The stages of the heat treatment process include heating, soaking, and cooling. Heating: Heating is the first stage in a heat-treating process.
What are the three stages of heat treatment?
Today you’ll have knowledge of the three stages of heat treatment. 1.3.1 Watch the video to learn how heat treatment is performed, describing heating, soaking, and cooling. The stages of the heat treatment process include heating, soaking, and cooling. Heating is the first stage in a heat-treating process.
What is the heat treatment process?
In very simple words I am going to explain the heat treatment process consists of a succession of heating and cooling cycles applied to a metal or alloy in order to obtain the desired properties, such as hardness, ductility, tensile strength, toughness, grain size, etc.
What is the primary objective of heating stage?
The primary objective in heating stage is to maintain uniform temperatures. If uneven heating occurs, one section of a part can expand faster than another and result in distortion or cracking. Uniform temperatures are attained by slow heating. The heating rate of a part depends on several factors.
What are the different types of heat-treating?
The various types of heat-treating processes are somewhat similar because they all involve the heating and cooling; they differ in the heating temperatures and the cooling rates used and the final results. The usual methods of heat-treating ferrous metals (metals with iron) are annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering.
What are the stages of heat treatment?
Three stages of heat treatment The stages of the heat treatment process include heating, soaking, and cooling.
What are the 3 stages of heat temperature?
Heat emergencies are health crises caused by exposure to hot weather and sun. Heat emergencies have three stages: heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke. All three stages of heat emergency are serious.
What are the three stages of annealing heat treatment process?
There are three main stages to an annealing process.Recovery stage.Recrystallization stage.Grain growth stage.
What is heat treatment process and types?
Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve the desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering, carburizing, normalizing and quenching.
What are the 3 steps to treating heat exhaustion?
If you suspect heat exhaustion, take these steps immediately:Move the person out of the heat and into a shady or air-conditioned place.Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly.Remove tight or heavy clothing.More items...
What are the three different types of heat treatments available?
The 4 Types of Heat Treatment Steel UndergoesHeat Treatment Steel: Annealing.Heat Treatment Steel: Normalizing.Heat Treatment Steel: Hardening.Heat Treatment Steel: Tempering.
What is the third step in the heat treatment of metals?
The usual methods of heat-treating ferrous metals (metals with iron) are annealing, normalizing, hardening, and tempering. Most nonferrous metals can be annealed, but never tempered, normalized, or case-hardened.
What are the steps in the annealing process?
Stages. The three stages of the annealing process that proceed as the temperature of the material is increased are: recovery, recrystallization, and grain growth.
What is heat treatment process PDF?
Heat treatment consists of heating the metal near or above its critical temperature, held for a particular time at that finally cooling the metal in some medium which may be air, water, brine, or molten salts.
What is the purpose of heat treatment?
The purpose of heat treatment is to make a metal more useful by changing or restoring its mechanical properties.
What is stage 2 in metal treatment?
Stage 2 – Soaking (holding) metal at a given temperature for a given time and cooling the metal to room temperature. Stage 3 – Cooling the metal to room temperature. steps in heat treatment.
What is the process of holding a metal at a certain temperature?
This process is called SOAKING. The length of time held at the proper temperature is called the SOAKING PERIOD, which depends on chemical analysis of the metal and the mass of the part.
How to achieve uniform temperature?
Uniform temperatures are attained by slow heating. The heating rate of a part depends on several factors. One important factor is the heat conductivity of the metal. A metal with a high-heat conductivity heats at a faster rate than one with a low conductivity. Also, the condition of the metal determines the rate at which it may be heated.
What is it called when metal is heated to a final temperature?
This process is called PREHEATING . Following pre-heat, metal is quickly heated to final target temperature. When apart has an intricate design, it may have to be preheated at more than one temperature to prevent cracking and excessive warping.
What does heat treat do to metal?
By heat treating, a metal can be made harder, stronger, and more resistant to impact .Also, heat treating can make a metal softer and more ductile. Some properties are improved at the expense of others; for example, hardening a metal may make it brittle and difficult to machine.
What gases are in a furnace?
These gases contain various proportions of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor and other various hydrocarbons. Fuel-fired furnaces can provide three distinct atmospheres when you vary the proportions of air and fuel. They are called oxidizing, reducing, and neutral.
What are the stages of heat treatment?
Three stages of heat treatment. The stages of the heat treatment process include heating, soaking, and cooling.
What is the first step in the heat treatment process?
Heating is the first stage in a heat-treating process. It is done to change the structure of alloys when heated to some specific temperature. The alloy is said to be at room temperature either by a solid solution, a mechanical mixture, or a combination of both. In a solid solution, two or more metals are used on each other to form a solution without showing their elements even when checked with a microscope. While in the mechanical mixture the elements and compounds are clearly visible and compacted by a matrix of base metal.
What is the cooling stage of a metal?
The cooling stage is the stage at which the metal completely changes to its new properties due to the cooling process. Read more: Heat treatment of metals: definition, purpose advantages, and disadvantages.
What is the final stage of heat treatment?
The final stage in the heat treatment process is the cooling stage . For the metal to be used in various applications, it must be cooled and returned to room temperature. After all, it would be impossible for industries to process and use metal sheets if they still possess very high temperatures. The type of cooling medium that is available for metals include solid, liquid, and gas.
What is the purpose of the soaking stage?
Once the heating stage is done, the metal material must then undergo the soaking stage. The main purpose of this stage is to hold and keep the metal at a specific temperature and time until its internal structure changes. Holding the metal under a specific temperature will make its physical appearance red as heat is distributed evenly to the material.
Do metals react with heat?
Different metals possess a wide variety of distinct properties and characteristics. Some of them can react erratically to heat, while others do not . Some metals may warp and distort when placed under high temperatures at a fast rate, while others do not easily get affected by extreme temperatures. These notable differences are necessary to make the very first stage of the heat treatment process a success.
Why is heat treatment important?
It is very important manufacturing process that can not only help the manufacturing process but can also improve the product, its performance, and its characteristics in many ways. By Heat Treatment process, Example: The plain carbon steel. The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased.
What are the changes in steel?
The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased. Internal stresses that are set up due to cold or hot working may be relieved. The machinability of Steel may be enhanced. The mechanical properties like tensile strength the Talati shock resistance toughness etc may be improved.
What is recrystallization in steel?
This causes complete recrystallization in steel to form New grain structure. This will release the internal stresses previously the strip in the steel and improve the machinability.
What is normalizing steel?
Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the Steel is heated to about 50 degree Celsius above the upper critical temperature followed by air cooling. This results in a softer state which will be lesser soft than that produced by annealing.
What temperature does annealing take place?
Annealing consists of heating of steel parts to a temperature at or near the critical temperature 900 degree Celsius hold it at that temperature for a suitable time and when allowed to cool slowly in the Furnace itself. The heating done during annealing affects the metal in two stages of recovery and recrystallization.
What happens when ammonia is in contact with steel?
During this process, when Ammonia comes in contact with steel is diffuses into nascent hydrogen and nascent nitrogen. This nascent nitrogen so produced diffuses into the surface of the workpiece forming hard nitrites which increase surface hardness.
What is normalizing carried for accomplishing?
Normalizing carried for accomplishing one or more of the following: To refine the grain size. Reduce or remove internal stresses. Improve the machinability of low carbon steel. Increase the strength of medium carbon steel. And also To improve the mechanical properties of the medium Carbon Steel.
What is the purpose of heat treatment?
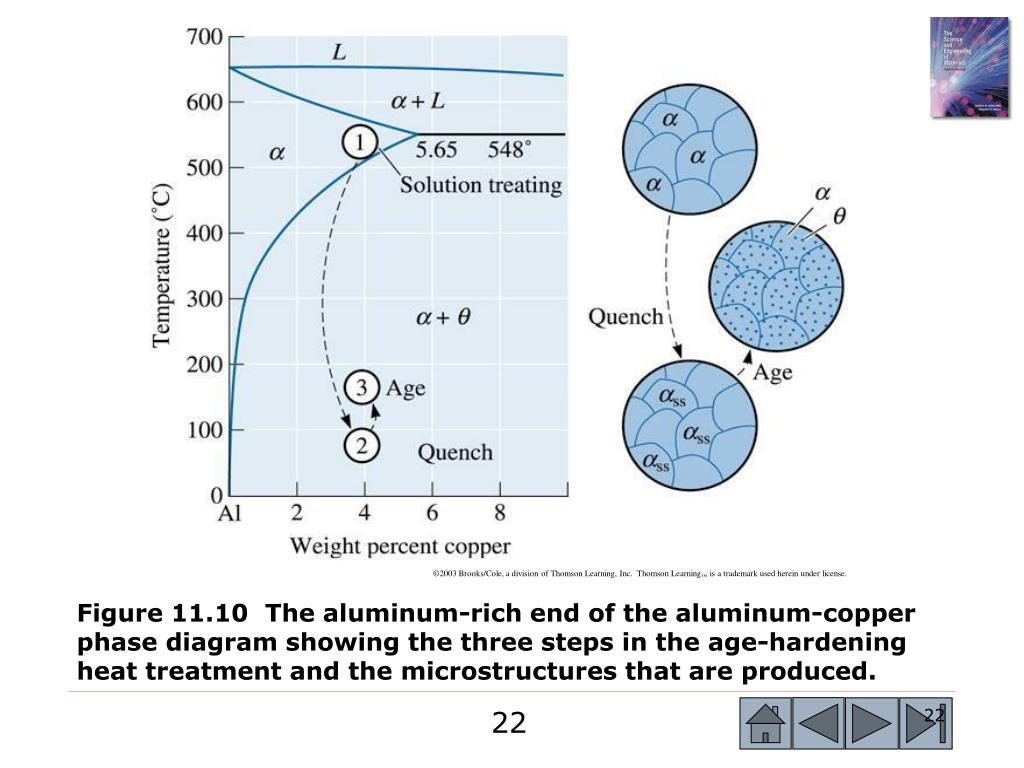
Purpose of heat treatment is to increase service life of a product by increasing its strength of hardness, or prepare the material for improve d manufacturability The basis of change in properties is phase or equilibrium diagrams. 3.
What are the two methods of controlling material properties?
Metals and alloys may not posses all the desired properties in the finished product. Alloying and heat treatment are two methods which are extensively used for controlling material properties. In heat treatment, the microstructures of materials are modified. The resulting phase transformation influences mechanical properties like strength, ...
What are the different types of heat treatment?
Types of Heat Treatment. 1. Annealing. Annealing is one of the most important processes of heat treatment. It is one of the most widely used operations in the heat treatment of iron and steel and is defined as the softening process.
What are the purposes of heat treatment?
The following are the purposes of heat treatment. To improve mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, ductility, shock resistance, and resistance to corrosion. Improve machinability. To relieve the internal stresses of the metal-induced during cold or hot working. To change or refine grain size.
What is tempered steel?
It is an operation used to modify the properties of steel hardened by quenching for the purpose of increasing its usefulness. Tempering or draw results in a reduction of brittleness and removal of internal strains caused during hardening. Steel must be tempered after the hardening process.
What is the process of hardening a metal?
Nitriding. Nitriding is the process of the case or surface hardening in which nitrogen gas is employed to obtain hard skin of the metal. In this process, steel is heated in the presence of ammonia environment. Due to this, a nitrogen atom is deposited and makes material hard.
What gas is released from a furnace?
The container with the part is placed in the furnace and ammonia gas is passed through it while the furnace is heated. During the process of heating nitrogen gas is released from ammonia in the form of atomic nitrogen, which reacts with the surface of the part, and forms iron nitrate.
What temperature is steel heated to?
The steel is heated to a temperature of about 40° to 50°C above its upper critical temperature. It is held at this temperature for a short duration. The steel is then allowed cool in still air at room temperature, which is known as air quenching.
How is steel heated?
The steel is heated above its critical temperature range. It is held at that temperature for a definite period of time. The steel is then rapidly cooled in a medium of quenching.

Overview of Heat Treatment
Heat Treatment Theory
- All heat treatments involve heating and cooling metals, but there are three main differences in process: the heating temperatures, the cooling rates, and the quenchingtypes that are used to land on the properties you want.In a futureblog post, we’ll cover the different types of heat treatment forferrous metals, or metal with iron, which consist of annealing, normalizing, hardeni…
Stages of Heat Treatment
- There are three stages of heat treatment: 1. Heat the metal slowly to ensure that the metal maintains a uniform temperature 1. Soak, or hold, the metal at a specific temperature for an allotted period of time 1. Cool the metal to room temperature