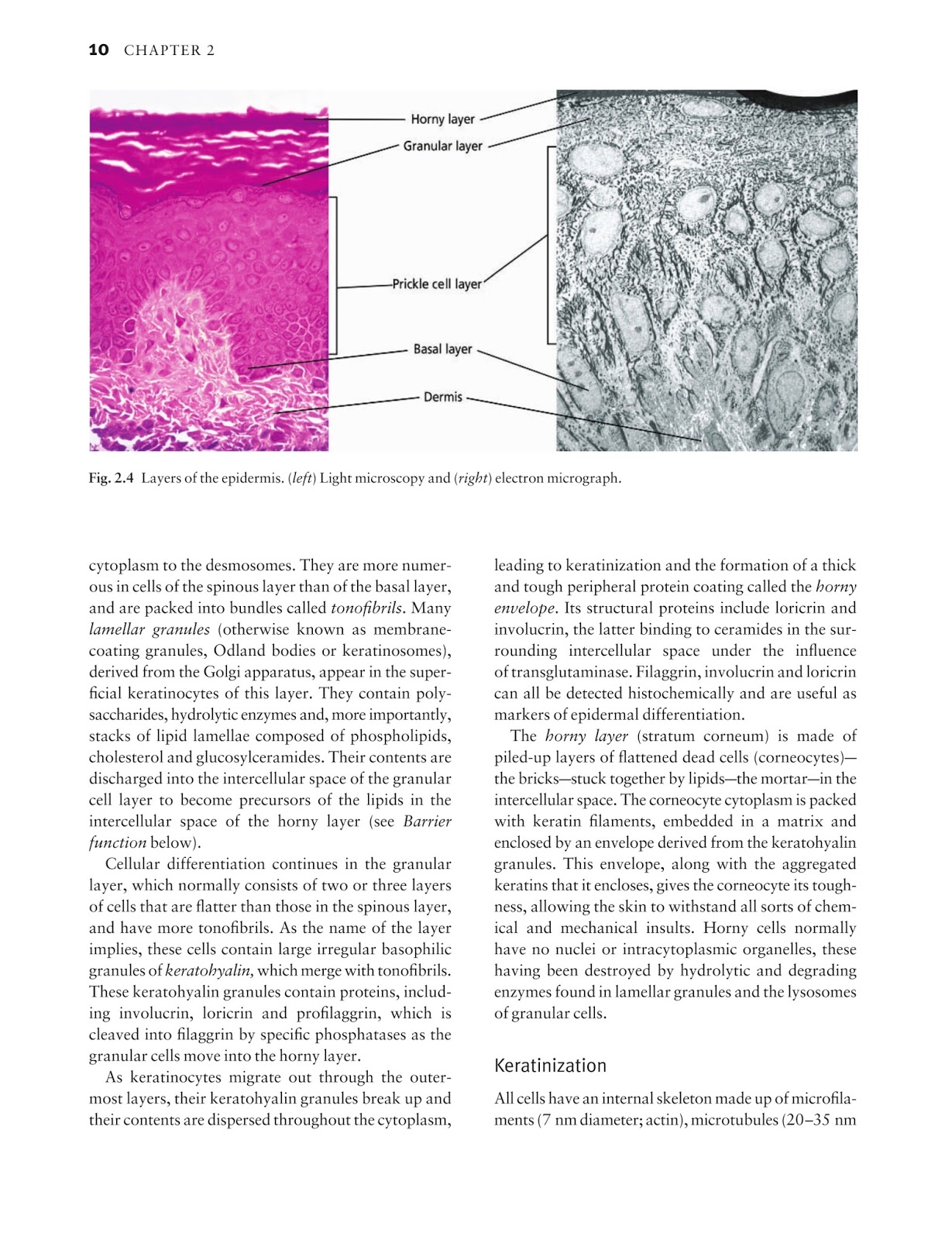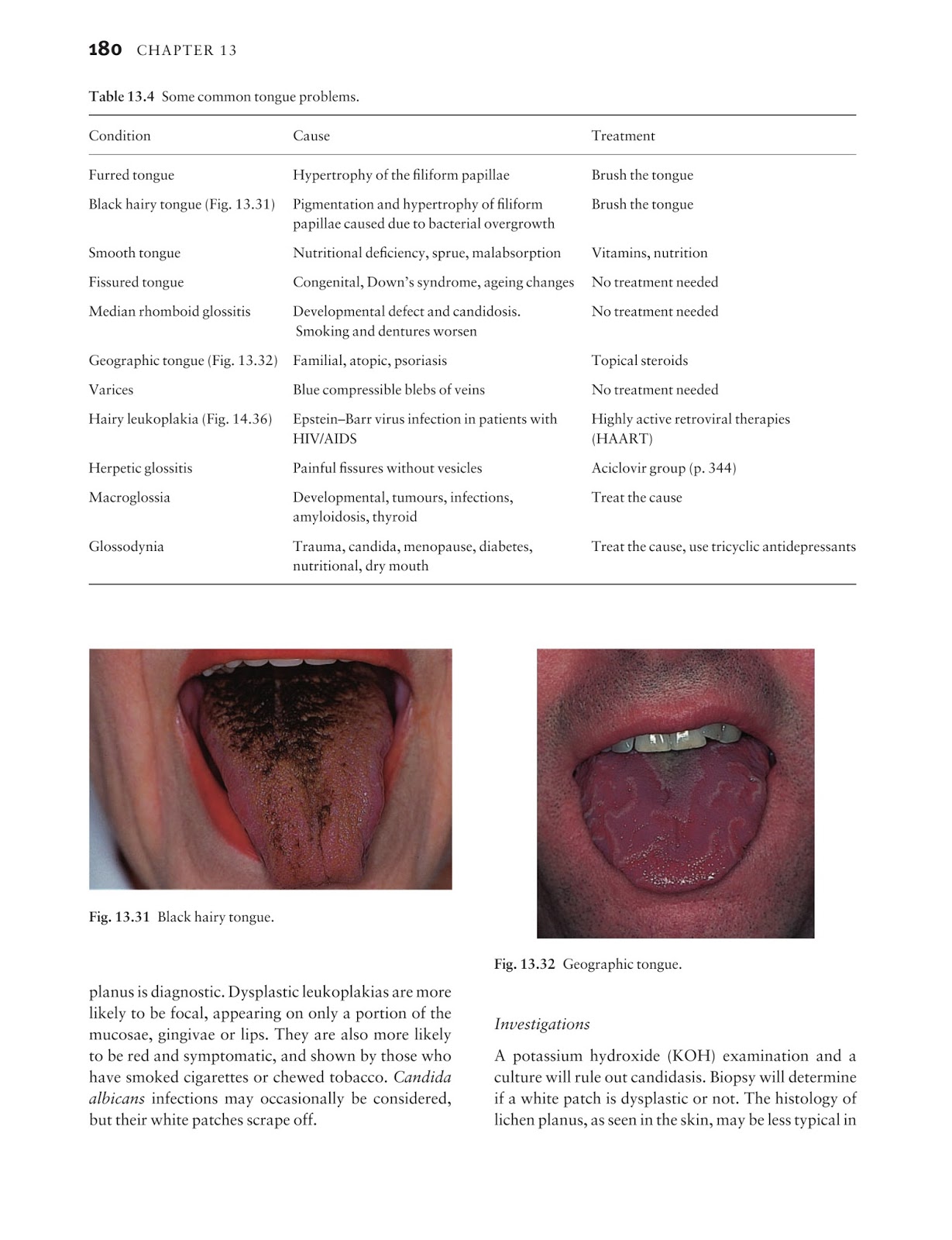
The formula mixes modern and traditional ingredients that overflow your body with antioxidants and target different aspects of your immune system. The list of ingredients includes vitamin C and E, beta-glucans, quercetin, and arabinogalactan.
Which monoclonal antibody is best?
Feb 01, 2022 · Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies. The SARS-CoV-2 genome encodes 4 major structural proteins: spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N), as well as nonstructural and accessory proteins. The spike protein is further divided into 2 subunits, S1 and S2, that mediate host cell attachment and invasion.
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies are man-made proteins that act like human antibodies in the immune system. There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in …
What to expect from monoclonal antibody treatment?
Oct 08, 2021 · Monoclonal antibody treatment (or monoclonal antibody therapy) for COVID-19 is a treatment that’s available to certain patients based on factors like duration of symptoms, age, and health history. This treatment isn’t a substitute for vaccination, but it can help prevent severe symptoms in patients who meet the criteria for receiving it.
Are there side effects of monoclonal antibody treatment?
Monoclonal antibody treatment is an additional way to help reduce the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. Public Health Factsheet . ... You should not receive the treatment if you have had a serious allergic reaction to any of the ingredients. Talk to your health care provider if you: • have allergies; • have a serious illness;

How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells.Mar 31, 2022
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
In the United States, there are three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody treatments with FDA Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the treatment of COVID-19: bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab,, and sotrovimab.
What is the difference between monoclonal antibodies and the COVID-19 vaccine?
COVID-19 vaccines help stimulate and prepare a person's immune system to respond if they are exposed to the virus. However, monoclonal antibodies boost the immune system only after a person is already sick, speeding up their immune response to prevent COVID-19 from getting worse.Nov 8, 2021
Can I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I was treated with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma?
If you were treated for COVID-19 symptoms with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, you should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
Is there an antibody cocktail for COVID-19?
