
Procedures
learning about your kidneys and how they should function. By stage 5, also called kidney failure, your kidneys can no longer function on their own and you will require treatment with kidney replacement therapy - dialysis or a kidney transplant will be required. Another treatment you may also choose to comprehensive conservative care.
Nutrition
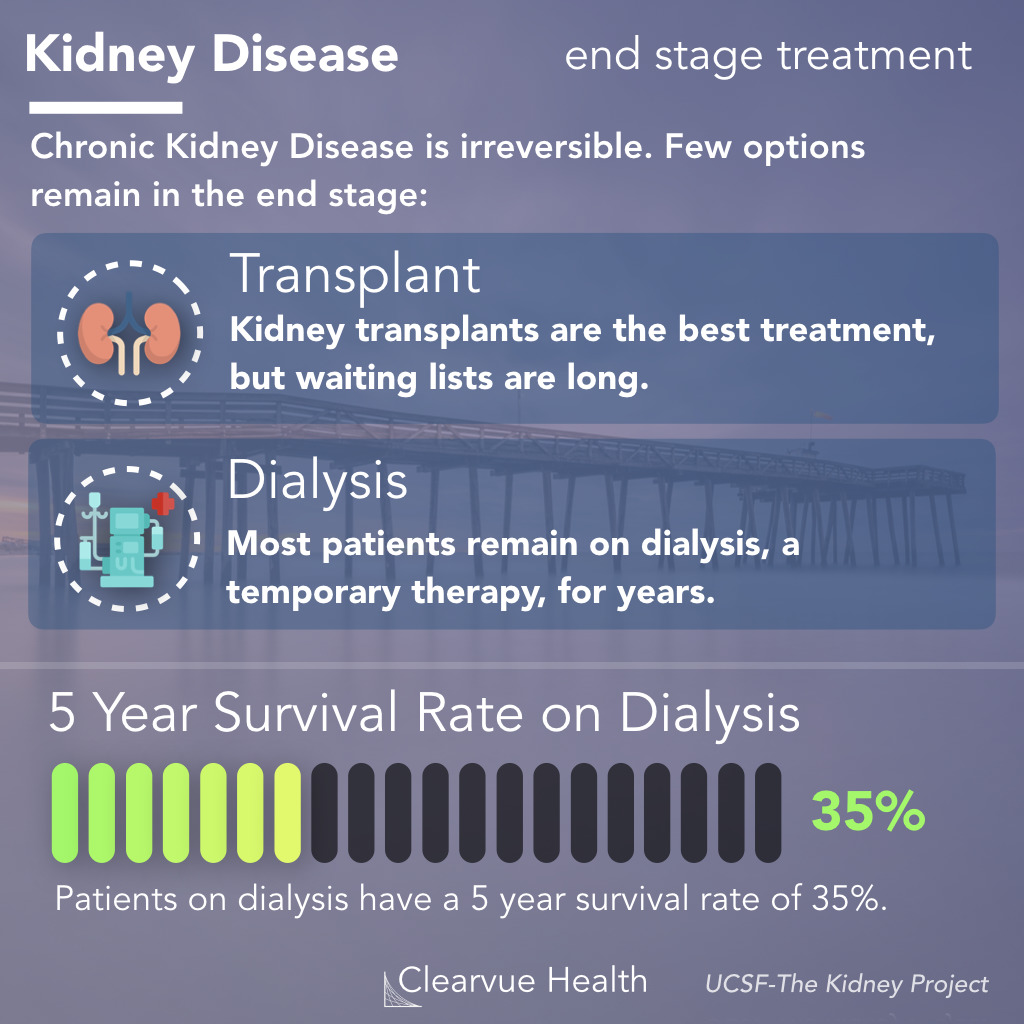
Without dialysis or a transplant, life expectancy for people with kidney failure usually ranges from days to weeks. There is no cure for kidney failure, but treatment can extend your life by years.
What are the three treatment options for Stage 5 CKD?
Treatment Options for Stage IV COPD
- No More Smoking. Even if you are diagnosed with advanced COPD, it's never too late to reap the rewards of smoking cessation.
