Symptoms
Achalasia usually occurs later in life, but it can also occur in children. Individuals who are middle-aged and older are at higher risk for the condition. Achalasia is also more common in people with autoimmune disorders. What are the symptoms of achalasia?
Causes
People with achalasia will often have trouble swallowing or feel like food is stuck in their esophagus. This is also known as dysphagia. This symptom can cause coughing and raise the risk of aspiration, or inhaling or choking on food. Other symptoms include: You might also have regurgitation or backflow.
Complications
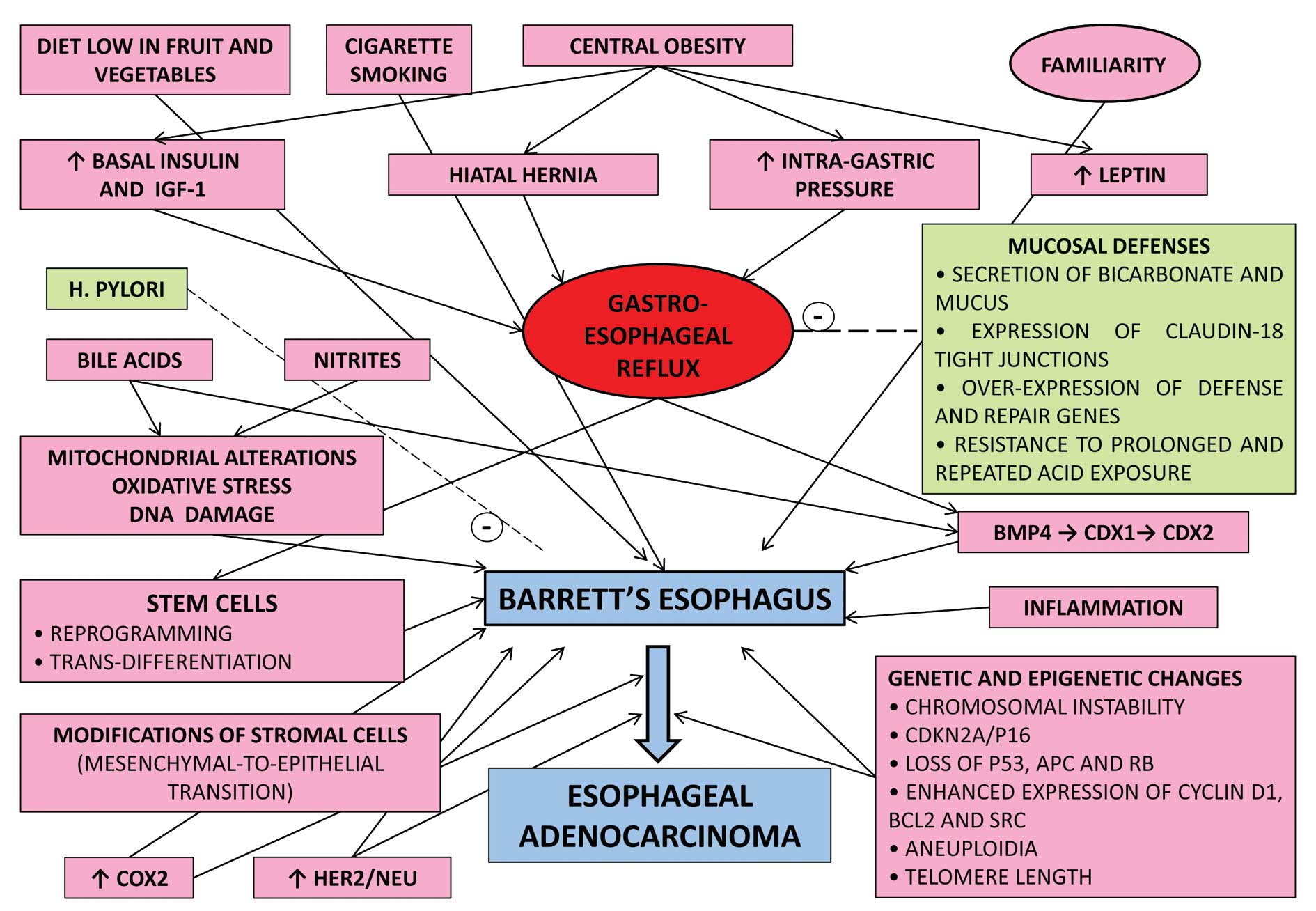
Achalasia is a chronic condition that can increase the risk for developing esophageal cancer.
