
Primary Sewage Treatment
Nov 12, 2021 · Stages of Sewage Treatment Plant There are generally three types of stages that are used in the STP Plant. These stages are Primary Stage, Secondary Stage, and Tertiary Stage. Primary Stage: The Primary Stage consists of the elimination of a part of the suspended solids and natural matter from the sewage.
Private Wastewater Systems
Oct 20, 2020 · What are the 4 stages of the sewage treatment process? 4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment Process Step 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. Step 3 – Dewatering.
Pre-Treatment
Sewage or wastewater treatment plant consists of two stages. Primary Treatment; It involves the removal of large or small-sized components in the wastewater through physical processes. Biological Treatment: Aerobic microorganisms are inoculated into the sewage treatment plant. These microbes utilize the organic components of the sewage and reduce the toxicity. This …
Secondary Sewage Treatment
Since this is a massive task, treatment of wastewater is done in three stages; primary, secondary, and tertiary; each of which deals with a different aspect of cleansing.
Tertiary Treatment
What are the 3 Stages of Wastewater Treatment? Primary Stage-separates settable organic solids & inorganic material that won’t degrade Secondary Stage-removes suspended & soluble solids converting them to settable solids using Biological Oxidation Tertiary Stage-uses chemical & physical treatment to create H2O closer to potable quality
What was the first step in the sewage treatment process?
Jan 12, 2020 · Keeping this in consideration, what are the four stages of sewage treatment? Treatment Steps. Step 1: Screening and Pumping. Step 2: Grit Removal. Step 3: Primary Settling. Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. Step 5: Secondary Settling. Step 6: Filtration. Step 7: Disinfection. Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
What is the first step in treating raw sewage?
May 03, 2021 · Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are …
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
Jan 14, 2020 · The First Step The first stage of a water treatment process is to remove large pieces of waste and debris from the wastewater. Human and animal waste, sticks and stones, and trash are removed using screens and rakes. Screens come in different sizes so that larger material is caught first.
What is the process that the sewage treatment goes through?
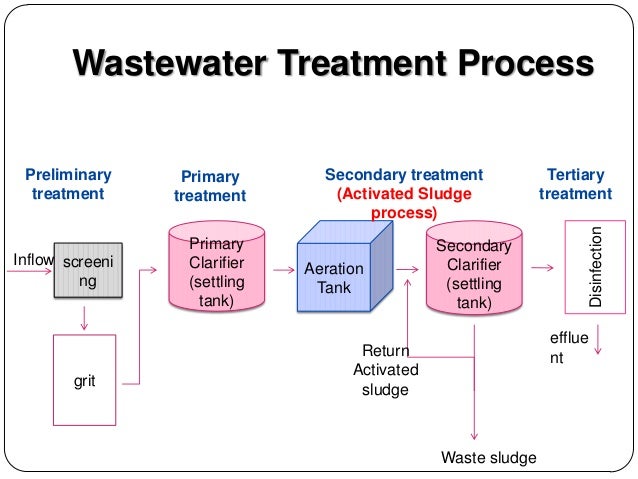
What are the 4 stages of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment PDF?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary.Mar 7, 2021
What is the first stage of sewage treatment?
Primary TreatmentPrimary Treatment In the first of the three steps, the goal is to separate the organic matter and sludge from the rest of the water. This is done by having the wastewater flow through large settlement tanks where the solids will sink to the bottom and the grease and oils rise.Mar 31, 2020
What is the first stage of sewage treatment process?
primary sedimentation stageThe first stage in the sewage treatment is the primary sedimentation stage. Sewage including all of the grey and black water from a home flows into a chamber called the primary sedimentation tank and holds waste until it has had enough time for heavy sediment to disperse to the bottom.
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.Nov 7, 2015
What is sewage treatment?
wastewater treatment, also called sewage treatment, the removal of impurities from wastewater, or sewage, before it reaches aquifers or natural bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, estuaries, and oceans.
What does the secondary stage of sewage treatment do?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What are the different stages in wastewater treatment and what does each phase do?
