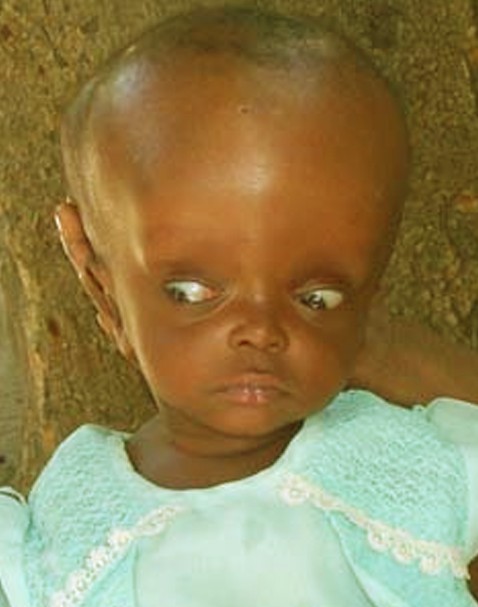
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in toddlers and children:
- Headaches.
- Eyes that are focused downward (sometimes called “sunsetting of the eyes”)
- Blurry vision.
- An unusually large head.
- Sleepiness or low energy.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Bad balance or coordination.
- Lack of appetite.
- Seizures.
- Peeing often or loss of bladder control.
What is the life expectancy of someone with hydrocephalus?
For older children or adults, hydrocephalus can also cause: blurred or double vision problems concentrating loss of coordination confusion incontinence seizures
What is the best treatment for hydrocephalus?
Follow-up. Redness, tenderness, pain or swelling of the skin along the length of the tube or incision. Irritability or drowsiness. Nausea, vomiting, headache or double vision. Fever. Abdominal pain. Return of preoperative neurological symptoms.
What is hydrocephalus and how can it be treated?
Early signs of hydrocephalus in infants include: bulging fontanel, which is the soft spot on the surface of the skull. a rapid increase in head circumference. eyes that are fixed downward. seizures. extreme fussiness. vomiting. excessive sleepiness. poor …
What are the possible prevention of hydrocephalus?
Symptoms in Adults – Balance and coordination issues, headaches, memory loss, bladder problems, gait changes, nausea, vomiting and confusion. Oftentimes this gets misdiagnosed as Alzheimer’s disease or dementia in adults over the age …
What is the best treatment for hydrocephalus?
Shunt system The most common treatment for hydrocephalus is the surgical insertion of a drainage system, called a shunt. It consists of a long, flexible tube with a valve that keeps fluid from the brain flowing in the right direction and at the proper rate.Sep 3, 2021
What are the three causes of hydrocephalus?
The three main causes of hydrocephalus are:A blockage. Tumors, cysts, birth defects, and other objects in the brain can block or affect the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.Poor fluid absorption. ... Too much fluid.Jun 26, 2020
What are the symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults?
Symptoms of Adult-onset HydrocephalusHeadaches.Nausea.Difficulty focusing the eyes.Unsteady walk or gait.Leg weakness.Sudden falls.Irritability.Drowsiness.More items...
What is the most common cause of hydrocephalus in adults?
Hydrocephalus Ex-vacuo: It primarily affects adults and occurs when a degenerative disease, like Alzheimer's disease, stroke or trauma, causes damage to the brain that may cause the brain tissue to shrink.
Can hydrocephalus be treated without surgery?
There is currently no definitive cure. Most patients are managed by shunting using a silicone tube and valve system, where CSF is diverted from the cerebral ventricles to another body site [3].Feb 5, 2016
What are 4 types of hydrocephalus?
The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ex vacuo, and normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medical imaging. Hydrocephalus is typically treated by the surgical placement of a shunt system.
Can hydrocephalus be treated with drugs?
There is little use for medication in hydrocephalus. In some acquired cases, as with tumors and infections, resolving the underlying condition will resolve the hydrocephalus, but most patients still require surgical intervention.Mar 20, 2013
How long can a person with hydrocephalus live?
Approximately, 50% of the affected patients die before three years of age and approximately 80% die before reaching adulthood. Treatment markedly improves the outcome for hydrocephalus not associated with tumors, with 89% and 95% survival in two case studies.Oct 27, 2020
Can hydrocephalus go away?
Hydrocephalus is a condition of the brain where there is a pressure-induced deterioration of brain functions. It does not go away on its own and needs special treatment. Hydrocephalus is due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cavities deep within the brain.Dec 15, 2020
What part of the brain is affected by hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles and puts pressure on the brain. Cerebrospinal fluid normally flows through the ventricles and bathes the brain and spinal column.Sep 3, 2021
How does hydrocephalus occur?
Hydrocephalus occurs when too much fluid builds up in the brain; specifically, excess CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) accumulates in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain. There are more than 100 possible causes of hydrocephalus, but the underlying reasons are: Too much CSF is produced.
How long does a shunt last?
It is difficult to predict how long shunts will last, but some practitioners note that about half of all shunts need to be revised or replaced after 6 years.
What are the symptoms of hydrocephalus?
The most common symptoms of hydrocephalus are headache, nausea, vomiting and fits. For babies, hydrocephalus can also cause: For older children or adults, hydrocephalus can also cause: Sometimes hydrocephalus can put pressure on the optic nerve in the eye.
What is the term for the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain?
Hydrocephalus is when cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain. Normally, CSF is made in the brain to cushion the brain, provide nutrients and remove toxins. It is removed from around the brain in a cycle. But CSF can build up if:
Can hydrocephalus cause strabismus?
For older children or adults, hydrocephalus can also cause: Sometimes hydrocephalus can put pressure on the optic nerve in the eye. This can cause strabismus (where the eyes aren’t straight), gaze palsies (the person can’t move their eyes together upwards) or nystagmus (a rapid abnormal movement in the eyes).
Can you get hydrocephalus as a child?
People can also get hydrocephalus as a child or as an adult after a head injury, after bleeding in the brain, after a brain tumour or after meningitis, which is an infection around the brain. Another cause of hydrocephalus is spina bifida, a birth defect that affects the spine.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
The symptoms of hydrocephalus tend to vary greatly from person to person and across different age groups. Infants and young children are more susceptible to symptoms from increased intracranial pressure like vomiting and adults can experience loss of function like walking or thinking.
What is the type of hydrocephalus that develops at birth or in adulthood?
Based on onset, presence of structural defects or high vs. normal CSF pressures, hydrocephalus can be divided into categories. Acquired Hydrocephalus: This is the type of hydrocephalus that develops at birth or in adulthood and is typically caused by injury or disease.
What is the term for the excess cerebrospinal fluid in the brain?
Definition. Hydrocephalus is a condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the fluid-containing cavities or ventricles of the brain. The term hydrocephalus is derived from the Greek words "hydro" meaning water and "cephalus" meaning the head. Although it translates as "water on the brain," the word actually refers to ...
What is the name of the condition that occurs when there is no obstruction to the flow of CSF within the ventricular
Congenital Hydrocephalus: It is present at birth and may be caused by events that occur during fetal development or as a result of genetic abnormalities. Communicating Hydrocephalus : This type of hydrocephalus occurs when there is no obstruction to the flow of CSF within the ventricular system.
How common is hydrocephalus in children?
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), hydrocephalus is believed to affect approximately one to two in every 1,000 children born in the U.S.
What is non communication hydrocephalus?
Non-communication (Obstructive) Hydrocephalus: It occurs when the flow of CSF is blocked along one of more of the passages connecting the ventricles, causing enlargement of the pathways upstream of the block and leading to an increase in pressure within the skull.
What is the name of the disease that causes the brain to shrink?
Hydrocephalus Ex-vacuo: It primarily affects adults and occurs when a degenerative disease, like Alzheimer’s disease , stroke or trauma, causes damage to the brain that may cause the brain tissue to shrink.
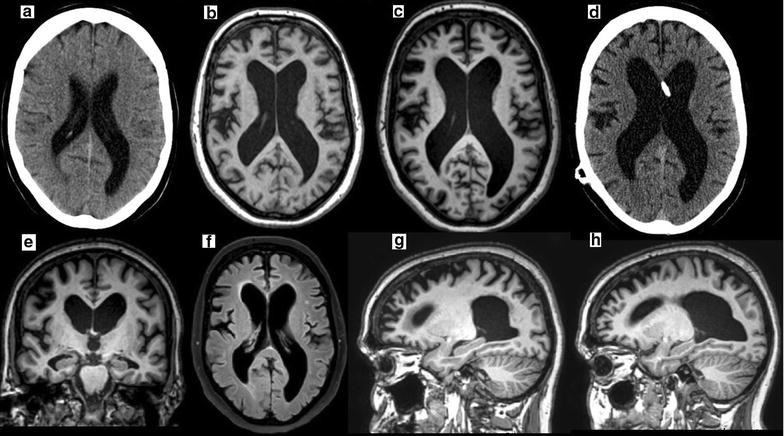
What is the best way to diagnose hydrocephalus?
MRIs use a magnetic field and radio waves to make a cross-sectional image of the brain. Computerized tomography (CT) scans can also help diagnose hydrocephalus in children and adults. CT scans use several different X-rays to form a cross-sectional image of the brain.
How do you know if you have normal pressure hydrocephalus?
One of the earliest signs is falling suddenly without losing consciousness . Other common symptoms of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) include: changes in the way you walk.
What is the name of the condition where fluid builds up in the skull and causes the brain to swell?
Hydrocephalus is a condition that occurs when fluid builds up in the skull and causes the brain to swell. The name means “water on the brain.”. Brain damage can occur as a result of the fluid buildup. This can lead to developmental, physical, and intellectual impairments. It requires treatment to prevent serious complications.
Why does hydrocephalus start before birth?
Underlying causes. In some cases, hydrocephalus starts before a baby is born. This can result from: a birth defect in which the spinal column doesn’t close. a genetic abnormality. certain infections that occur during pregnancy, such as rubella. This condition can also occur in infants, toddlers, and older children due to:
What are the causes of central nervous system infections?
central nervous system infections such as meningitis, especially in babies. bleeding in the brain during or shortly after delivery, especially in babies born prematurely. injuries that occur before, during, or after delivery. head trauma. central nervous system tumors.
How to tell if an infant has hydrocephalus?
Early signs of hydrocephalus in infants include: bulging fontanel, which is the soft spot on the surface of the skull. a rapid increase in head circumference. eyes that are fixed downward. seizures. extreme fussiness. vomiting. excessive sleepiness. poor feeding.
How many babies are born with hydrocephalus?
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) estimates that 1 to 2 of every 1,000 babies are born with hydrocephalus.
The Causes and Symptoms of Hydrocephalus
There are a number of different reasons that can lead to excess CSF fluid in the brain. In some individuals, it can be inherited genetically or may be associated with certain developmental disorders, like spina bifida or encephalocele.
Diagnosing and Treating Hydrocephalus
A diagnosis can be made by a neurosurgeon or another head and brain specialist. During the examination, your specialist will look for physical symptoms listed above, review your medical history and if possible, ask the patient about their symptoms.
What causes pressure hydrocephalus?
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus results from the gradual blockage of the CSF-draining pathways in the brain. The ventricles enlarge to handle the increased volume of CSF, thus compressing the brain from within and eventually damaging or destroying the brain tissue.
What is the meaning of hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the ventricles (fluid-containing cavities) of the brain and may increase pressure within the head.
What is the cause of hydrocephalus ex-vacuo?
Hydrocephalus ex-vacuo occurs when a stroke or injury damages the brain and brain matter actually shrinks. The brain may shrink in older patients or those with Alzheimer's disease, and CSF volume increases to fill the extra space. In these instances, the ventricles are enlarged, but the pressure usually is normal.
What is the water on the brain called?
Although hydrocephalus often is described as "water on the brain," the "water" is actually CSF — a clear fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. CSF has three crucial functions: It acts as a "shock absorber" for the brain and spinal cord; It acts as a vehicle for delivering nutrients to the brain and removing waste; and.
What is the success rate of hydrocephalus?
The success rate varies from 25 to 74 percent for NPH cases in which its cause is unknown. In general, the earlier hydrocephalus is diagnosed, the better the chance for successful treatment. The longer the symptoms have been present, the less likely it is that treatment will be successful.
How old do you have to be to get hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can occur at any age, but is most common in infants and adults age 60 and older. It affects adult males and females, as well as people of different races, about equally.
Can hydrocephalus be rehabilitated?
If any neurological problems persist, rehabilitation may be required to further your improvement. However, recovery may be limited by the extent of the damage already caused by the hydrocephalus and your brain's ability to heal. Because hydrocephalus is an ongoing condition, long-term follow-up by a doctor is required.
What does it mean when a person has hydrocephalus?
Some experts refer to hydrocephalus as either “communicating” -- meaning the cerebrospinal fluid is flowing freely -- or “non-communicating ,” which is when there’s a blockage. Hydrocephalus Diagnosis.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
In babies, they include: An unusually large head that gets bigger quickly. The soft spot on top of a baby’s head is firm or bulging. Eyes that are focused downward (sometimes called “sunsetting of the eyes”) Crankiness or irritability.
What happens if hydrocephalus is blocked?
It’s important to get medical help right away if anything goes wrong after treatment for hydrocephalus. Complications of shunt systems can happen when the shunt is blocked and stops working or when an infection occurs. This can cause cerebral spinal fluid to build up again. Signs and symptoms may include: Headache.
Why does my brain swell?
This is caused by a tumor, cyst, head injury, or a brain infection. Normal pressure hydrocephalus . This usually shows up in older adults and leads to a swelling in the small, open areas of the brain but without any change in pressure. Doctors aren’t sure what causes this type.
Why does my brain keep taking in cerebrospinal fluid?
Inflammation, injuries, or infections like bacterial meningitis can keep your brain tissues from taking in cerebrospinal fluid. Too much fluid . In rare cases, your body makes more cerebrospinal fluid than your brain can handle. Types of Hydrocephalus.
What is the term for the buildup of fluid in the brain?
What Is Hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus -- which roughly means “water on the brain” -- is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. This fluid doesn’t flow or get absorbed the way it should.
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid?
It’s called cerebrospinal fluid, and it cushions your brain from injuries and has nutrients and proteins that help keep it healthy and working. Cerebrospinal fluid also: Allows the relatively heavy brain to float within the skull. Removes waste products of the brain’s metabolism.
What are the symptoms of hydrocephalus?
Seek prompt medical care if you or someone you are with has symptoms suggestive of hydrocephalus, such as progressive memory loss, personality changes, difficulty thinking, increasing sleepiness, headache, coordination and walking problems, urinary incontinence, or vomiting.
What are the symptoms of hydrocephalus in older adults?
Older children who are able to express their symptoms and adults may have symptoms, such as: Changes in mood, personality or behavior. Difficulty initiating movements or slowed movement.
What are the symptoms of a shrill cries?
High-pitched, shrill cries in an infant or small child. Irritability, fussiness, poor feeding, and poor sleeping in infants and young children. Respiratory or breathing problems such as shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, labored breathing, wheezing, not breathing, or choking. Seizure. Stiff or rigid neck.
How do you know if you have hydrocephalus?
Common symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants and small children. Infants and small children may not be able to express their symptoms directly, but some changes may be apparent including: Bulging of the soft spot on top of the head, near the front (anterior fontanelle) Developmental delays and failure to thrive. Downward gaze.
How many children have hydrocephalus?
It is not known how many adults are affected by hydrocephalus, but it is estimated that it occurs in about one in every 500 children (Source: NINDS ). Hydrocephalus can have serious complications, so it is important that it be evaluated and treated without delay.
Why does hydrocephalus occur after birth?
It can also occur after birth as a result of certain infections, bleeding in the brain, injury, ...
Where is hydrocephalus produced?
The fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid, is produced in cavities located deep within the brain known as ventricles. The fluid fills the ventricles and flows into the spinal cord and out into the subarachnoid space where it absorbed.
Why do you need to treat hydrocephalus?
Both types of hydrocephalus require urgent treatment to reduce the pressure on the brain; otherwise, there is a serious risk of damage to the brainstem, which regulates functions such as our breathing and heartbeat.
What are the symptoms of congenital hydrocephalus?
Symptoms of congenital hydrocephalus (present at birth): breathing difficulties. arm and leg muscles may be stiff and prone to contractions. some developmental stages may be delayed, such as sitting up or crawling. the fontanel, the soft spot on the top of the head, is tense and bulges outward.
How does CSF affect the brain?
The brain produces about 1 pint of CSF each day, and old CSF is absorbed into blood vessels. If the process of producing and removing CSF is disturbed, CSF can accumulate, causing hydrocephalus.
Why does hydrocephalus occur?
Hydrocephalus occurs when too much fluid builds up in the brain; specifically, excess CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) accumulates in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain. There are more than 100 possible causes of hydrocephalus, but the underlying reasons are: Too much CSF is produced.
What are the problems that can cause a baby to develop brains?
For instance, hydrocephalus is common in children with severe spina bifida (a birth defect of the spinal cord). Infections during pregnancy – these can affect the development of the baby’s brain.
What is water in the brain?
Diagnosis. Treatments. Complications. Prevention. Hydrocephalus, also called water in the brain, is a condition where there is an abnormal build up of CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain.
What causes pressure hydrocephalus?
This condition affects people aged at least 50 – in most cases, doctors don’t know what caused it. Sometimes, it may develop after a stroke, infection, or injury to the brain. There are two theories: CSF is not reabsorbed into the bloodstream properly.
Why does hydrocephalus happen?
Hydrocephalus happens when the natural system for draining and absorbing extra CSF doesn’t work right. The ventricles enlarge to accommodate the extra fluid and then press on different parts of the brain, causing a number of different symptoms. Hydrocephalus has many different causes.
What age do you get hydrocephalus?
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a type of hydrocephalus that usually happens in older adults. The average age of a person with NPH is over age 60.
How old is a person with NPH?
The average age of a person with NPH is over age 60. NPH is different from other types of hydrocephalus in that it develops slowly over time. The drainage of CSF is blocked gradually, and the extra fluid builds up slowly.
What parts of the brain are affected by NPH?
The parts of the brain most often affected in NPH are those that control the legs, the bladder, and the "cognitive" mental processes such as memory, reasoning, problem solving , and speaking.
What is the fluid that surrounds the brain?
Your brain and spinal cord are surrounded by a clear liquid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It’s made and stored in cavities in your brain called ventricles. It circulates around your brain, moving from ventricle to ventricle. It cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord, supplies them with nutrients, and removes some ...
How to prevent NPH?
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Prevention. There is no known way to prevent NPH. A healthy lifestyle, including not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise, may help avoid conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and stroke that might contribute to NPH.
Can NPH cause inability to control bowels?
Other symptoms include abnormal gait (difficulty walking), inability to hold urine ( urinary incontinence ), and, occasionally, inability to control the bowels. The dementia symptoms of NPH can be similar to those of Alzheimer's disease. The walking problems are similar to those of Parkinson's disease.
