
Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine is a branch of translational research in tissue engineering and molecular biology which deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function".
Full Answer
Can human stem cells be used for Regenerative Medicine?
Intestinal stem cells can be grown in vitro in organoid structures, though only a fraction of the cells contained are stem cells with regenerative capabilities. Hence, techniques to enrich stem cell populations are being pursued through the development of multiple two-dimensional and three-dimensional culture protocols, as well as co-culture techniques and multiple growth …
What is stem-cell therapy?
Mar 28, 2018 · Human embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are derived from the inner layer of the blastocyst and, due to their pluripotency, are used in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Human fetal mesenchymal stem cells (hfMSCs) can be harvested from stem cells present in the amniotic fluid or the umbilical cord.
Why are stem cells the New Frontier in regenerative medicine?
Recently, human dental mesenchymal stem cells (DMSCs) have received extensive attention in the field of regenerative medicine due to their accessibility and multipotency. Since their origin is within the neural crest, they can be differentiated into neural crest-derived cells including neuron and glia cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Can animal models facilitate the utilization of stem cells in regenerative medicine?
Mar 19, 2022 · Stem cells are the body's master cells. All other cells arise from stem cells, including blood cells, nerve cells and others. Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called ...

What are the 3 types of human stem cells?
Where do stem cells come from?Embryonic stem cells. These stem cells come from embryos that are 3 to 5 days old. ... Adult stem cells. These stem cells are found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat. ... Adult cells altered to have properties of embryonic stem cells. ... Perinatal stem cells.
What type of stem cells are used in regenerative medicine?
Promises of stem cells in regenerative medicine: the six classes of stem cells, that is, embryonic stem cells (ESCs), tissue specific progenitor stem cells (TSPSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), umbilical cord stem cells (UCSCs), bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have many ...Jul 19, 2016
What are stem cell models?
The proliferation and differentiation capacity of human stem cells allows scientists to use them as more clinically relevant models to study the causes, pathologies, and mechanisms of certain diseases, and further develop rational therapeutic strategies.Sep 29, 2020
What types of stem cell therapies are in use today?
Currently, some stem cell-based therapies utilizing adult stem cells are clinically available and mainly include bone marrow transplants of hematopoietic stem cells and skin grafts for severe burns (23).May 15, 2020
What is the main use of regenerative medicine?
Regenerative medicine is focused on developing and applying new treatments to heal tissues and organs and restore function lost due to aging, disease, damage or defects. The human body has the natural ability to heal itself in many ways.
What are stem cells used for in medicine?
Stem cells could help medicine in three general ways: cell-based therapies, drug discovery and basic knowledge. Cell therapies would use stem cells, or cells grown from stem cells, to replace or rejuvenate damaged tissue. Scientists also want to use stem cells to understand disease and find drugs that might treat it.Jun 14, 2007
How do you trace a cell phone lineage?
Genetic lineage tracing is generally performed by combining an inducible Cre expressed in a cell type of interest with a Cre-activated reporter usually expressing a fluorescent protein. This allows indefinite labeling of cells with a visual marker following induction of Cre activity.
How do I reprogram my cells?
In order to turn adult cells back into pluripotent or embryonic-like stem cells, scientists use viruses to insert four genes – Sox2, Oct4, Klf4, and cMyc – into the cells. These reprogrammed cells, called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), have generated a huge amount of excitement in the field.
When did scientists first discover stem cells?
Scientists discovered ways to derive embryonic stem cells from early mouse embryos nearly 30 years ago, in 1981. The detailed study of the biology of mouse stem cells led to the discovery, in 1998, of a method to derive stem cells from human embryos and grow the cells in the laboratory.
What are the 4 types of stem cells?
Types of Stem CellsEmbryonic stem cells.Tissue-specific stem cells.Mesenchymal stem cells.Induced pluripotent stem cells.
What are the five different types of stem cells?
The five different types of stem cells discussed in this article are:Totipotent (or Omnipotent) Stem Cells.Pluripotent Stem Cells.Multipotent Stem Cells.Oligopotent Stem Cells.Unipotent Stem Cells.Feb 2, 2022
What are the two types of stem cells based on the sources?
Types of stem cells Stem cells are divided into 2 main forms. They are embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells. The embryonic stem cells used in research today come from unused embryos.