The three stages of wastewater treatment are known as primary, secondary and tertiary. Each stage purifies water to a higher level. In some applications, only one or two stages are necessary. The level of treatment necessary depends on the water's intended use case, and what environment it will be discharged into.Apr 16, 2021
How many stages are there in the sludge digestion process?
There are three distinct stages that occur in the natural process of sludge digestion due to biological action.
What is stage 2 of wastewater treatment?
Stage 2. – Includes Secondary Treatment using different methods of Biological Oxidation to further purify wastewater. The Conventional Activated Sludge Process is the most popular, using Aeration in a long, but effective process that entails mixing and aerating wastewater in a solution of microorganisms grown in the system that breakdown organic material and separates dissolved solids. This can be accomplished by:
What is the main objective of wastewater treatment?
The main objective of Wastewater Treatment is to separate solids from liquid then to treat both turning the solids into nonhazardous Bio-solids and water into non-threatening environmentally safe water to add back to the environment where it came from with the intention of using it again. 1. Primary Wastewater Treatment.
How does secondary treatment remove organic matter?
The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria that is naturally found in it. Increased oxygen encourages the growth of bacteria, which consume and breakdown the complex organic compounds.
How much BOD is removed from sewage?
Weekly averages may be up to 50 percent higher. A sewage treatment plant providing both primary and secondary treatment is expected to remove at least 85 percent of the BOD and suspended solids from domestic sewage.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the part of the Wastewater Treatment process that breaks down organic matter, removes dissolved and colloidal solids. This organic waste material would create a high Oxygen demand on the receiving stream if it were let go into the environment. Secondary treatment is traditionally applied to the liquid portion of sewage after initial Preliminary and Primary treatment has removed settleable solids and inorganic floating material.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic Digestors. Most large Wastewater Treatment Plants use 2 Stage Anaerobic Digestion to treat the solids removed from the Primary and Secondary Treatment facilities. Treatment is needed for the Solids to be deemed safe for landfills.
What is the purpose of sludge treatment?
The basic goals of treating sludge before final disposal are to reduce its volume and to stabilize the organic materials.
What is treated wastewater?
Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow .#N#As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.#N#The water that flows from the secondary clarifier has substantially reduced organic material and should be approaching expected effluent specifications.
What is the process of removing large items from the influent?
Removal of large items from the influent to prevent damage to the facility’s pumps, valves and other equipment .#N#The process of treating and reclaiming water from wastewater (any water that has been used in homes, such as flushing toilets, washing dishes, or bathing, and some water from industrial use and storm sewers) starts with the expectation that after it is treated it will be clean enough to reenter the environment.#N#The quality of the water is dictated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Clean Water Act, and wastewater facilities operate to specified permits by National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES). According to the EPA, The Clean Water Act (CWA) establishes the basic structure for regulating discharges of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulating quality standards for surface waters. Under the CWA, EPA sets wastewater standards for industry. The EPA has also developed national water quality criteria recommendations for pollutants in surface waters. EPA's National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program controls discharges.#N#As an example of expected standards, the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of average wastewater effluent is 200 mg/L and the effluent after treatment is expected to be >30 mg/L. It is crucial a wastewater facility meets these expectations or risk stiff penalty.#N#The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill.
What is a bar screen in wastewater treatment?
A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from ...
What is activated sludge?
These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.
Why is chlorine added to water?
Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria in the contact chamber. With the enhanced concentration of bacteria as part of the aeration stage, there is a need to test the outgoing effluent for bacteria presence or absence and to disinfect the water.
Why is wastewater important?
Why clean it? There are several reasons, but the most important is that wastewater is full of bacteria that can harm you. Nitrogen and phosphorus damage lakes and rivers by increasing the rate at which harmful algae grows. This algae starve lakes of oxygen and lead to fish and other aquatic creatures to die.
How does chlorine get rid of odors?
It’s treated with chemicals to kill any remaining bacteria and goes to tanks where the chlorinated water is exposed to UV to reduce chlorine to safe levels. From there, it’s piped to holding tanks or back into lakes, streams, or other bodies of water.
