Self-care
- Wash your mouth with one tablespoon of the oil you choose (make sure that the oil goes through your teeth and covers the gum)
- Washing for 15 minutes
- Spit the oil out and rinse off your mouth with water
- Repeat the technique every day for about a month
Nutrition
When you visit a dentist for a dental cleaning and checkup every six months, your dentist can catch early signs of gum disease and cure it. However, if your gum disease has progressed, it cannot be cured, but it can be treated. If you suspect that you have advanced gum disease, visit a dentist as soon as you can.
What is the best natural cure for gum disease?
- Scaling and planing. These procedures are also known as deep cleaning and are the first line of treatment against gum disease. ...
- Locally administered antibiotics. At times, our dentist can also opt for antibiotics to discourage the growth of harmful bacteria.
- If non-surgical interventions don’t work, then surgery is the next best option. ...
Is there a cure for gum disease?
This should include:
- Brushing – brush your teeth every day after each meal. ...
- Flossing – you need to remove the food particles that get stuck between your teeth after each meal as they are breeding grounds for toxic bacteria. ...
- Rinsing – the final step in your daily routine should be using a mouthwash to rinse away the left over bacteria. ...
What kind of dentist treats gum disease?
How to reverse periodontal disease naturally without surgery?
See more

What's the best treatment for gum disease?
Antibiotics. Topical or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection. Topical antibiotics can include antibiotic mouth rinses or insertion of gels containing antibiotics in the space between your teeth and gums or into pockets after deep cleaning.
How do dentists fix gum disease?
Professional gingivitis care includes: Professional dental cleaning. Your initial professional cleaning will include removing all traces of plaque, tartar and bacterial products — a procedure known as scaling and root planing. Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and beneath your gums.
What is the latest treatment for gum disease?
The FDA-approved laser gum disease treatment uses a tiny laser fiber (about the thickness of three hairs) that is inserted between the tooth and gum. The laser zaps away only bacteria and infected tissue with much less discomfort compared to standard procedures.
Can gum disease heal?
So how do I cure gum disease? Gum disease can be cured. Essentially, it's all about removing bacteria from your mouth and allowing the gums to heal back to a healthy state. If you want to get rid of gum disease, the first step is to get the right education so that you know how to clean your teeth effectively at home.
Can salt cure gum disease?
Salt water can help to remove the plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums. Salt has healing properties that can treat and heal inflamed or swollen gums caused by gum disease. Even though salt water is extremely effective in helping to treat gum disease, salt water cannot cure gum disease.
Is mouthwash good for gum disease?
Mouthwash Use, Along With Brushing & Flossing, Can Help Prevent Gum Disease. In clinical studies, it's been shown that antibacterial mouthwashes can reduce plaque biofilm, kill bacteria in hard-to-reach places below the gums, and eliminate bacteria on non-tooth oral surfaces including the cheeks, tongue, and more.
Can gum disease heal without surgery?
Depending on how advanced your gum disease is, a non-surgical treatment might be sufficient to reverse the disease and leave you with a healthier mouth. Non-surgical treatments for gum disease include deep cleaning the mouth, using antibacterial products and follow-up care to monitor the disease.
What vitamins should I take for receding gums?
Vitamin B Benefits Vitamin B deficiency can cause receding gums, a sensitivity of mucous membranes, and toothaches. Vitamin B improves general oral health, prevents canker sores, and reduces tongue inflammation. Vitamin B Sources: Fish, meat, poultry, green vegetables, beans, legumes, and mushrooms.
Is gum disease painful?
It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and harden. In advanced stages, periodontal disease can lead to sore, bleeding gums; painful chewing problems; and even tooth loss.
Is gum infection serious?
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications. Periodontitis (per-e-o-don-TIE-tis), also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth.
How long does it take for gum disease to go away?
If you have the first stage of gum disease, gingivitis, you can usually expect to heal and recover within 14 days of getting a deep cleaning, assuming you take your prescribed antibiotics and maintain proper oral hygiene by brushing and flossing thoroughly.
How are gum diseases treated?
Gum (periodontal) diseases are treated in a variety of ways depending on the stage of disease, how you may have responded to earlier treatments, and your overall health.
How to treat gum disease?
What are non-surgical treatments for gum disease? 1 Professional dental cleaning: During a typical checkup, your dentist or dental hygienist removes plaque and tartar that build up and harden on the tooth surface. (Plaque is the ‘film' that covers teeth, which can lead to cavities and gum disease. Tartar is the hard, yellowish deep deposit on teeth,) When plaque and tartar reach this level of build up, they can only be removed with professional cleaning. Cleaning removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line of all your teeth. If you have some signs of gum disease, your dentist may recommend professional dental cleaning more than twice a year. 2 Scaling and root planing: This is a deep-cleaning, non-surgical procedure that is done under local anesthesia. Hardened plaque and tartar (also called calculus) are scraped away (scaling) from above and below the gum line. Also, any rough spots on the tooth root are made smooth (planing). Smoothing the rough spots removes bacteria and provides a clean surface for the gums to reattach to the teeth. 3 Customized: Sometimes control of plaque and inflammation of gum tissue can be done without surgery. Antibiotics, with products like minocycline HCl (Arrestin®) or chlorhexidine (PerioChip®), can be placed in the mouth in the space between the gums and teeth (the periodontal pocket).