How many discrepancies were found in 2013 studies of autologous bone marrow stem cells on ventricular
In 2013, studies of autologous bone-marrow stem cells on ventricular function were found to contain "hundreds" of discrepancies. Critics report that of 48 reports, just five underlying trials seemed to be used, and that in many cases whether they were randomized or merely observational accepter-versus-rejecter, was contradictory between reports of the same trial. One pair of reports of identical baseline characteristics and final results, was presented in two publications as, respectively, a 578-patient randomized trial and as a 391-subject observational study. Other reports required (impossible) negative standard deviations in subsets of people, or contained fractional subjects, negative NYHA classes. Overall, many more people were reported as having receiving stem cells in trials, than the number of stem cells processed in the hospital's laboratory during that time. A university investigation, closed in 2012 without reporting, was reopened in July 2013.
How to regenerate tissue in adult?
A possible method for tissue regeneration in adults is to place adult stem cell "seeds" inside a tissue bed "soil" in a wound bed and allow the stem cells to stimulate differentiation in the tissue bed cells. This method elicits a regenerative response more similar to fetal wound-healing than adult scar tissue formation.
What are the effects of stem cells on animal models of brain degeneration?
Research has been conducted on the effects of stem cells on animal models of brain degeneration, such as in Parkinson's disease, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease. Preliminary studies related to multiple sclerosis have been conducted.
How do corneal stem cells help restore vision?
Since 2003, researchers have successfully transplanted corneal stem cells into damaged eyes to restore vision. "Sheets of retinal cells used by the team are harvested from aborted fetuses, which some people find objectionable." When these sheets are transplanted over the damaged cornea, the stem cells stimulate renewed repair, eventually restore vision. The latest such development was in June 2005, when researchers at the Queen Victoria Hospital of Sussex, England were able to restore the sight of forty people using the same technique. The group, led by Sheraz Daya, was able to successfully use adult stem cells obtained from the patient, a relative, or even a cadaver. Further rounds of trials are ongoing.
What is the FDA approved for?
The FDA has approved five hematopoietic stem-cell products derived from umbilical-cord blood, for the treatment of blood and immunological diseases. In 2014, the European Medicines Agency recommended approval of limbal stem cells for people with severe limbal stem cell deficiency due to burns in the eye.
How are red blood cells grown?
In this process, HSCs are grown together with stromal cells, creating an environment that mimics the conditions of bone marrow, the natural site of red-blood-cell growth.
What is HSCT in chemo?
For over 30 years, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat people with conditions such as leukaemia and lymphoma; this is the only widely practiced form of stem-cell therapy. During chemotherapy, most growing cells are killed by the cytotoxic agents. These agents, however, cannot discriminate between the leukaemia or neoplastic cells, and the hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow. This is the side effect of conventional chemotherapy strategies that the stem-cell transplant attempts to reverse; a donor's healthy bone marrow reintroduces functional stem cells to replace the cells lost in the host's body during treatment. The transplanted cells also generate an immune response that helps to kill off the cancer cells; this process can go too far, however, leading to graft vs host disease, the most serious side effect of this treatment.
What is the procedure based on the separation of the vascular stroma contained in adipose
The procedure based on the separation of the vascular stroma contained in adipose tissue has allowed access to stem cells without resorting to embryonic tissue, facilitating its use in regenerative medicine [1, 12].
What are the characteristics of stem cell harvesting?
Characteristics of stem cell harvesting. Adipose tissue is a specific variety of connective tissue; composed of a group of cells called adipocytes, specialised in storing fats. The adipose tissue consists of the joining, through reticular fibres, of the adipocytes forming lobes, between which run numerous blood vessels.
What are the cell types found in SVF?
The cell types found in SVF include: preadipocytes, fibroblasts, adult mesenchymal stem cells, monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes as well as pericytes related to angiogenesis. [23–25]. Harvesting cell lines. Maintaining cultures of mesenchymal cell lines allows a greater quantity of pluripotent stem cells (PSC) to be harvested.
What is the role of the stroma in the growth and spread of a tumour?
The stroma is of great importance in the nutrition of tumour cells [68, 70]. The stroma participates in the regulation of growth and spread of a tumour through interaction with parenchymal cells.
What are the cells that make up the mesoderm?
It is a tissue that originates in the mesoderm and is formed by adipocytes and a fraction of stromal cells that include vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, monocytes, macrophages, pre-adipocyte lymphocytes and ADSCs.
What are the advantages of ADSCs?
Among the advantages of ADSCs, the greater ease of access and harvesting by means such as subcutaneous lipoaspiration, a much less painful procedure than harvesting bone marrow stem cells, and their use, is less associated with ethical controversies because they are harvested from autologous fat, unlike ES cells [12].
Where are human embryonic stem cells derived from?
Human embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are derived from the inner layer of the blastocyst and, due to their pluripotency, are used in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Human fetal mesenchymal stem cells (hfMSCs) can be harvested from stem cells present in the amniotic fluid or the umbilical cord. They are multipotent, but like the ...
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
How many cells are in an embryo?
Embryonic stem cells. These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells. These are pluripotent (ploo-RIP-uh-tunt) stem cells, meaning they can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body.
What are the master cells of the body?
Stem cells are the body's master cells. All other cells arise from stem cells, including blood cells, nerve cells and others. Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called ...
Why are adult stem cells more likely to contain abnormalities?
Adult stem cells also are more likely to contain abnormalities due to environmental hazards, such as toxins, or from errors acquired by the cells during replication.
What are perinatal stem cells?
Perinatal stem cells. Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells. Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus.
What type of cells are used to test for drugs?
Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness. Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality. This type of testing will most likely first have a direct impact on drug development first for cardiac toxicity testing.
What is the name of the cell that divides to form more cells?
Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.
What is NIGMS in medical?
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (NIBIB) Regenerative Medicine (Partnership in Education) NIGMS is a part of the National Institutes of Health that supports basic research to increase our understanding of biological processes and lay the foundation for advances in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What are the regenerative capacities of animals?
More complex animals such as mammals have limited regenerative capacities. These include: 1 Forming thick scars in tissues and skin to promote the healing of injured or amputated body parts. 2 Regrowing hair and skin. 3 Healing a bone fracture by using new tissue to knit the bone pieces together.
What animal has a backbone?
The axolotl, or Mexican salamander, is an animal with a backbone that can regenerate the form and function of almost any limb, organ, or other body part. More complex animals such as mammals have limited regenerative capacities. These include:
Why are stem cells important?
Stem cells play an important role in regeneration because they can develop into many different cell types in the body and renew themselves millions of times, something specialized cells in the body—such as nerve cells—cannot do. The primary roles of stem cells are to maintain and repair the tissue in which they’re found.
What is the role of stem cells in the body?
The primary roles of stem cells are to maintain and repair the tissue in which they’re found. Scientists are exploring whether a person’s own stem cells could “grow” replacement tissue that wouldn’t be rejected by the body’s immune system.
How do organisms regenerate?
How do different organisms regenerate? Organisms regenerate in different ways. Plants and some sea creatures, such as jellyfish, can replace missing parts by extensively remodeling their remaining tissues. Some animals such as lobsters, catfish, and lizards replace missing parts by first growing a blastema.
How many whole bodies can a hydra form?
This rapidly advancing field is called regenerative medicine. This tiny freshwater animal Hydra can form two whole bodies after being cut in half. Credit: iStock.
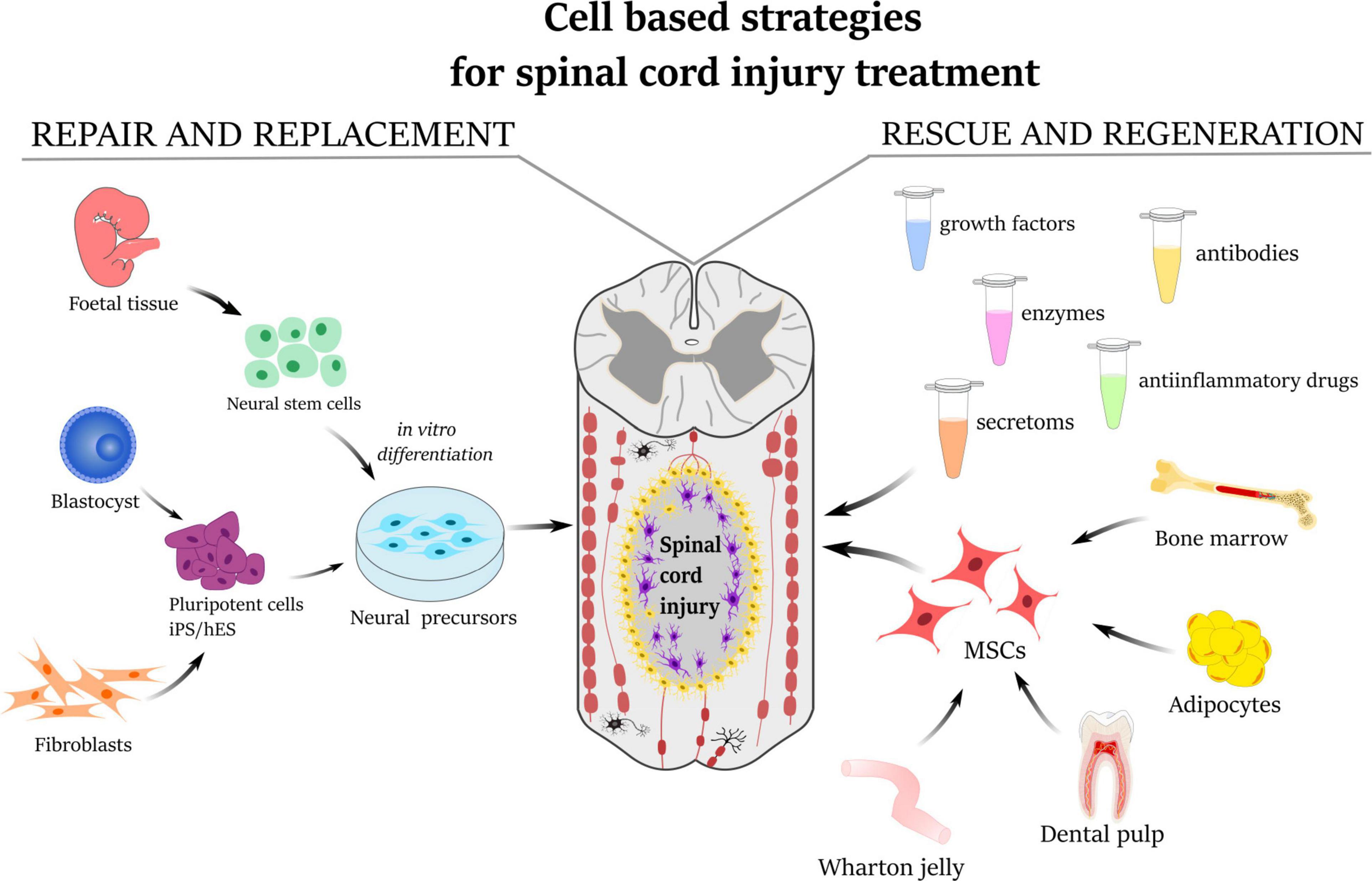
Overview
Research
Stem cells are being studied for a number of reasons. The molecules and exosomes released from stem cells are also being studied in an effort to make medications. In addition to the functions of the cells themselves, paracrine soluble factors produced by stem cells, known as the stem cell secretome, have been found to be another mechanism by which stem cell-based therapies mediate their effects in degenerative, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases.
Medical uses
For over 30 years, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat people with conditions such as leukaemia and lymphoma; this is the only widely practiced form of stem-cell therapy. During chemotherapy, most growing cells are killed by the cytotoxic agents. These agents, however, cannot discriminate between the leukaemia or neoplastic cells, and the hematopoietic stem cellswithin the bone marrow. This is the side effect of conventional chemot…
Veterinary medicine
Research has been conducted on horses, dogs, and cats can benefit the development of stem cell treatments in veterinary medicine and can target a wide range of injuries and diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke, tendon and ligament damage, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis and muscular dystrophyboth in large animals, as well as humans. While investigation of cell-based therapeutics generally reflects human medical needs, the high degree of frequency and severity …
Society and culture
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, there was an initial wave of companies and clinics offering stem cell therapy, while not substantiating health claims or having regulatory approval. By 2012, a second wave of companies and clinics had emerged, usually located in developing countries where medicine is less regulated and offering stem cell therapies on a medical tourismmodel. Like the first wave companies and clinics, they made similar strong, but unsubstantiated, claims, mai…
See also
• Autologous stem-cell transplantation
• Cardiovascular Cell Therapy Research Network (CCTRN)
• Fetal tissue implant
• Induced pluripotent stem cell
External links
• EuroStemCell: types of stem cells and their uses