What is achalasia and who is at risk?
Because of uncertain etiology, treatment is only palliative and is directed at decreasing lower esophageal sphincter pressure, improving esophageal emptying and relieving the symptoms of achalasia. Current treatment options include pharmacological, endoscopic and surgical.
What are the symptoms of achalasia?
Does achalasia increase the risk of esophageal cancer?
What are the treatment options for esophageal achalasia?

What are the risk factors for achalasia?
Who is at risk for achalasia?Having certain genes.Having a problem with your immune system that causes it to attack nerve cells in your esophagus.Having herpes simplex virus or other viral infections.Having Chagas disease. This is an infection caused by a parasite.
What is the best treatment for achalasia?
Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy and Fundoplication The most effective treatment for achalasia is Heller myotomy (esophagomyotomy), a procedure in which the muscle fibers of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) are divided.
How can achalasia be prevented?
Achalasia patients need to eat slowly, chew very well, drink plenty of water with meals, and avoid eating near bedtime. It is helpful to sleep with the head elevated by raising the head of the bed or using a wedge pillow.
What is the latest treatment for achalasia?
Pneumatic dilation is currently the most effective nonsurgical option for treatment of achalasia. Pneumatic dilation is generally performed under sedation with fluoroscopic guidance to accurately position the balloon across the LES.
How is achalasia managed?
Achalasia treatment focuses on relaxing or stretching open the lower esophageal sphincter so that food and liquid can move more easily through your digestive tract. Specific treatment depends on your age, health condition and the severity of the achalasia.
Can achalasia come back after surgery?
Can Achalasia Return After Surgery? In some cases, achalasia can return after Heller myotomy or other procedures. While the vast majority of patients are ultimately satisfied with this surgery, occasionally symptoms return. Sometimes these present themselves soon after, but in other cases they may appear years later.
How can I improve my esophagus function?
Lifestyle and home remediesAvoid foods that may increase reflux. ... Use good pill-taking habits. ... Lose weight. ... If you smoke, quit. ... Avoid certain medications. ... Avoid stooping or bending, especially soon after eating.Avoid lying down after eating. ... Raise the head of your bed.
Does stress cause achalasia?
Other possible causes of achalasia can be stress, bacterial infections or genetic inheritance. In patients with achalasia cause damage to the nerve cells of the esophagus for unknown reasons.
Can acid reflux cause achalasia?
Both acid reflux and achalasia happen when the “door” from your esophagus to your stomach is broken. With acid reflux, the door doesn't close when it should. With achalasia, the door doesn't open when it should. The door is called the lower esophageal sphincter.
Can narrowing of the esophagus be reversed?
Various treatment methods can treat benign esophageal strictures effectively. However, esophageal strictures can reoccur, and people may need to have repeat dilations to reopen the esophagus. According to one source, 30 percent of people who have an esophageal dilation will require another dilation within a year.
Can you live a normal life with achalasia?
The prognosis in achalasia patients is excellent. Most patients who are appropriately treated have a normal life expectancy but the disease does recur and the patient may need intermittent treatment.
How long is surgery for achalasia?
The procedure can take up to three hours to complete. Most people remain in the hospital for one day. The most common potential side effect of the procedure is GERD. If necessary, a fundoplication may be performed later.
What is Achalasia?
Achalasia is a serious condition that affects your esophagus, It is a rare disease of the muscle of the lower esophageal body and the lower esophageal sphincter that prevents relaxation of the sphincter and an absence of contractions, or peristalsis, of the esophagus. This condition can be related to damaged nerves in your esophagus.
Causes of Achalasia
Achalasia can happen for different reasons. It can be difficult for your doctor to find a specific cause. This condition may be hereditary, or it may be the result of an autoimmune condition. With this type of condition, your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your body.
Risk Factors for Achalasia
Achalasia usually occurs later in life, but it can also occur in children. Individuals who are middle-aged and older are at higher risk for the condition. Achalasia is also more common in people with autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms of Achalasia
People with achalasia will often have trouble swallowing or feel like food is stuck in their esophagus. This is also known as dysphagia. This symptom can cause coughing and raise the risk of aspiration, or inhaling or choking on food. Other symptoms include:
Diagnosis of Achalasia
Your doctor might suspect you have achalasia if you have trouble swallowing both solids and liquids, particularly if it gets worse over time.
Treatments for Achalasia
Most achalasia treatments involve your LES. Several types of treatment can either temporarily reduce your symptoms or permanently alter the function of the valve.
Outlook for Achalasia
The outlook for this condition varies. Your symptoms might be mild, or they may be severe. Treatment can be highly successful. Multiple treatments are sometimes necessary.
What is the meaning of Achalasia?
Achalasia is a rare condition in which the esophagus (food pipe) is unable to move food and liquids into the stomach.
What are the causes of Achalasia?
The exact cause of achalasia is unknown. However, it is thought to occur due to the following causes:
What are the risk factors of Achalasia?
Achalasia can occur in all races and is seen equally in men and women. Certain factors increase the risk of developing achalasia and may include:
What are the complications of Achalasia?
The complications can occur due to regurgitation of the undigested food into the esophagus, and then being drawn into the windpipe (trachea), which can lead to the lungs. These complications are:
How to diagnose Achalasia?
The doctor will first ask you about your symptoms, any pre-existing medical history, or family history of the patient. The doctor may recommend the following tests to confirm the diagnosis of achalasia:
What is the treatment of Achalasia?
The treatment of achalasia focuses on the relaxation or opening of the lower esophageal sphincter allowing the food and liquid to move easily through the digestive tract. The treatment depends on the age of the patient, the overall health of the patient, and the severity of the disease. The different surgical modalities include:
How to prevent Achalasia?
Achalasia cannot be prevented as such. It is a lifelong condition, and treatment helps in relieving the symptoms associated with the condition. Certain lifestyle changes can help in relieving the symptoms associated with achalasia, which include:
Surgical treatments
For people who are at low risk of surgical complications, treatments can include the following procedures:
Medications
In some cases, medications like muscle relaxers and isosorbide or nifedipine are used to relieve achalasia cardia symptoms. Diet changes to the thickness and textures of foods and liquids may also help.
What is the best treatment for achalasia?
Surgery is the most effective treatment for people with achalasia. Our surgeons use a procedure called a Heller myotomy, which involves cutting the abnormally thickened muscle surrounding the esophageal valve.
Why is achalasia rare?
This rare illness occurs when the nerves that signal swallowing become damaged. It is unclear why achalasia develops. We also don’t know why some people who have it go on to develop esophageal cancer. Symptoms of Achalasia. The main symptom of achalasia is difficulty swallowing liquids.
How to diagnose achalasia?
Diagnosis of Achalasia. To diagnose this condition, we use endoscopy, x-rays of the esophagus, and tests to measure pressure within the esophagus. Treatment for Achalasia. The most effective treatment involves cutting the sphincter muscle, either surgically or endoscopically, to allow food to pass through the esophagus.
How does fundoplication help with achalasia?
This approach allows liquid and food to pass normally through the esophagus and dramatically improves quality of life for many people with achalasia. A separate operation called a fundoplication procedure, in which a surgeon tightens the valve between the esophagus and the stomach, is always performed at the same time.
Why do I have achalasia?
It can be difficult for your doctor to find a specific cause. This condition may be hereditary, or it may be the result of an autoimmune condition. With this type of condition , your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your body. The degeneration of nerves in your esophagus often contributes to the advanced symptoms of achalasia.
How common is achalasia?
Achalasia is an uncommon disorder with an annual incidence of approximately 1.6 cases per 100,000 individuals and prevalence of 10 cases per 100,000 individuals [1]. Men and women are affected with equal frequency. The disease can occur at any age, but onset before adolescence is rare. Achalasia is usually diagnosed in patients between the ages of 25 and 60 years. Achalasia may occur in association with adrenal insufficiency and alacrima in patients with triple A syndrome or Allgrove syndrome, a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder
What is the most serious complication of achalasia cardia?
Aspiration Pneumonia: This is the most serious complication of achalasia cardia but rare. In some cases due to sudden regurgitation process, gastric contents from the stomach enter in to the lungs leading to bronchopneumonia. Patient may present with sudden breathlessness, choking, vomiting episodes and respiratory distress.
Who first described achalasia?
Sir Thomas Willis described achalasia in 1672. In 1881, von Mikulicz described the disease as a cardiospasm to indicate that the symptoms were due to a functional problem rather than a mechanical one. In 1929, Hurt and Rake realized that the disease was caused by a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax. They coined the term achalasia, meaning failure to relax.
Can achalasia be suspected?
Physician may suspect achalasia based on symptoms and physical examination. Achalasia should be suspected if patient have difficulty swallowing both solids and liquids and also regurgitation that has not resolved despite treatment with proton pump inhibitors.