What are surgical treatments for gum disease?
Flap surgery/pocket reduction surgery: During this procedure, the gums are lifted back and tartar is removed. In some cases, irregular surfaces of the damaged bone are smoothed. This limits the areas where disease-causing bacteria can hide. The gums are then placed so that the tissue fits snugly around the tooth. Reducing the space between the gum and tooth also limits the areas where harmful bacteria can grow. The chance of serious health problems that can arise from periodontal disease is also reduced.
What are medications used to treat gum disease?
Antibiotics can be used either in combination with surgery and other therapies or alone. Antibiotics reduce or temporarily kill the bacteria of periodontal disease. They also prevent the destruction of the tooth's attachment to the bone.
What is the name of the antibiotic that is used to treat gingivitis?
Chlorhexidine (Peridex®, PerioChip®, PerioGard® and other over-the-counter trade names) is an antibiotic used to control plaque and gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) in the mouth or in periodontal pockets (the space between the gums and teeth).
What is guided tissue regeneration?
Guided tissue regeneration: Performed when the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed, this procedure stimulates bone and gum tissue growth. Done in combination with flap surgery, a small piece of mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue.
Can antibiotics be used alone?
Antibiotics can be used either in combination with surgery and other therapies or alone. Antibiotics reduce or temporarily kill the bacteria of periodontal disease. They also prevent the destruction of the tooth's attachment to the bone.
What is gum disease treatment?
Gum disease treatment is one of the most common dental treatments performed by dentists, along with dental fillings. Almost 90% of the population will need gum disease (periodontal disease) treatment some time in their life.
Why is gum disease important?
With periodontal disease being the number one cause of tooth loss, gum disease treatments are extremely important for the preservation of teeth and maintaining good oral health and proper mouth functionality. The increase of life expectancy and the focus on better quality of life has made the treatment ...
What causes gum disease?
Gum disease is the result of bacterial infection of periodontal tissues. Several causes may lead to gum health problems, however the main cause of gum disease is considered the growth of dental plaque due to poor oral hygiene.
What is the goal of periodontal therapy?
When periodontal disease has been diagnosed, the main therapeutic goals of periodontal therapy / treatment are to: Prevent the recurrence of periodontitis / eliminate periodontal pockets to allow the patient to easily maintain good oral health. Replace lost teeth, if it is too late to be saved.
What is the term for a reversible gum disease that does not cause permanent damage?
Gingivitis is a reversible form of gum disease that does not cause permanent damages. If the gum disease is not treated early, it progresses to the more severe form, periodontitis, that causes irreversible damages to periodontal tissues. Lack of proper gum disease treatment may cause a number of severe dental problems that include:
Why do you need gum surgery?
In the advanced stages of periodontal disease, treatments that involve gum surgery are necessary to either restore some of the damage caused to periodontal tissues or to create a more maintainable periodontal environment to prevent the recurrence of the disease. They include:
Why do people wear dentures for years?
Having to wear dentures for several years because they had lost their teeth from periodontitis and tooth decay might have been expected for our grandfathers but no more in modern societies. Especially in our time when the advances in dentistry have to offer us several types of effective treatments for gum disease.
What is the treatment for gum disease?
The treatment goals for gingivitis are to identify and eliminate the factors that make the person more susceptible to gum disease. Most factors can be eliminated by establishing more consistent and thorough oral hygiene habits and professional dental cleanings. If there are certain risk factors such as smoking or uncontrolled diabetes that are contributing to the gum disease, they need to be addressed or eliminated to have success in reversing gingivitis. After the plaque and tartar are removed by a dentist or dental hygienist, the patient can usually eliminate gingivitis by brushing and flossing after every meal. Under the supervision of a dentist, a patient can use a prescription mouth rinse that specifically targets oral bacteria that cause gum disease. This is especially helpful in patients where conventional oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing are impaired due to age or special needs.
What types of specialists treat gum disease?
