treat LTBI. They kill the sleeping TB germs before they make you sick. It can take many months for the medicine to kill the TB germs because they are strong.
Can latent tuberculosis be treated?
A course of antibiotic medicine will treat latent TB. You may be given Rifampicin and Isoniazid for three months (which may be together in a tablet called Rifinah) or Isoniazid by itself for six months. Your doctor or TB specialist nurse will talk you through the treatment and answer any questions you may have.
Does everyone with latent TB need treatment?
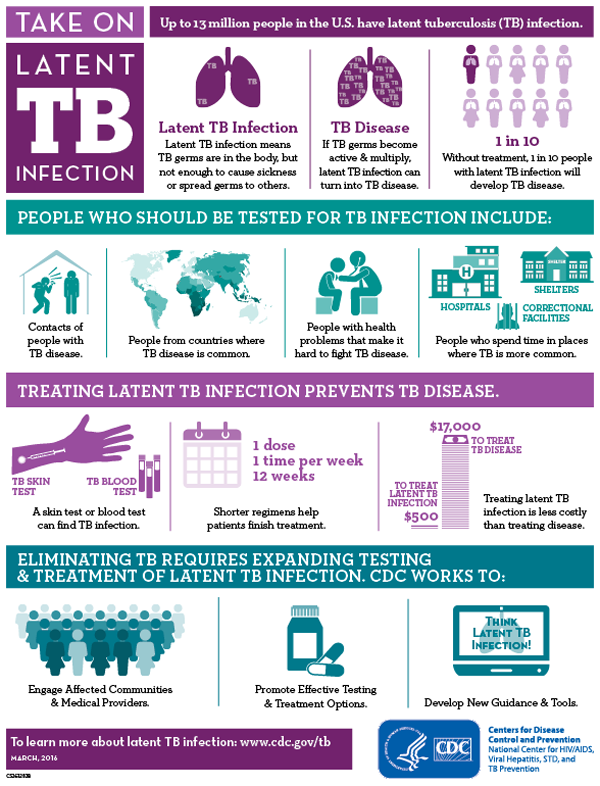
The only sign of TB infection is a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test or TB blood test. Persons with latent TB infection are not infectious and cannot spread TB infection to others. Overall, without treatment, about 5 to 10% of infected persons will develop TB disease at some time in their lives.
What is the shortest treatment for latent TB?
The 12-dose regimen is the shortest of several available regimens recommended for treating latent TB infection.
What makes latent TB become active?
However, latent TB bacteria can 'wake up' and become active in the future, making you ill. This can happen many years after you first breathe in TB bacteria. Latent TB bacteria are more likely to wake up if you experience lifestyle stresses or other illnesses that weaken your immune system.
How can you prevent latent TB from becoming active?
You can take medicine to prevent getting active TB disease. Levofloxacin is a medicine used to treat LTBI. It kills the sleeping TB germs before they make you sick. It can take many months for the medicine to kill the TB germs because the germs are strong.
How long does latent TB last?
What is the Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active TB Disease?Latent TB InfectionActive TB DiseaseUsually treated by taking one medicine for 9 months.Treated by taking three or four medicines for at least 6 months.3 more rows
How long does it take to treat latent tuberculosis?
Treatment Regimens for Latent TB Infection (LTBI)Drug(s)DurationFrequencyIsoniazid (INH)* and Rifapentine (RPT)†3 monthsOnce weeklyRifampin (RIF)§4 monthsDailyIsoniazid (INH)* and Rifampin)§3 monthsDailyIsoniazid (INH)6 monthsDaily3 more rows
Can latent TB come back after treatment?
Even if you successfully beat tuberculosis, you can get tuberculosis infection again. In fact, TB reinfection is becoming more common. Tuberculosis is a potentially life-threatening, airborne bacterial infection that can be found worldwide.
What are the long term effects of isoniazid?
Severe and sometimes fatal hepatitis has been reported with isoniazid therapy and may occur even after many months of treatment. The risk for hepatitis increases with advancing age, concomitant alcohol use, chronic liver disease, and injection drug use.
What is the side effect of isoniazid?
Common side effects may include: numbness, tingling, or burning pain in your hands or feet; nausea, vomiting, upset stomach; or. abnormal liver function tests.
Is Latent TB Treatment Safe?
As with all medicines, there may be side effects. Some are mild, while others may be more serious. Depending on the treatment you receive, you may...
How Do I Take Latent TB medication?
It is important that you take your medicine regularly and complete the full course, to make sure all TB bacteria are removed from your body.Try to...
I Am Worried About Getting Treated For Latent Tb, but I Don’T Want to Get Ill?
You will receive support throughout your treatment from a doctor or TB specialist nurse. They will talk you through the treatment and answer any qu...
When I Finish My Treatment, Will I Be Free of TB Forever?
If you complete your treatment as prescribed, your risk of developing active TB is much lower. However, it is possible you could breathe in the TB...
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
How many drugs are needed for TB?
TB infection is treated with one or two drugs, whereas TB disease initially requires four drugs.
What is LTBI in healthcare?
Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is the presence of M. tuberculosis organisms (tubercle bacilli) without symptoms or radiographic or bacteriologic evidence of TB disease. Approximately 90-95% of those infected are able to mount an immune response that halts the progression from LTBI to TB disease. However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out. Health care providers must communicate the risks and benefits of treatment to their patients and encourage adherence and treatment completion.
What is the CDC's role in TB?
However, because prevention of TB has major public health implications, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend testing populations that are at increased risk for TB infection and treating those for whom TB disease has been ruled out.
How is acceptance of LTBI influenced?
A patient’s acceptance of LTBI treatment is often influenced by the initial approach of the health care provider. When discussing the risks and benefits of treatment it is important to explain that
How many people with latent TB will develop active TB?
About 1 in 10 people with latent TB will develop active TB. And there is no way to know if you will be one of them. It is possible to become ill with active TB many years after you breathe in TB bacteria. Treatment is the only way to remove the TB bacteria from your body.
How long before eating can you take TB medicine?
Try to take your TB medicine at least one hour before you eat food or two hours afterwards. You can eat anything you like, but you should avoid drinking alcohol.
How to know if you have TB?
If you complete your treatment as prescribed, your risk of developing active TB is much lower. However, it is possible you could breathe in the TB bacteria again in future. The chances of this are low for most people, but is useful to know the most common symptoms of active TB so you can see your GP if you have any of them: 1 a cough which lasts for three weeks or longer 2 fever (a high temperature) 3 night sweats 4 weight loss 5 no appetite 6 tiredness.
What to do if you have started treatment?
If you have started treatment, but are still have concerns, remember your doctor and nurse are there to help.
Can you breathe in TB?
However, it is possible you could breathe in the TB bacteria again in future. The chances of this are low for most people, but is useful to know the most common symptoms of active TB so you can see your GP if you have any of them: a cough which lasts for three weeks or longer. fever (a high temperature) night sweats.
Is latent TB shorter than active TB?
Latent TB treatment is often shorter than treatment for active TB, and it involves less medication. These are all good reasons to treat the latent TB bacteria while you are healthy and before they have a chance to wake up.
What is the difference between LTBI and TB?
The Difference between Latent TB Infection (LTBI) and TB Disease. A Person with Latent TB Infection. A Person with TB Disease. Has no symptoms. Has symptoms that may include. a bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer. pain in the chest. coughing up blood or sputum. weakness or fatigue.
What is it called when you breathe in TB?
This is called latent TB infection. In most people who breathe in TB bacteria and become infected, the body is able to fight the bacteria to stop them from growing. People with latent TB infection: Have no symptoms. Don’t feel sick.
How do you know if you have TB?
TB bacteria can live in the body without making you sick. This is called latent TB infection. In most people who breathe in TB bacteria and become infected, the body is able to fight the bacteria to stop them from growing. People with latent TB infection: 1 Have no symptoms 2 Don’t feel sick 3 Can’t spread TB bacteria to others 4 Usually have a positive TB skin test reaction or positive TB blood test 5 May develop TB disease if they do not receive treatment for latent TB infection
Why do TB bacteria become active?
TB bacteria become active if the immune system can’t stop them from growing. When TB bacteria are active (multiplying in your body), this is called TB disease. People with TB disease are sick. They may also be able to spread the bacteria to people they spend time with every day.
What does a skin test show for TB?
Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection. Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection. Has a normal chest x-ray and a negative sputum smear. May have an abnormal chest x-ray, or positive sputum smear or culture.
Can TB spread to others?
Can’t spread TB bacteria to others. Usually have a positive TB skin test reaction or positive TB blood test. May develop TB disease if they do not receive treatment for latent TB infection. Many people who have latent TB infection never develop TB disease.
Can TB be inactive?
In these people, the TB bacteria remain inactive for a lifetime without causing disease. But in other people, especially people who have a weak immune system, the bacteria become active, multiply, and cause TB disease. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
How long should a pharmacist fill a TB prescription?
Pharmacists should fill prescriptions one month at a time. Clinicians are encouraged to write the prescription for one month, with monthly refills. However, clinicians may use their discretion for individual patients. Pharmacists should contact their state and local TB programs with specific questions.
What is 3HP for TB?
3HP is one of several regimens CDC recommends for treatment of latent TB infection. The term 3HP comes from the regimen duration (once weekly doses for three months) and the abbreviations of each of the two drugs, isoniazid (INH) and rifapentine (RPT), in the regimen.
Introduction
Communicating The Value of LTBI Treatment
- A patient’s acceptance of LTBI treatment is often influenced by the initial approach of the health care provider. When discussing the risks and benefits of treatment it is important to explain that 1. As long as TB germs are in the body, they can begin to multiply and cause disease 2. Certain individuals are at especially high risk for progression to TB disease. They include persons with r…
Identifying Barriers to Adherence
- Many variables affect a patient’s adherence to the recommended treatment regimen, including 1. Appointment hours that conflict with patient’s schedule 2. Misinformation about TB 3. Health beliefs and practices 4. Limited financial resources 5. Co-existing medical conditions 6. Medication side effects 7. Language barriers 8. Real or perceived stigma related to LTBI treatment
Strategies For Maximizing Adherence
- Partner with local health departments and community-based organizations that can provide 1. Case managementto ensure continuity of services 2. Directly observed therapy (DOT), whereby a health care worker observes the ingestion of medication; highly recommended when using intermittent regimens and for high-risk patients, such as those whose treatme...