What are the side effects of PTSD treatment?
Side effects may include dry mouth, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, sexual dysfunction, and insomnia. After treatment with an antidepressant has stabilized a person's depression, doctors typically continue medication for about one year.
How does treatment for PTSD work?
Post-traumatic stress disorder treatment can help you regain a sense of control over your life. The primary treatment is psychotherapy, but can also include medication. Combining these treatments can help improve your symptoms by: Teaching you skills to address your symptoms.
How long does PTSD last with treatment?
Some people recover within 6 months, while others have symptoms that last much longer. In some people, the condition becomes chronic. A doctor who has experience helping people with mental illnesses, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, can diagnose PTSD.
What is the best treatment for PTSD?
Psychotherapy. Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of psychotherapy that has consistently been found to be the most effective treatment of PTSD both in the short term and the long term. CBT for PTSD is trauma-focused, meaning the trauma event(s) are the center of the treatment.
What are 3 treatments for PTSD?
What Are the Treatments for PTSD?Therapy.Cognitive Processing Therapy.Prolonged Exposure Therapy.Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing.Stress Inoculation Training.Medications.
What kind of medication is used to treat PTSD?
Certain selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are recommended for treating PTSD.
Does PTSD go away with treatment?
Sometimes the effects of PTSD will go away after a few months. Sometimes they may last for years – or longer. Most people who have PTSD will slowly get better, but many people will have problems that do not go away. There is no way to tell who will get better without treatment.
Can PTSD come back after treatment?
PTSD symptoms can come back if you don't continue to engage in the healthy behaviors and coping skills that you learned during treatment. Therefore, it is very important to take steps to make sure that the skills you learned in treatment stay fresh in your mind.
Is PTSD brain damage?
According to recent studies, Emotional Trauma and PTSD do cause both brain and physical damage. Neuropathologists have seen overlapping effects of physical and emotional trauma upon the brain.
What is the gold standard treatment for PTSD?
behavior therapy, or TF-CBT, is considered the gold standard treatment for children and adolescents with PTSD.
What is the best treatment for PTSD?
Medications. The most studied type of medication for treating PTSD are antidepressants, which may help control PTSD symptoms such as sadness, worry, anger, and feeling numb inside. Other medications may be helpful for treating specific PTSD symptoms, such as sleep problems and nightmares.
How long does it take to recover from PTSD?
Some people recover within 6 months, while others have symptoms that last much longer. In some people, the condition becomes chronic. A doctor who has experience helping people with mental illnesses, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, can diagnose PTSD.
What is PTSD in psychology?
Overview. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a disorder that develops in some people who have experienced a shocking, scary, or dangerous event. It is natural to feel afraid during and after a traumatic situation. Fear triggers many split-second changes in the body to help defend against danger or to avoid it.
What is PTSD in the body?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a disorder that develops in some people who have experienced a shocking, scary, or dangerous event. It is natural to feel afraid during and after a traumatic situation. Fear triggers many split-second changes in the body to help defend against danger or to avoid it. This “fight-or-flight” response is ...
Can PTSD be chronic?
Signs and Symptoms. While most but not all traumatized people experience short term symptoms, the majority do not develop ongoing (chronic) PTSD. Not everyone with PTSD has been through a dangerous event. Some experiences, like the sudden, unexpected death of a loved one, can also cause PTSD.
How long does PTSD last?
Symptoms must last more than a month and be severe enough to interfere with relationships or work to be considered PTSD. The course of the illness varies. Some people recover within 6 months, while others have symptoms that last much longer. In some people, the condition becomes chronic.
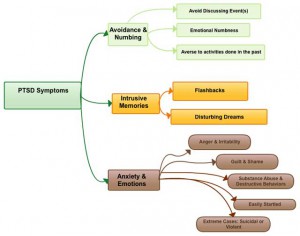
What are the symptoms of avoidance?
Avoidance symptoms include: Staying away from places, events, or objects that are reminders of the traumatic experience. Avoiding thoughts or feelings related to the traumatic event. Things that remind a person of the traumatic event can trigger avoidance symptoms.
What are the symptoms of PTSD?
One of the 17 symptoms of PTSD is a negative perception of the self and the world at large. Client-centered therapy seeks to build a person’s self-esteem after a traumatic incident, reassuring them that they are worthy of success and healing. 6. Self-Isolation; Feeling Distant.
What is the most common symptom of PTSD?
Insomnia. Insomnia is another typical symptom of PTSD. To go to bed, a person has to let their guard down, which is especially difficult for hypervigilant trauma sufferers. Additionally, the nightmares they may face at bedtime can make sleep an unattractive proposition.
Which part of the brain is most affected by stress?
The hippocampus, amygdala and prefrontal cortex are strongly associated with stress and memory.
What does intrusive thinking mean?
What do intrusive thoughts look like? A person going about their day is suddenly confronted by unwelcome, distressing memories of what happened to them. This may happen in a related setting – for example, a person who has gone through a car accident may begin to panic in a vehicle – or out of the blue.
Do trauma survivors have nightmares?
Trauma survivors regularly deal with nightmares. Research from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs ( the VA) has indicated that 71% to 96% of those with PTSD may have nightmares. Those with co-occurring mental illnesses are also at higher risk for vivid, disturbing dreams.
Can PTSD cause nightmares?
Research from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs ( the VA) has indicated that 71% to 96% of those with PTSD may have nightmares. Those with co-occurring mental illnesses are also at higher risk for vivid, disturbing dreams. 3. Avoiding Reminders of the Event. PTSD changes the way a person lives their life.
How does PTSD affect people?
PTSD changes the way a person lives their life. One of the major effects of trauma is avoidance. For example, someone who nearly drowned will probably avoid swimming again. However, they might even avoid taking baths or going to the beach because it reminds them too much of what happened.
What does PTSD feel like?
Having negative thoughts and feelings: PTSD can make you feel negative, angry, sad, distrustful, guilty, or numb. Reliving or re-experiencing the traumatic event: This can take the form of flashbacks or dreams.
What are some examples of PTSD?
Examples include friends you met in the military service, the part of town where you experienced the trauma, or crowds in general. Some people with PTSD try to stay so busy that they don’t think about the event. Being on edge: The disorder can make it hard for you to relax or enjoy the things you used to.
What is PTSD in psychology?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health issue that may develop after a traumatic event. It causes negative, anxious emotions. Some people with PTSD relive the event over and over. Others avoid any reminders of it. PTSD interferes with life, work and relationships.
What is PTSD mental health?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health issue that may develop after a traumatic event. It causes negative, anxious emotions. Some people with PTSD relive the event over and over. Others avoid any reminders of it.
Can you predict PTSD?
There’s no way to predict who will develop PTSD from a traumatic event. However, PTSD is more common in people who have experienced: Certain types of trauma, particularly military combat or sexual assault. Injury during the event. Lack of support from loved ones after a traumatic event. Long-lasting or repeated trauma.
Is PTSD more common in military?
However, PTSD is more common in people who have experienced: Certain types of trauma, particularly military combat or sexual assault. Injury during the event. Lack of support from loved ones after a traumatic event. Long-lasting or repeated trauma.
Can PTSD make you feel bad?
You also may have trouble sleeping or concentrating. Having negative thoughts and feelings: PTSD can make you feel negative, angry, sad, distrustful, guilty, or numb. Reliving or re-experiencing the traumatic event: This can take the form of flashbacks or dreams.
What is the best treatment for PTSD?
Trauma-focused Psychotherapies. Trauma-focused Psychotherapies are the most highly recommended type of treatment for PTSD. "Trauma-focused" means that the treatment focuses on the memory of the traumatic event or its meaning. These treatments use different techniques to help you process your traumatic experience.
What are the medications used for PTSD?
These are antidepressant medications called SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) and SNRIs (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors).
What are the best psychotherapies for trauma?
The trauma-focused psychotherapies with the strongest evidence are: 1 Prolonged Exposure (PE)#N#Teaches you how to gain control by facing your negative feelings. It involves talking about your trauma with a provider and doing some of the things you have avoided since the trauma. 2 Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT)#N#Teaches you to reframe negative thoughts about the trauma. It involves talking with your provider about your negative thoughts and doing short writing assignments. 3 Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)#N#Helps you process and make sense of your trauma. It involves calling the trauma to mind while paying attention to a back-and-forth movement or sound (like a finger waving side to side, a light, or a tone).
Do psychotherapists focus on trauma?
Some psychotherapies do not focus on the traumatic event, but do help you process your reactions to the trauma and manage symptoms related to PTSD. The research behind these treatments is not as strong as the research supporting trauma-focused psychotherapies (listed above).
What is CPT therapy?
It involves talking about your trauma with a provider and doing some of the things you have avoided since the trauma. Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) Teaches you to reframe negative thoughts about the trauma.
How PTSD affects your life
Most people who experience a traumatic event heal from it without lasting impacts or symptoms in their daily life.
Who gets PTSD?
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), around 4% percent of the U.S. population lives with PTSD, and among U.S. adults, roughly 2% of men experience PTSD.
What causes PTSD in men and how is it different?
Every case of PTSD is different, and no single factor is present in every case.
Symptoms and signs of PTSD in men
To receive a PTSD diagnosis, the NIMH says a mental health professional must confirm that you’ve experienced the following symptoms for at least a month:
Getting a PTSD diagnosis
If you believe that you may have PTSD, there are many resources and mental health professionals available to help you.
PTSD treatment options
Because PTSD can manifest differently from person to person, multiple treatment options are available. Your therapist will work with you to find the best one for your symptoms.
Next steps
It’s important to remember that PTSD can happen to anyone. It isn’t specific to just one gender or type of person.
What are the medications used for PTSD?
Medications ». Four medications received a conditional recommendation for use in the treatment of PTSD: sertraline, paroxetine, fluoxetine and venlafaxine. at a glance. at a glance. About. Currently only the SSRIs sertraline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil) are FDA-approved for the treatment of PTSD.
How long is a trauma treatment session?
As conducted in research studies, treatment consists of 16 individual sessions, each lasting between 45 minutes and one hour. Sessions are typically scheduled once per week. Each of the 16 sessions has a specific objective. This intervention is intended for individuals who have experienced a single traumatic event.
What is CBT therapy?
The category of CBT encompasses various types and elements of treatment used by cognitive behavioral therapists, while Cognitive Processing Therapy, Cognitive Therapy and Prolonged Exposure are all more specialized treatments that focus on particular aspects of CBT interventions.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on the relationships among thoughts, feelings and behaviors; targets current problems and symptoms; and focuses on changing patterns of behaviors, thoughts and feelings that lead to difficulties in functioning.
How many sessions are there in cognitive behavioral therapy?
For example, altering a person’s unhelpful thinking can lead to healthier behaviors and improved emotion regulation. It is typically delivered over 12-16 sessions in either individual or group format.
How many sessions are there in CPT?
CPT is generally delivered over 12 sessions and helps patients learn how to challenge and modify unhelpful beliefs related to the trauma.
What is cognitive therapy?
Derived from cognitive behavioral therapy, cognitive therapy entails modifying the pessimistic evaluations and memories of trauma, with the goal of interrupting the disturbing behavioral and/or thought patterns that have been interfering in the person’s daily life.
How to treat PTSD?
PTSD therapy has three main goals: 1 Improve your symptoms 2 Teach you skills to deal with it 3 Restore your self-esteem
How to help someone with PTSD?
Improve your symptoms. Teach you skills to deal with it. Restore your self-esteem. Most PTSD therapies fall under the umbrella of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). The idea is to change the thought patterns that are disturbing your life.
What drugs affect the brain?
Several types of drugs affect the chemistry in your brain related to fear and anxiety. Doctors will usually start with medications that affect the neurotransmitters serotonin or norepinephrine (SSRIs and SNRIs), including: 1 Fluoxetine ( Prozac) 2 Paroxetine (Paxil) 3 Sertraline ( Zoloft) 4 Venlafaxine (Effexor)
What medications are prescribed for PTSD?
Because people respond differently to medications, and not everyone's PTSD is the same, your doctor may prescribe other medicines "off label," too. (That means the manufacturer didn't ask the FDA to review studies of the drug showing that it's effective specifically for PTSD.) These may include: 1 Antidepressants 2 Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) 3 Antipsychotics or second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) 4 Beta-blockers 5 Benzodiazepines
What is PTSD in 2020?
Medically Reviewed by Smitha Bhandari, MD on January 21, 2020. Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a type of anxiety disorder, can happen after a deeply threatening or scary event. Even if you weren't directly involved, the shock of what happened can be so great that you have a hard time living a normal life.
What is PTSD in psychology?
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a type of anxiety disorder, can happen after a deeply threatening or scary event. Even if you weren't directly involved, the shock of what happened can be so great that you have a hard time living a normal life. People with PTSD can have insomnia, flashbacks, low self-esteem, ...
Can PTSD cause insomnia?
Even if you weren't directly involved, the shock of what happened can be so great that you have a hard time living a normal life. People with PTSD can have insomnia, flashbacks, low self-esteem, and a lot of painful or unpleasant emotions. You might constantly relive the event -- or lose your memory of it altogether.