Periodontists are dentists who have completed additional training in periodontology after dental school. They are focused entirely on the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of disease of the gum and bone surrounding the teeth. In advanced cases of gingivitis or periodontitis, a general dentist may recommend a gross debridement of superficial plaque and tartar and will then refer the affected patient to a periodontist for evaluation. Periodontists may recommend a variety of nonsurgical or surgical procedures to help stabilize the gum condition. Periodontists are also very skilled at performing treatments of other conditions of the gums and bone including gum and bone grafts, functional and esthetic gingivectomy, gingivoplasty, implants, and crown lengthening. Because gum disease in its advanced stages is the primary cause of tooth loss today, periodontists are especially important in working to treat a difficult disease.
What is the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
While gingivitis is inflammation of the gums around the teeth, periodontitis occurs when the bone below the gums gets inflamed or infected. Periodontitis derives from the word periodontal, which means "around the tooth" and refers to the structures that surround and support teeth such as gum and bone. Periodontology is the study of the supporting structures of the teeth.
What is gum disease (gingivitis)?
Gums that bleed easily during flossing or brushing is a sign of gum disease (gingivitis).
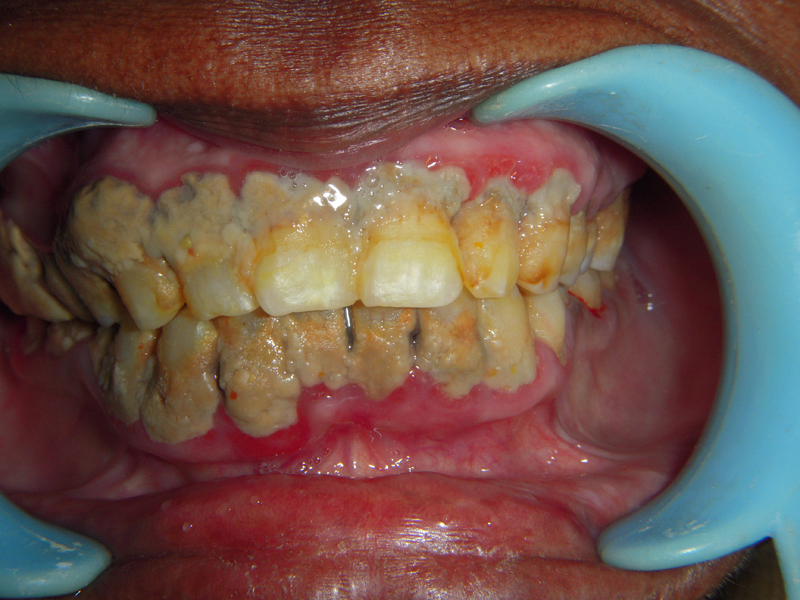
What does gum disease look like? What are gum disease symptoms and signs?
A person with gum disease will typically have one or more of the following signs and symptoms:
How do health care professionals diagnose gum disease?
The following methods and symptoms and signs are very useful in the diagnosis of gum disease during routine checkups:
Is gum disease associated with other health problems?
There have been many attempts to understand the link between gum disease and other systemic health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease. Comparing the bacteria that cause dental plaque with the bacteria involved in heart disease suggests a correlation between gum disease and heart disease, but researchers have been unable to establish a cause and effect relationship. According to the American Academy of Periodontology, recent studies have shown that periodontal disease bacteria may play a role in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. These types of relationships are difficult to prove or disprove, so it is fair to assume that aiming for a life free of gum disease will only help in leading a generally healthier life.
How to get rid of bacteria in gums?
Consider using diluted hydrogen peroxide in a water flosser, like a Waterpik. These oral irrigators send a stream of water around the teeth and under the gums, which helps remove and kill harmful bacteria.
What is the best way to remove gum abscess?
Salt causes fluids to move away from the swelling. If you need a gum abscess home remedy, warm saltwater is a good place to start.
What is the best mouthwash for gum inflammation?
A mouthwash containing a small amount of lemongrass oil can lower bacterial plaque levels. A wash with 0.25% lemongrass oil can reduce plaque better than chlorhexidine gluconate, a proven anti-bacterial rinse used to treat gum inflammation.³
What does it mean when your gums are swollen?
Swollen, inflamed gums are a sign that bacteria are infecting your gums. To prevent further damage to your gums, teeth and jaw, find out what home remedies you can use to help prevent gum disease until you can see a dentist.
Why do my gums bleed after flossing?
If you’re dealing with pain or swelling in your gums or you spit blood after brushing or flossing, your body may be telling you that something’s not quite right. Bleeding from any part of your body suggests an injury, and bleeding gums aren’t an exception.
How to get rid of plaque in mouth?
You can make your own sage rinse at home. Add two tablespoons of fresh sage or one teaspoon of dried sage to a cup or two of boiling water. Let it simmer on low for about 10 minutes before straining it.
What is the best way to treat a cut?
Hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide, a mild antiseptic, is often helpful in the prevention of skin infections from minor cuts and scrapes. Swishing with hydrogen peroxide may also help relieve minor mouth irritations and kill bacteria that could lead to gum disease.