- Flu and Pneumonia Vaccines. ...
- Short-Acting Bronchodilators. ...
- Long-Acting Bronchodilators. ...
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation. ...
- Steroid Medications. ...
- Oxygen Therapy and Opioids. ...
- Lung Surgery. ...
- Good Nutrition High in Calories. ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with renal failure?
How Long Can You Live With End Stage Kidney Failure In general, hospice patients are estimated by their physicians to have six months or less to live. When patients living with kidney failure choose to forgo dialysis, their longevity depends on the amount of kidney function they have, the severity of their symptoms and their overall medical ...
What are options for end stage COPD?
How long can you live with end stage renal failure?

What are the treatment options for end-stage kidney disease?
A kidney transplant is often the treatment of choice for end-stage renal disease, compared with a lifetime on dialysis. The kidney transplant process takes time. It involves finding a donor, living or deceased, whose kidney best matches your own.
What is the best treatment for someone who has renal kidney failure?
There are two treatment options for kidney failure: dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis) and kidney transplantation. Talk with your family so you can decide which treatment will best fit your lifestyle needs. Also you always have the choice to change to a different type of treatment in the future.
What are the three treatment options that are available for kidney renal failure?
Treatment for end-stage kidney diseaseDialysis. Dialysis artificially removes waste products and extra fluid from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do this. ... Kidney transplant. A kidney transplant involves surgically placing a healthy kidney from a donor into your body.
What is the most effective treatment for end-stage organ failure?
Treatment. ESRD may need to be treated with dialysis or kidney transplant. You may need to stay on a special diet or take medicines to help your body work well. Dialysis does some of the job of the kidneys when they stop working well.
How do you treat kidney failure without dialysis?
Conservative management treats kidney failure without dialysis or a transplant. You'll work with your health care team to manage symptoms and preserve your kidney function and quality of life as long as possible.
Can you recover from kidney failure without dialysis?
People with kidney failure may survive days to weeks without dialysis, depending on the amount of kidney function they have, how severe their symptoms are, and their overall medical condition.
What is the final stage of kidney failure?
Overview. End-stage renal failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is the final, permanent stage of chronic kidney disease, where kidney function has declined to the point that the kidneys can no longer function on their own.
What are the types of dialysis?
There are 3 main types of dialysis: in-center hemodialysis, home hemodialysis, and peritoneal dialysis. Each type has pros and cons.
Can End stage renal disease be reversed?
Kidney damage, once it occurs, can't be reversed. Potential complications can affect almost any part of your body and can include: Fluid retention, which could lead to swelling in your arms and legs, high blood pressure, or fluid in your lungs (pulmonary edema)
Which action has the highest priority in the care of a client with chronic renal failure?
Lastly, the highest priority for the patient with CKD should be assigned to the prevention of AKI, which is an action of proven efficacy.
When is dialysis no longer option?
Without life-sustaining dialysis or a kidney transplant, once a person with kidney disease reaches stage 5 (end stage renal disease or ESRD), toxins build up in the body and death usually comes within a few weeks. The decision to stop treatment should be an informed and voluntary choice.
What is end stage renal disease?
What is End-Stage Renal Disease? Kidney failure is known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD) because it’s the last stage of chronic kidney disease. This means that one or both of your kidneys no longer function on their own. ESRD can be very scary for patients and their families.
What is the best treatment for ESRD?
A kidney transplant is another option for individuals with ESRD. This surgical procedure removes the kidneys that are no longer functioning and replaces them with one healthy kidney. (Our bodies only need one healthy kidney to effectively filter waste and water from the blood).
How does dialysis work?
Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of your stomach to filter blood. A sterile solution (dialysate) with minerals and glucose runs through a tube into the peritoneal cavity (the space between the abdominal walls). This cleansing fluid stays in the peritoneal cavity for a few hours to absorb waste products and fluids from your body. Then, it is drained out by a tube and into a separate bag. This process is done several times through out each day.
How often is hemodialysis done?
