
The vaptans constitute a new class of pharmaceuticals developed for the treatment of the hypervolemic and euvolemic forms of hyponatremia. These agents are nonpeptide vasopressin
Vasopressin
Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone, arginine vasopressin or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon of that cell, which terminates in the posterior pituitary, and is releas…
What IV fluids are given for hyponatremia?
May 13, 2014 · In addition, these patients may exacerbate their hyponatremia through the ingestion of solute-poor fluids (e.g., water or tea). 9 The most common treatment option proposed for patients with hypovolemic hyponatremia is replacement of both salt and water through the intravenous infusion of sodium chloride solutions. 9 – 11 Our review did not …
What lab tests indicate hypovolemia?
Feb 07, 2017 · A combination of hypotonic fluids and desmopressin may be required for treating overcorrection in hypovolemic hyponatremia, because a persistent water diuresis may ensue after correction of hypovolemia. 66 Experimental data indicate improved outcomes with reinduction of hyponatremia after rapid overcorrection. 67 Another point that merits discussion is the …
What causes hypervolemic hyponatremia?
Because AVP, which is intimately involved in regulating osmolar homeostasis, is often elevated in patients with hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia, treatments that directly target the effects of this hormone may provide a more predictable correction of serum [Na(+)] than those traditionally used.
What is causing that hyponatremia, SIADH vs CSW?
Abstract. The etiology of hyponatremia is often multifactorial. The most common causes include hypovolemia from gastrointestinal (GI) or other fluid losses, thiazide diuretics, and SIAD [
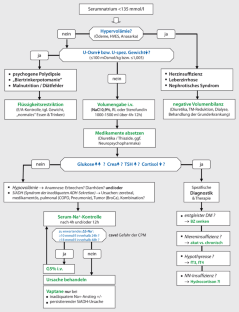
How is hypovolemic hyponatremia treated?
The most common treatment option proposed for patients with hypovolemic hyponatremia is replacement of both salt and water through the intravenous infusion of sodium chloride solutions.
What is the best treatment for hyponatremia?
TreatmentIntravenous fluids. Your doctor may recommend IV sodium solution to slowly raise the sodium levels in your blood. ... Medications. You may take medications to manage the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headaches, nausea and seizures.May 23, 2020
What is emergency treatment for hyponatremia?
Patients with chronic hyponatremia and severe symptoms (eg, severe confusion, coma, seizures) should receive hypertonic saline, but only enough to raise the serum sodium level by 4-6 mEq/L and to arrest seizure activity. After this, we recommend no further correction of the sodium for the first 24 hours.Aug 24, 2020
What is the medication of choice for hyponatremia?
Medication Summary The primary treatments used in the management of hyponatremic patients rely on the use of intravenous sodium-containing fluids (normal saline or hypertonic saline) and fluid restriction. Less commonly, loop diuretics (eg, furosemide) or demeclocycline are used.Jul 16, 2021
What is hypovolemic hyponatremia?
Hypovolemic hyponatremia is a state in which the total body water and sodium content are decreased and the relative decrease in total body sodium is greater than the decrease in total body water [11].Jan 15, 2019
What causes hypovolemic hyponatremia?
Hypovolemic hyponatremia Causes include vomiting, excessive sweating, diarrhea, burns, diuretic use... read more .) Deficiencies in both total body water and total body sodium exist, although proportionally more sodium than water has been lost; the sodium deficit causes hypovolemia.
What IV fluid is best for hyponatremia?
For serious symptomatic hyponatremia, the first line of treatment is prompt intravenous infusion of hypertonic saline, with a target increase of 6 mmol/L over 24 hours (not exceeding 12 mmol/L) and an additional 8 mmol/L during every 24 hours thereafter until the patient's serum sodium concentration reaches 130 mmol/L.Jul 16, 2021
When do you admit a patient for hyponatremia?
Admit patients with severely symptomatic hyponatremia manifested by coma, recurrent seizures, or evidence of brainstem dysfunction to an ICU and monitor serum sodium levels closely. Admit patients with a propensity toward inappropriate free water ingestion to a unit where free water access is restricted.Aug 24, 2020
How do you raise your sodium level?
Intravenous (IV) fluids with a high-concentration of sodium, and/or diuretics to raise your blood sodium levels. Loop Diuretics - also known as "water pills" as they work to raise blood sodium levels, by making you urinate out extra fluid.
What is hypovolemic hypernatremia?
Hypovolemic hypernatremia Hypernatremia associated with hypovolemia occurs with sodium loss accompanied by a relatively greater loss of water from the body. Common extrarenal causes include most of those that cause hyponatremia.
What medications increase sodium levels?
Drug Induced HypernatraemiaDiuretics.Sodium bicarbonate.Sodium chloride.Corticosteroids.Anabolic steroids.Adrenocorticotrophic steroids.Androgens.Oestrogens.
What causes hyponatremia in patients?
In these patients, the main causes of hyponatremia are renal disorders, endocrine deficiencies, reset osmostat syndrome, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), and drugs or medications. Because of their prevalence and importance, SIADH and drugs deserve special mention, and the author will elaborate on these causes later ...
What causes a high osmolality in a diabetic?
Increased plasma osmolality (more than 300 mOsm per kg of water) in a patient with hyponatremia is caused by severe hyperglycemia, such as that occurring with diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. It is caused by the presence of glucose molecules that exert an osmotic force and draw water from the intracellular compartment into the plasma, with a diluting effect. Osmotic diuresis from glucose then results in hypovolemia. Fortunately, hyperglycemia can be diagnosed easily by measuring the bedside capillary blood glucose level.
How to know if you have hyponatremia?
Most patients with hyponatremia are asymptomatic. Symptoms do not usually appear until the plasma sodium level drops below 120 mEq per L (120 mmol per L) and usually are nonspecific (e.g., headache, lethargy, nausea). 11 In cases of severe hyponatremia, neurologic and gastrointestinal symptoms predominate. 3 The risk of seizures and coma increases as the sodium level decreases. The development of clinical signs and symptoms also depends on the rapidity with which the plasma sodium level decreases. In the event of a rapid decrease, the patient can be symptomatic even with a plasma sodium level above 120 mEq per L. Poor prognostic factors for severe hyponatremia in hospitalized patients include the presence of symptoms, sepsis, and respiratory failure. 12
Why is SIADH important?
SIADH is an important cause of hyponatremia that occurs when normal bodily control of antidiuretic hormone secretion is lost and anti diuretic hormone is secreted independently of the body’s need to conserve water. Antidiuretic hormone causes water retention, so hyponatremia then occurs as a result of inappropriately increased water retention in the presence of sodium loss. The diagnostic criteria for SIADH are listed in Table 2. 28
What is reset osmostat syndrome?
The reset osmostat syndrome occurs when the threshold for antidiuretic hormone secretion is reset downward. Patients with this condition have normal water-load excretion and intact urine-diluting ability after an oral water-loading test.
What is hyponatremia in medicine?
Drug and Medication Use. Treatment. References. Hyponatremia is an important electrolyte abnormality with the potential for significant morbidity and mortality. Common causes include medications and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) secretion. Hyponatremia can be classified according to the volume status ...
What causes hypervolemic hyponatremia?
The three main causes of hypervolemic hyponatremia are congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal diseases such as renal failure and nephrotic syndrome.
What causes hypovolemia?
Hypovolemic Hyponatremia. The etiology of hyponatremia is often multifactorial. The most common causes include hypovolemia from gastrointestinal (GI) or other fluid losses , thiazide diuretics, and SIAD [<citeref rid="ref1">1</citeref>].
What causes hypovolemic hyponatremia?
Among the common causes of hypovolemic hyponatremia are GI fluid loss, a range of endocrinopathies [<citeref rid="ref7">7</citeref>], and thiazide-induced hyponatremia, which is best considered as a distinct entity, in particular because recent data suggest that it has a genetic predisposition.
What are the side effects of hypovolemic hyponatremia?
When this occurs, low blood sodium side effects such as headaches, restlessness, confusion, muscle cramping and spasms, and a lack of energy can be experienced . On a more serious note, seizures, a decrease of consciousness or coma are also possible with untreated Hypervolemic hyponatremia. Since it is difficult to diagnose this condition with only a physical exam, a doctor would order urine and blood tests to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the treatment for hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia treatment includes a recommendation of easing up on fluids if your condition is due to diuretics, diet, or excess water intake. The more severe cases of this condition would involve more drastic measures of treatment such at intravenous fluids which would include a solution of sodium to raise the levels of sodium in the blood. ...
Can hypervolemic hyponatremia cause seizures?
On a more serious note, seizures, a decrease of consciousness or coma are also possible with untreated Hypervolemic hyponatremia. Since it is difficult to diagnose this condition with only a physical exam, a doctor would order urine and blood tests to confirm the diagnosis.
How to treat hyponatremia?
If you have severe, acute hyponatremia, you'll need more-aggressive treatment. Options include: 1 Intravenous fluids. Your doctor may recommend IV sodium solution to slowly raise the sodium levels in your blood. This requires a stay in the hospital for frequent monitoring of sodium levels as too rapid of a correction is dangerous. 2 Medications. You may take medications to manage the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headaches, nausea and seizures.
What to do if you have a headache and nausea?
Preparing for your appointment. Seek emergency care for anyone who develops severe signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as nausea and vomiting, confusion, seizures, or lost consciousness. Call your doctor if you know you are at risk of hyponatremia and are experiencing nausea, headaches, cramping or weakness.
Can a doctor diagnose hyponatremia?
However, because the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia occur in many conditions, it's impossible to diagnose the condition based on a physical exam alone.
Can you take medication for hyponatremia?
Medications. You may take medications to manage the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as headaches, nausea and seizures.
Can you cut back on fluids with hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia treatment is aimed at addressing the underlying cause, if possible. If you have moderate, chronic hyponatremia due to your diet, diuretics or drinking too much water, your doctor may recommend temporarily cutting back on fluids.

Clinical significance
Chemistry
Symptoms
Assessment
Causes
Diagnosis
Pathophysiology
Treatment
Contraindications
- Acute severe hyponatremia (i.e., less than 125 mmol per L) usually is associated with neurologic symptoms such as seizures and should be treated urgently because of the high risk of cerebral edema and hyponatremic encephalopathy.32 The initial correction rate with hypertonic saline should not exceed 1 to 2 mmol per L per hour, and normo/hypernatrem...
Research