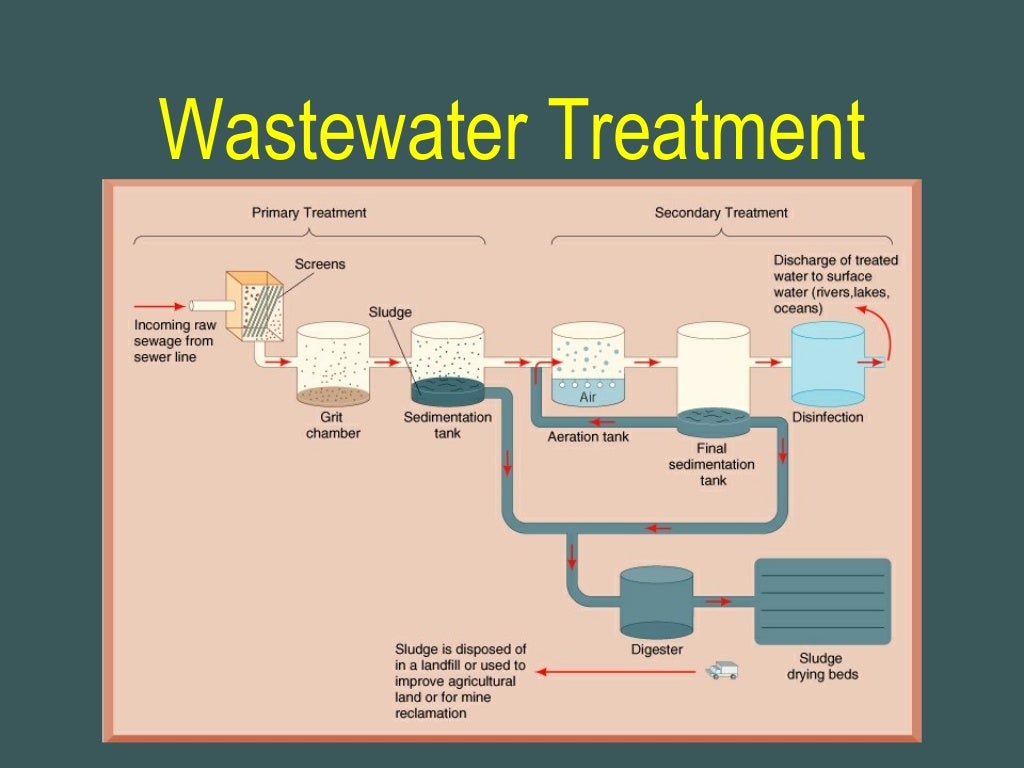
What Are the 3 Stages of Wastewater Treatment
- Primary Stage-separates settable organic solids & inorganic material that won’t degrade
- Secondary Stage-removes suspended & soluble solids converting them to settable solids using Biological Oxidation
- Tertiary Stage-uses chemical & physical treatment to create H2O closer to potable quality
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Water Treatment Process: Follow Water Through a Surface Water Treatment Plant
- Coagulation. ...
- Flocculation. ...
- Sedimentation (or Clarification) The water continues on to the sedimentation basin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Chlorination Operations. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What are the steps in waste water treatment?
- Stage One — Bar Screening.
- Stage Two — Screening.
- Stage Three — Primary Clarifier.
- Stage Four — Aeration.
- Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier.
- Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection)
- Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing.
- Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
What are the three stages of wastewater treatment?
- Primary treatment (stage 1) Primary wastewater treatment involves sedimentation. ...
- Secondary treatment (stage 2) Secondary treatment involves removing soluble organic matter solids that escaped primary treatment. ...
- Tertiary treatment (stage 3) Tertiary treatment, also known as polishing, disinfects water to the highest standards. ...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
What is the first step in sewage treatment?
- Step 1: Screening and Pumping. The incoming wastewater passes through screening equipment where objects such as rags, wood fragments, plastics, and grease are removed.
- Step 2: Grit Removal.
- Step 3: Primary Settling.
- Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge.
- Step 5: Secondary Settling.
- Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
- Sludge Treatment.
What are the three types of wastewater?
There are three types of wastewater, or sewage: domestic sewage, industrial sewage, and storm sewage.
What are the different stages of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What is the most common stage of wastewater treatment?
The most common is chlorine. Chlorination kills bacteria and viruses, but this treatment has the disadvantage of requiring a stage for dichlorination before discharge into the environment.
What are the three major components of a wastewater system?
The system consists of three basic elements: collection chambers, sewer network and a vacuum station. Any type of (low-)flush toilet (including pour-flush) can be used.
What happens in the tertiary stage of wastewater treatment?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
What is the second stage of water treatment?