Hemodialysis treatments are usually administered three times per week as an outpatient at a dialysis center. Each session can last from two to four hours.
What are the advantages of a kidney transplant?
The main advantage of a kidney transplant is quality of life: Individuals who undergo a kidney transplant are usually able to return to a normal, active lifestyle. In fact, many find themselves enjoying things they never were able to before the transplant, such as travel, exercise and more time with family and friends.
How much water does the kidney filter?
The kidneys are small but mighty organs, and they have a big job of filtering 200 quarts of blood, and about two quarts of waste and water every day.
Why aren't my kidneys working?
When your kidneys aren’t working as well as they should – because of a chronic disease or acute illness – it’s difficult to remove waste and fluids, and dangerous toxins begin to build up into your body.
How to treat chronic renal failure?
Treatment may include: Medications (to help with growth, prevent bone density loss, and/or to treat anemia) Diuretic therapy or medications (to increase urine output) Specific diet restrictions or modifications. Dialysis.
What is end stage renal disease?
End-stage renal disease is when the kidneys permanently fail to work.
What is dialysis for ESRD?
Dialysis is a procedure that is performed routinely on persons who suffer from acute or chronic renal failure, or who have ESRD. The process involves removing waste substances and fluid from the blood that are normally eliminated by the kidneys. Dialysis may also be used for individuals who have been exposed to or ingested toxic substances to prevent renal failure from occurring. There are two types of dialysis that may be performed, including the following:
What is renal failure?
Renal failure refers to temporary or permanent damage to the kidneys that results in loss of normal kidney function. There are two different types of renal failure--acute and chronic. Acute renal failure has an abrupt onset and is potentially reversible. Chronic renal failure progresses slowly over at least three months ...
What is the term for a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts filled with fluid in the kidney?
Chronic renal failure. Polycystic kidney disease. A genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts filled with fluid in the kidneys. Any condition that may impair the flow of oxygen and blood to the kidneys such as cardiac arrest.
How long does it take for a kidney to fail?
Chronic renal failure progresses slowly over at least three months and can lead to permanent renal failure. The causes, symptoms, treatments, and outcomes of acute and chronic are different. Conditions that may lead to acute or chronic renal failure may include, but are not limited to, the following: Acute renal failure.
What is the risk factor for acute renal failure?
Exposure to heavy metals or toxic solvents (a risk factor for acute renal failure)
What are the two treatments for end stage renal disease?
The two treatments for end-stage renal disease are dialysis and kidney transplant.
What is end stage renal disease?
End-stage renal disease is a condition in which the kidneys no longer function normally. "Renal" describes anything having to do with the kidneys. Nearly everyone is born with two kidneys. They both need to fail for end-stage renal disease to develop.
What is the leading cause of end stage renal disease?
Diabetes is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Kidney disease can result from type 1 or type 2 diabetes. With either type, poor control of blood sugar increases the risk of end-stage renal disease. Other common causes of end-stage renal disease are:
What tests should be done for kidney function?
These checkups should include urine and blood tests to measure your kidney function.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
Kidney disease is diagnosed through urine and blood tests. These tests measure levels of creatinine and urea nitrogen in the urine and blood.
Why do people have two kidneys?
Nearly everyone is born with two kidneys. They both need to fail for end-stage renal disease to develop. Kidneys eliminate poisons from the body, and keep a normal balance of fluid and certain minerals in the body. When the kidneys can no longer perform this function, a person becomes very ill and ultimately dies.
What happens when the kidneys stop working?
When the kidneys can no longer perform this function, a person becomes very ill and ultimately dies. In end-stage renal disease, the kidneys function at a fraction of their normal capacity. When this occurs, there are only two options: 1) replace the job the kidneys are supposed to do by using a machine, instead (kidney dialysis) or 2) ...
What is the treatment for end stage renal disease?
Treatments for End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD) ESRD is the last stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is treated with dialysis or a kidney transplant. The doctor will talk to you about the risks and benefits of both treatments. Dialysis is not a cure for ESRD. It will need to be done for life or until a kidney donor is found.