The treatment, bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together, was granted FDA emergency use authorization in February. Eli Lilly and the FDA stipulated that the antibody cocktail is authorized as a COVID-19 prophylaxis only for individuals who have been exposed to the virus.Sep 16, 2021
What is the first drug that was approved by the FDA to treat COVID-19?
Remdesivir is the first drug approved by the FDA for treatment of hospitalized COVID patients over the age of 12.Jan 25, 2022
Which drug is approved by FDA to treat COVID-19?
Veklury (Remdesivir) is an antiviral drug approved for use in adults and pediatric patients [12 years of age and older and weighing at least 40 kilograms (about 88 pounds)] for the treatment of COVID-19 requiring hospitalization.Mar 31, 2022
How many types of COVID-19 vaccines are available in the US?
Three COVID-19 vaccines are authorized or approved for use in the United States to prevent COVID-19. Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna (COVID-19 mRNA vaccines) are preferred. You may get Johnson & Johnson's Janssen COVID-19 vaccine in some situations.
Should you still get the COVID-19 vaccine if you were treated with monoclonal antibodies?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, there is no need to delay getting a COVID-19 vaccine.Feb 17, 2022
Do I need the COVID-19 vaccine if I still have antibodies?
Yes, the COVID-19 vaccines are recommended, even if you had COVID-19.Nov 23, 2021
Can I get COVID-19 again after having the vaccine?
Getting COVID-19 after you've been vaccinated or recovered is still possible. But having some immunity -- whether from infection or vaccination -- really drops the odds of this happening to you.Nov 9, 2021
Naked Monoclonal Antibodies
Naked mAbs are antibodies that work by themselves. There is no drug or radioactive material attached to them. These are the most common type of mAb...
Conjugated Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) joined to a chemotherapy drug or to a radioactive particle are called conjugated monoclonal antibodies. The mAb is use...
Bispecific Monoclonal Antibodies
These drugs are made up of parts of 2 different mAbs, meaning they can attach to 2 different proteins at the same time. An example is blinatumomab...
Possible Side Effects of Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are given intravenously (injected into a vein). The antibodies themselves are proteins, so giving them can sometimes cause so...
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibodies?
These are known as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or Moabs). Monoclonal antibodies are used to treat many diseases, including some types of cancer. To make a monoclonal antibody, researchers first have to identify the right antigen to attack.
Why are m onoclonal antibodies used to treat cancer?
NOTE: Some m onoclonal antibodies used to treat cancer are referred to as targeted therapy because they have a specific target on a cancer cell that they aim to find, attach to, and attack.
What are mAbs made of?
There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in -omab.
What is the antibody that blocks HER2?
For example, trastuzumab (Herceptin) is an antibody against the HER2 protein. Breast and stomach cancer cells sometimes have large amounts of this protein on their surface. When HER2 is activated, it helps these cells grow. Trastuzumab binds to these proteins and stops them from becoming active.
Why do mAbs deliver radiation?
The drug and radiation are delivered directly to the target cells because the mAb looks for the target, then the radiation affects the target and nearby cells to a certain extent. Chemolabeled antibodies: These mAbs have powerful chemotherapy (or other) drugs attached to them. Examples include:
How are conjugated mAbs used?
These mAbs are used as a homing device to take one of these substances directly to the cancer cells. The mAb circulates throughout the body until it can find and hook onto the target antigen. It then delivers the toxic substance where it is needed most. This lessens the damage to normal cells in other parts of the body. Conjugated mAbs are also sometimes referred to as tagged, labeled, or loaded antibodies.
How do naked mAbs work?
(See Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Their Side Effects .) Other naked mAbs work mainly by attaching to and blocking antigens on cancer cells (or other nearby cells) that help cancer cells grow or spread.
What is the EUA for bamlanivimab?
On November 9, 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy, bamlanivimab, for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients with positive COVID-19 test results who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization. Bamlanivimab may only be administered in settings in which health care providers have immediate access to medications to treat a severe infusion reaction, such as anaphylaxis, and the ability to activate the emergency medical system (EMS), as necessary. Review the Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers EUA of Bamlanivimab regarding the limitations of authorized use.
When did the EUA for Casirivimab come out?
On November 21, 2020 , the FDA issued an EUA for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy, casirivimab and imdevimab, administered together, for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients with positive COVID-19 test results who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19 and/or hospitalization.
Can you use bamlanivimab in emergency settings?
Bamlanivimab may only be administered in settings in which health care providers have immediate access to medications to treat a severe infusion reaction, such as anaphylaxis, and the ability to activate the emergency medical system (EMS), as necessary.
Does Medicare cover PHE?
In order to ensure immediate access during the COVID-19 PHE, Medicare will cover and pay for these infusions in accordance with Section 3713 of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act).