What is an anaphylactic reaction?
ANAPHYLACTIC REACTION: PRIMARY ASSESSMENT 1. Patient may complain of not feeling well or malaise, generalized feeling of weakness or discomfort. 2. Closely assess the airway for signs of obstruction (stidor or crowing sounds). 3. Positive pressure ventilation may be necessary to force the air past the swollen upper airway. 4.
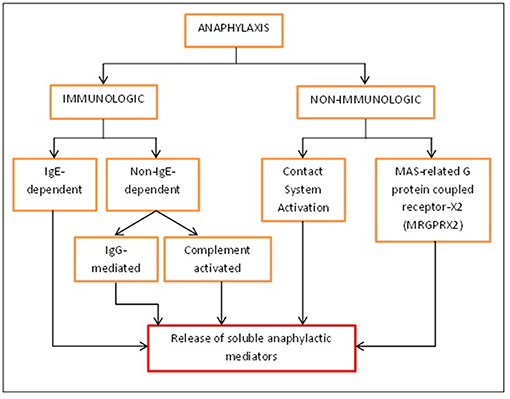
What are the chemical mediators of anaphylaxis?
Signs and Symptoms of Anaphylactic Reaction Involves skin, circulatory, respiratory, CNS, gastrointestinal. Signs and symptoms caused by capillary leakage, vasodilation, or bronchial constriction and inflammation Two key categories of signs and symptoms that indicate a severe anaphylactic reaction Compromised Airway and Respiratory and Shock
How long does it take for anaphylaxis to occur?
anaphylactic reaction sever, exaggerated, systemic, allergic reaction associated with severe swelling of the upper and lower airways, constriction of the bronchioles, leakage of fluid from the capillaries ,systemic vessel dilation, and an increased production of mucus immune system fight off invasion by foreign substances antigens
What triggers anaphylaxis?
Anaphylaxis (Central Nervous System) Increased anxiety Light-headedness Unresponsiveness Disorientation Restlessness Seizures Headache Anaphylaxis (Gastrointestinal System) Nausea/vomiting Abdominal cramping Diarrhea Difficulty in swallowing Loss of bowel control Anaphylaxis (Genitourinary System) Urgent need to urinate Cramping of the uterus

What are the symptoms and treatment of an anaphylactic reaction?
What is the usual treatment for an anaphylactic reaction?
Which four symptoms can occur during an allergic reaction?
- sneezing and an itchy, runny or blocked nose (allergic rhinitis)
- itchy, red, watering eyes (conjunctivitis)
- wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath and a cough.
- a raised, itchy, red rash (hives)
- swollen lips, tongue, eyes or face.
What are the 5 most common triggers for anaphylaxis?
- foods – including nuts, milk, fish, shellfish, eggs and some fruits.
- medicines – including some antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin.
- insect stings – particularly wasp and bee stings.
- general anaesthetic.