Can you get ESRD with dialysis?
It is treated with dialysis or a kidney transplant. The doctor will talk to you about the risks and benefits of both treatments. Dialysis is not a cure for ESRD. It will need to be done for life or until a kidney donor is found. Some people choose not to start dialysis. Treatment will then focus on comfort care.
What is the term for a kidney failure without dialysis?
The two terms end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and failure (ESRF) are used to describe the irreversible loss of kidney function which, without treatment by dialysis or kidney transplantation, is likely to lead to fatal complications such as hyperkalaemia or pulmonary oedema over a period of days or weeks. Residual renal function in terms of glomerular filtration rate in such patients is generally below 10 ml/min/1.73m2.
Who is best to assess dialysis?
The assessment of patient suitablity for dialysis is best carried out by an MDT. When there is uncertainty, either in the mind of the patient or in the decision of the MDT, a trial of dialysis is indicated.
Why is early recognition of patients destined for ESRF important?
Early recognition of patients destined for ESRF is also necessary to allow time for them to become fully informed about their treatment options and to institute therapy electively. However, ESRD may occur unpredictably, for example following acute kidney injury, and 20% of patients still present requiring urgent or emergency dialysis.1,2
Why create an arteriovenous fistula in preparation for haemodialysis?
Create an arteriovenous fistula in preparation for haemodialysis to avoid using central line access
How often should PD occur?
In appropriately selected and trained patients, infective peritonitis should occur less than every 18–24 patient-months. Sclerosing peritonitis leading to intractable bowel obstruction is a rare but serious complication.13,14
Can you get dialysis if you are not eligible for transplant?
Patients not eligible for transplantation will usually be suitable for treatment by dialysis if that is their wish.11Extensive or severe comorbidity that limits life expectancy to less than a few months is generally considered a contraindication to dialysis, but some patients with a better prognosis may elect not to be dialysed and instead to receive conservative and, later, palliative care.
Is peritoneal dialysis more efficient than haemodialysis?
Per itoneal dialysis (PD) is less efficient than ha emodialysis (HD) in removing waste products. It usually needs to be carried out daily at home, whereas conventional HD is a thrice-weekly treatment carried out either at home or in hospital. PD may not provide adequate dialysis for large patients and those who have lost all renal function, and many patients will transfer to HD within 2–3 years of starting PD unless they receive a kidney transplant.12
What is conservative management for kidney failure?
Conservative management for kidney failure means that your health care team continues your care without dialysis or a kidney transplant. The focus of care is on your quality of life and symptom control. The decision to start dialysis is yours. For most people, dialysis may extend and improve quality of life.
What to do if your kidneys are getting worse?
As your kidney disease gets worse, your health care provider may talk with you about preparing for kidney failure. Talking early with your provider about your treatment options—and making a choice before you need any one of these treatments—helps you take charge of your care.
What is the difference between kidney transplant and peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of your belly to filter your blood inside your body, removing wastes. Kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney from a person who has just died , or from a living person , into your body to filter your blood.
How long can you live on dialysis?
If you decide not to begin dialysis treatments, you may live for a few weeks or for several months, depending on your health and your remaining kidney function. Many of the complications of kidney failure can be treated with medicines, but only dialysis or transplant can filter wastes from your blood.
How to do well with kidney failure?
Doing well with kidney failure is a challenge, and it works best if you. stick to your treatment schedule. review your medicines with your health care provider at every visit. You are the only one who knows how your body is responding to each of your medicines.
What is the function of hemodialysis?
Hemodialysis can replace part of your kidney function. In hemodialysis, your blood goes through a filter outside your body and filtered blood is returned to your body. Hemodialysis. helps balance important minerals, such as potassium, sodium, and calcium in your blood.
How does hemodialysis work?
During hemodialysis, your blood is pumped through a filter outside your body. Before you can start hemodialysis, you’ll need to have minor surgery to create a vascular access—a place on your body where you insert needles to allow your blood to flow from and return to your body during dialysis.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment