
Procedures
Many patients can be treated with medications and a heart-healthy lifestyle, and a procedure such as a stent or bypass is only needed for them when there are disabling and/or progressive symptoms, or the blockage is in a dangerous location.
Nutrition
What increases my risk for heart block?
- Past heart attack or heart failure
- Heart valve conditions or surgery on your heart valves
- Some medicines, or being exposed to toxins
- Lyme disease
- Older age
Can heart block be cured?
Medication: In the allopathic system of medicine, medication can only help treat the symptoms of blocked coronary arteries, it cannot fix them. Ayurvedic Approach: The way of understanding of medoroga prakarana according to yogaratnakara and other acharyas are unique.
What medications cause complete heart block?
You treatment depends on the type of heart block you have: With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen. With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
Can medicines reduce heart block?
When is a pacemaker needed for heart block?
Can heart blocks be cured?
Heart block may resolve on its own, or it may be permanent and require treatment. There are three degrees of heart block. First-degree heart block is the mildest type and third-degree is the most severe.
What is the best medicine for heart block?
Calcium channel blockers can help improve symptoms of chest pain. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). These medicines lower blood pressure. They may help keep coronary artery disease from getting worse.
Are heart blocks serious?
Is heart block serious or dangerous? It can be. Type of heart block, its location and severity, and symptoms vary from person to person. If left untreated, severe heart block can cause sudden cardiac arrest (your heart suddenly stops beating), but most commonly can cause either lightheadedness or fainting spells.
Can you clear a heart blockage without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
What is the main reason for heart block?
Coronary artery disease with and without a heart attack is one of the most common causes of heart block. Diseases that weaken the heart muscle (cardiomyopathies) can also damage the wire.
How long can you live with heart block?
The survival rate in the 68 cases of CHB was higher at one year (68%) as well as at 5 years (37%) than that reported by other investigators.
How common is heart block?
How common are heart blocks? First degree and Mobitz type 1 heart blocks are uncommon but not rare. It is estimated that 0.5-2% of otherwise healthy adults have these types of heart blocks.
What heart block feels like?
Symptoms and causes Typical symptoms of heart block are similar to those of many other arrhythmias and may include dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, fatigue, chest pain, or shortness of breath. Some patients, especially those with first-degree heart block, may not experience symptoms at all.
How does exercise help with heart failure?
Increases the amount of daily activities patient can perform without the symptoms of heart failure. Extends the exercise capacity of heart failure patients as measured by the distance they can walk in 6 minutes. Reduces the number of days patients spend in the hospital and the total number of hospitalizations.
How to cure atrial flutter?
Currently, atrial flutter is successfully "cured" by radiofrequency catheter ablation; but treatment to restore atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm has been the traditional use of medications and external cardioversion.
What is radiofrequency ablation?
A technique pioneered at UCSF, radiofrequency catheter ablation destroys or disrupts parts of the electrical pathways causing the arrhythmias, providing relief for patients who may not have responded well to medications, or who would rather not or can't take medications.
What is the treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
For conditions like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, in which a hair-thin strand of tissue creates an extra electrical pathway between the upper and lower chambers of the heart, radiofrequency ablation offers a cure.
What is an implantable cardioverter?
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator is a device for people who are prone to life-threatening rapid heart rhythms. It is slightly larger than a pacemaker and usually is implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone. It is connected to a defibrillation/pace wire (s) positioned inside the heart via a vein. It has the capability of delivering an electric shock to the heart when it determines the heart rate is too fast. It also is capable of pacing or stimulating the heart when it is going too slow.
What is a pacemaker?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first of a new type of pacemaker that paces both ventricles of the heart to coordinate their contractions and improve their pumping ability. According to the test results presented to the FDA, cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT): 1 Increases the amount of daily activities patient can perform without the symptoms of heart failure 2 Extends the exercise capacity of heart failure patients as measured by the distance they can walk in 6 minutes 3 Improves the overall quality of life as judged by standard measurements 4 Promotes changes in heart anatomy to improve cardiac function 5 Reduces the number of days patients spend in the hospital and the total number of hospitalizations
How do pacemakers work?
They are small devices that are implanted beneath the skin below the collarbone and connected to a pace wire (s) positioned inside the heart via a vein; this delivers a small electrical impulse to stimulate the heart to beat when it is going too slow.
What happens after a heart block?
Life After Heart Block . Your heartisn’t plugged into an outlet. And you don’t use a switch to turn it on. But just like a lamp, your heartruns on an electrical system. Every time your heart beats, an electrical signal travels from the upper to the lower chambers. Along the way, the signal tells your heart to contract and pump blood.
What is the name of the monitor that a doctor will use to check your heart?
They may also ask you to wear a monitor, called a Holter, for anywhere from a day to a month to track the rhythm of your heart. Treatment.
Is a pacemaker considered a minor surgery?
This is considered “minor” surgery and you’ll be sedated for it. Like a backup electrical system, it reminds the heart to beat at a normal rate if it slows or stops. Life After Heart Block. Just like your heart, your pacemaker needs to be treated right to work well.
How to prevent heart block?
A healthy lifestyle contributes to overall good health — including heart health. Exercise, eat a well-balanced diet, and don’t smoke. Understanding the risks of your medicines and reviewing them with your healthcare provider can reduce the risk of medicine-induced heart block.
What happens when your heart is blocked?
When you have heart block, there is interference with the electrical signals that usually move from the atria to the ventricles. These signals tell your heart when to beat. This is known as a conduction disorder. If the electrical signals can’t move from your atria to your ventricles, they can’t tell your ventricles to contract ...
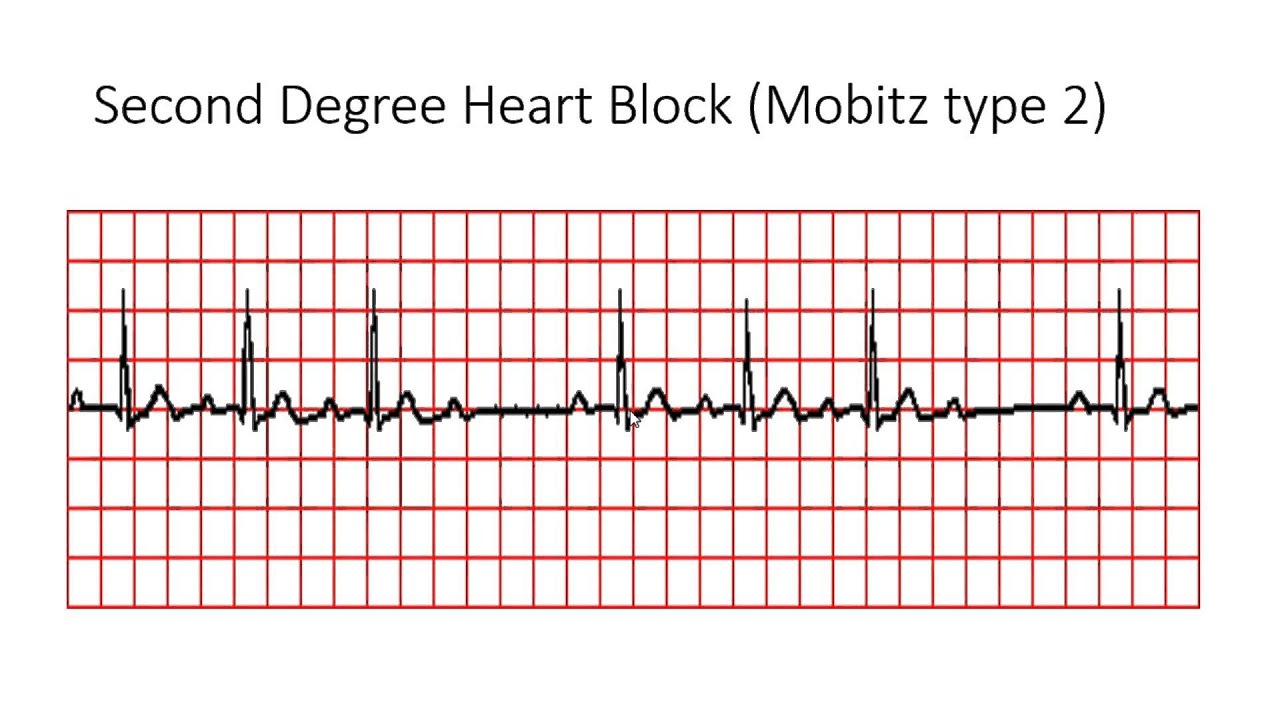
What is the difference between a first degree heart block and a second degree heart block?
The electrical signals slow down as they move from your atria to your ventricles. First-degree heart block might not require treatment of any kind. Second-degree heart block means that the electrical signals between your atria and ventricles can intermittently fail to conduct. There are 2 types of second-degree heart block.
What causes wire damage in the heart?
Cardiomyopathies which are diseases that weaken the heart muscle can also result in wire damage. Any disease that can infiltrate the heart such as sarcoidosis and certain cancers or any disease that results in heart inflammation such as certain autoimmune disease or infections can result in heart block.
How to improve quality of life with pacemaker?
Also, always keep follow-up appointments to make sure your treatment is on track. To improve your quality of life with a pacemaker, you may need to: Avoid situations in which your pacemaker may be disrupted, such as being near an electrical device or devices with strong magnetic fields.
Can heart block cause heart failure?
First degree heart block may cause minimal problems, however third degree heart block can be life-threatening. Heart block may cause no symptoms or it may cause dizziness, fainting, the feeling of skipped heart beats, chest pain, difficulty breathing, fatigue, or even cardiac arrest.
Do you need a pacemaker for a heart block?
You treatment depends on the type of heart block you have: With first-degree heart block, you might not need treatment. With second-degree heart block, you may need a pacemaker if symptoms are present or if Mobitz II heart block is seen . With third-degree heart block, you will most likely need a pacemaker.
What is a first degree AV block?
First-degree AV block is due to delayed conduction in the atrium, AV node or in the His-Purkinje system. 4,5 On an ECG, this manifests as a prolonged PR interval with a duration greater than 200 ms. Though the PR interval is prolonged, it should remain constant, and a P wave should precede every QRS complex. Most cases of first-degree AV block will also have a narrow QRS complex, indicating the block is in the proximal portion of the conducting system–likely the AV node itself; 4,6 approximately 13% of first-degree AV block, though, may have a wide QRS, indicating a more distal block. 4
What causes AV block?
The incidence increases with advancing age. 5 In adults, the most common causes are drug toxicity (generally from rate-controlling medications), coronary artery disease and degenerative processes. 4 In children, the most common cause of complete AV block is congenital: abnormal development of the AV node. 4.
What is cardiac rhythm interpretation?
Cardiac rhythm interpretation is one of the most important skills EMS providers must master. It’s essential to be able to rapidly and accurately interpret rhythm disturbances, as patients with tachy- and brady-dysrhythmias may be unstable and require emergent assessment and treatment.
Does atropine increase cardiac output?
This decrease in vagal tone may sometimes also increase AV conduction. Along with this, it also acts on the more distal components of the conduction system. The goal when using atropine is to increase cardiac output and therefore systemic perfusion.
Which ring insulates the atria and ventricles from one another?
A fibrous ring called the annulus fibrosis electrically insulates the atria and ventricles from one another; thus, the only way for electrical impulses to travel between the atria and ventricles is through the AV node.
Is AV block a variable prognosis?
Asymptomatic patients with underlying heart disease have a variable prognosis, but the prognosis is related to the progression of the underlying heart disease as opposed to the AV block itself. Progression to a higher grade of AV block is rare, unless the patient is experiencing an acute MI.
Can Mobitz block be seen in athletes?
Mobitz type I blocks can sometimes be seen in normal people while asleep and also in conditioned athletes, though both of these are rare findings. It can also be associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI) and as a result of antiarrhythmic or rate-controlling medications.
What test is used to diagnose a left bundle branch block?
Tests that can be used to diagnose a bundle branch block or its causes include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). An ECG records the electrical impulses in your heart using wires attached to the skin on your chest and sometimes your limbs.
What is the best test to check for bundle branch block?
Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to provide detailed images of the heart's structure and the thickness of your heart muscle. It can show whether your heart valves are moving normally. Your doctor can use this test to pinpoint a condition that caused the bundle branch block.
Where is the pacemaker implanted?
A pacemaker is a compact device implanted under the skin of your upper chest with two wires that connect to the right side of your heart. The pacemaker releases electrical impulses when needed to keep your heart beating regularly.
Can you treat bundle branch block?
Most people with bundle branch block don't have symptoms and don't need treatment. For example, left bundle branch block is not treated with medications. However, treatment depends on your specific symptoms and other heart conditions.
What does it mean when your heart is blocked?
Complete heart block (complete AV block) means that the heart's electrical signal doesn't pass from the upper to the lower chambers. When this occurs, an independent pacemaker in the lower chambers takes over. The ventricles can contract and pump blood, but at a slower rate than that of the atrial pacemaker.
How long does it take for a heart block to go through the AV node?
The time it takes for the impulse to get from the atria to the ventricles (the PR interval) should be less than about 0.2 seconds.
Why is my heart blockage so slow?
They're usually are very slow and can't generate the signals needed to maintain full functioning of the heart muscle. On the electrocardiogram, there's no normal relationship between the P and the QRS waves. Complete heart block is most often caused in adults by heart disease or as a side effect of drug toxicity.
What does AV block mean?
Medications for Heart Block. Sometimes the signal from the heart's upper to lower chambers is impaired or doesn't transmit. This is "heart block" or "AV block.". This does not mean that the blood flow or blood vessels are blocked.
Can a heart block occur before birth?
Heart block also can be present at -- or even before -- birth. (This is called congenital heart block.) It also may result from an injury to the electrical conduction system during heart surgery.

Clinical significance
Classification
Symptoms
Mechanism
Specialist to consult
Signs and symptoms
- In people with heart block, also called AV block, the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat is partially or completely blocked from reaching the ventricles.
Causes
- Heart block is classified as first-, second- or third-degree, depending on the extent of electrical signal impairment.