Secondary Treatment The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What is the first step in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
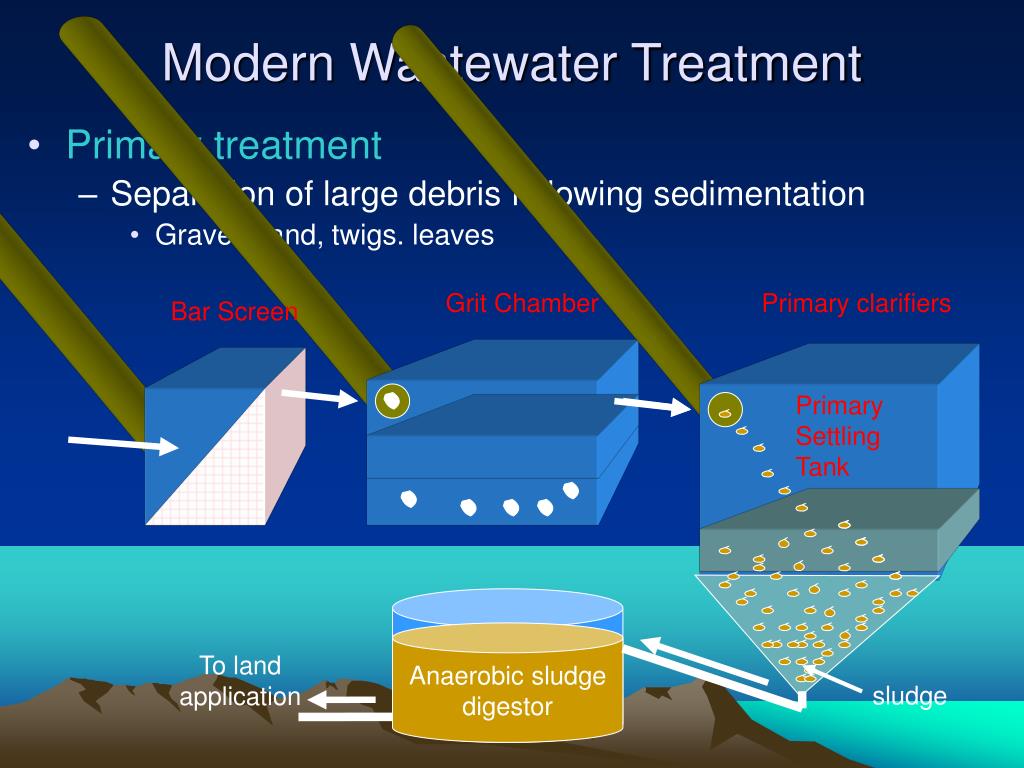
What is primary wastewater treatment?
Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation.
Which one is the correct stages for water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What are the three main purposes of water treatment?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water.
What is primary treatment and secondary treatment?
Differences between primary and secondary wastewater treatmentPrimary Wastewater TreatmentSecondary Wastewater TreatmentIn this method, the waste is processed through a physical procedure with equipment and filtration.The wastewater is purified through biological processes using microorganisms.3 more rows
What is wastewater treatment
Treatment of wastewater is a major step in preventing the pollution of our freshwater resources. The process uses specialized machines to remove pollutants such as metals, debris, microorganisms, and biowaste from the water before it is returned to its source, be it surface water or groundwater.
There are four types of wastewater treatments
This treatment method involves the following steps: infiltration, grit removal, primary sedimentation tank, secondary sedimentation tank, and secondary clarification. This process is used to treat domestic wastewater and commercial waste.
Stages of wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment is the process of cleaning wastewater before it is discharged back into waterways or utilized as a reclaimed water source. Here are the three stages that help us achieve that.
What is stage 2 of wastewater treatment?
Stage 2. – Includes Secondary Treatment using different methods of Biological Oxidation to further purify wastewater. The Conventional Activated Sludge Process is the most popular, using Aeration in a long, but effective process that entails mixing and aerating wastewater in a solution of microorganisms grown in the system that breakdown organic material and separates dissolved solids. This can be accomplished by:
What is the main objective of wastewater treatment?
The main objective of Wastewater Treatment is to separate solids from liquid then to treat both turning the solids into nonhazardous Bio-solids and water into non-threatening environmentally safe water to add back to the environment where it came from with the intention of using it again. 1. Primary Wastewater Treatment.
What is the last treatment before the wastewater enters the receiving stream?
Once the Phosphorous and Nitrates are eliminated then the effluent is sent out to a Chlorine Contact Tank for disinfection. UV or Chlorine can be used for Disinfection and Dissolved oxygen is added as the last treatment before the Wastewater which is now considered Treated Effluent enters the receiving stream.
What is slurry residual material?
These are the Solids that are removed in the primary treatment and secondary systems. Sewage sludge, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of the wastewater treatment processes, still needs more treatment and is considered volatile. Anaerobic Digestors.
How much BOD is removed from sewage?
Weekly averages may be up to 50 percent higher. A sewage treatment plant providing both primary and secondary treatment is expected to remove at least 85 percent of the BOD and suspended solids from domestic sewage.
What is the most standard secondary treatment?
The most Standard secondary treatment techniques that are used mostly in North America today, are the Conventional Activated Sludge Process. After effluent leaves the sedimentation tank in the primary stage it flows or is pumped to a Secondary treatment using one or the other of these processes.
How long does waste water stay in the body?
Wastewater is allowed to pass through this body for a period of time and is then retained for two to three weeks. Because Aeration is the most typical of the Secondary Methods used today and 9 out of 10 systems use Aeration Systems for a few different reasons. Space and ease of operation are a few.
What is the process of wastewater treatment?
Wastewater then goes through screening, in which large items, such as bottle tops and plastics, are removed from the water supply.
What is the purpose of a water treatment system?
These tanks mix wastewater with a small amount of sludge, known as seed sludge, to promote the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that will consume the remaining organic matter.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment. The tertiary stage of treatment is where wastewater’s impurities are actually removed from the supply. During this stage, as much as 99% of the impurities are eliminated, making water that is close to drinking water quality.
How much of the Earth's water is fresh water?
Out of all of the water on the Earth, just 3% of it is fresh water.
What are the three stages of wastewater treatment?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary. Each stage purifies water to a higher level. In some applications, only one or two stages are necessary. The level of treatment necessary depends on the water’s intended use case, and what environment it will be discharged into.
What are the methods of secondary treatment?
Other methods of secondary treatment include filter beds, aerated ponds, biofilters, activated sludge and rotating biological contactors. However, membrane bioreactors are the most efficient technology and the most modern.
What happens to sewage sludge after gravity?
With gravity, heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids rise to the top. Chemicals can also be added as coagulants to remove more solids. Sedimentation creates sewage sludge as a by-product at the bottom of the tank. Once this has settled, the treated water is released for secondary treatment.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment, also known as polishing, disinfects water to the highest standards. This stage is necessary to produce water to specification, such as technical waters, and to treat wastewater for public water systems.
How to remove organic contaminants?
Removal of organic contaminants is best achieved using a membrane bio reactor, where a biological process takes place in the reactor where microorganisms consume the organic matter for energy. The microorganisms replicate to create solids. The solids are then filtered by the membrane to produce effluent.
What is aerobic wastewater treatment?
Aerobic. Aerobic wastewater treatment takes place in the presence of oxygen. In its availability, microbes remove suspended solids and organic wastes from wastewater. The availability of oxygen in the right amount is of paramount importance for successfully conducting this process.
What are the three types of anaerobic processes?
The anaerobic process can be one of the three types: activated sludge, tricking filter, and oxidation pond.
What is the purpose of anaerobic purification?
The anaerobic method of purifying wastewater leads to the production of biogas. It is a clean fuel and helps in the conservation of the environment. The outcomes of this procedure depend on the supply and retention of heat. It is vital for methanogenesis, acetogenesis, acidogenesis, and hydrolysis.
What are the byproducts of anaerobic treatment?
The byproducts released as a result of this process include methane, carbon dioxide and other products.
What are the advantages of microbes in wastewater treatment?
One of the primary advantages of using microbes for the treatment of wastewater is that they can survive in distinct conditions. These include both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. They may be administered together or individually, depending on the needs for the treatment of wastewater.
Why are wastewater plants important?
Wastewater plants provide the right environment for the multiplication of microbes. Such plants produce organic impurities that the microbes absorb to thrive. At the end of the treatment, wastewater plants release energy, water, and carbon dioxide. Wastewater carries many potential disease-causing microbes. The biological process serves as ...
Is wastewater treated with primary or secondary treatment?
Removing them with the help of primary treatment may not be possible. In such cases, the secondary treatment of wastewater serves as a viable option.
What happens after a wastewater treatment plant meets all permit specifications?
After meeting all permit specifications, clean water is reintroduced into the environment. Although testing is continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the plant meets permit specifications.
Why is wastewater pumped into a secondary clarifier?
Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank.
What is activated sludge?
These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.
What is the process of removing large items from the influent?
Removal of large items from the influent to prevent damage to the facility’s pumps, valves and other equipment .#N#The process of treating and reclaiming water from wastewater (any water that has been used in homes, such as flushing toilets, washing dishes, or bathing, and some water from industrial use and storm sewers) starts with the expectation that after it is treated it will be clean enough to reenter the environment.#N#The quality of the water is dictated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Clean Water Act, and wastewater facilities operate to specified permits by National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES). According to the EPA, The Clean Water Act (CWA) establishes the basic structure for regulating discharges of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulating quality standards for surface waters. Under the CWA, EPA sets wastewater standards for industry. The EPA has also developed national water quality criteria recommendations for pollutants in surface waters. EPA's National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program controls discharges.#N#As an example of expected standards, the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of average wastewater effluent is 200 mg/L and the effluent after treatment is expected to be >30 mg/L. It is crucial a wastewater facility meets these expectations or risk stiff penalty.#N#The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill.
What happens if water flows too slow?
If the water flow is too slow, it impacts the process up stream. The solids that fall to the bottom of the clarifier are know as sludge and pumped out regularly to ensure it doesn’t impact the process of separation. The sludge is then discarded after any water is removed and commonly used as fertilizer.
What is a bar screen in wastewater treatment?
A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from ...
What is the function of an aeration tank?
The primary function of the aeration tank is to pump oxygen into the tank to encourage the breakdown of any organic material (and the growth of the bacteria), as well as ensure there is enough time for the organic material to be broken down.
