
Medication
Treatment Approaches for GERD
- GERD Treatment: Lifestyle and Dietary Changes. Dietary and lifestyle changes are the first step in treating GERD. ...
- GERD Treatment: Medication. If lifestyle and dietary changes do not work, your doctor may prescribe certain medications. ...
- TIF and Other Endoscopic Therapy. ...
- Surgery for GERD
Procedures
- Stage 1: Mild GERD: It is accompanied by mild symptoms and can be treated with home remedies and lifestyle changes.
- Stage 2: Moderate GERD: Symptoms become more frequent and can be controlled with some medications.
- Stage 3: Severe GERD: Symptoms become further more severe and are failed to be controlled by basic medications. ...
Nutrition
These seven best heartburn medications include:
- Famotidine (Pepcid)
- Omeprazole (Prilosec)
- Esomeprazole (Nexium)
- Mylicon
- Calcium carbonate (TUMS)
- Maalox
- Sodium Bicarbonate
What is the best treatment of Gerd?
Our Editor 10 diet for gerd Review:
- The Acid Watcher Diet: A 28-Day Reflux Prevention and Healing Program
- Acid Reflux Diet: 101 Best Foods To Treat & Cure GERD
- The Complete Acid Reflux Diet Plan: Easy Meal Plans & Recipes to Heal GERD and LPR
How is Gerd diagnosed and treated?
What is the best medication to take for GERD?
What type of diet is best for GERD?

What is the recommended treatment for GERD?
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). PPIs are better at treating GERD symptoms than H2 blockers, and they can heal the esophageal lining in most people with GERD. You can buy PPIs over the counter, or your doctor can prescribe one. Doctors may prescribe PPIs for long-term GERD treatment.
What is GERD protocol?
Avoid foods that decrease the pressure in the lower esophagus, such as fatty foods, alcohol and peppermint. Avoid foods that affect peristalsis (the muscle movements in your digestive tract), such as coffee, alcohol and acidic liquids. Avoid foods that slow gastric emptying, including fatty foods. Avoid large meals.
What is the gold standard treatment for GERD?
PPIs: The most potent acid suppressive agents available are PPIs, and they tend to be the standard of care for patients with GERD.
What are three goals in the treatment of GERD?
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) involves a stepwise approach. The goals are to control symptoms, to heal esophagitis, and to prevent recurrent esophagitis or other complications.
What is the strongest medication for GERD?
PPIs are the most powerful medications available for treating GERD. These agents should be used only when this condition has been objectively documented. They have few adverse effects. However, data have shown that PPIs can interfere with calcium homeostasis and aggravate cardiac conduction defects.
What is the safest drug for acid reflux?
Proton pump inhibitors are accepted as the most effective initial and maintenance treatment for GERD. Oral pantoprazole is a safe, well tolerated and effective initial and maintenance treatment for patients with nonerosive GERD or erosive esophagitis.
What are the 4 stages of GERD?
GERD is broken down into different stages based on how serious your symptoms are and how often they occur:Stage 1: Mild GERD. Minimal acid reflux occurs once or twice a month. ... Stage 2: Moderate GERD. ... Stage 3: Severe GERD. ... Stage 4: Precancer or cancer.
Which antacid is best for GERD?
Best for GERD: Nexium 24HR Acid Reducer Heartburn Relief Capsules. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is caused by stomach acid rising all the way up into your esophagus, throat, and mouth, and can cause a painful burning sensation, belching, and difficulty swallowing.
What is the best PPI for GERD?
In the relief of symptom outcome, omeprazole at 40 mg per day (95.2%) from the PPI family ranked first, followed by lansoprazole at 60 mg per day (92.3%), pantoprazole at 80 mg per day (88.1%), and famotidine at 80 mg per day (36.5%) from the H2RA family.
What happens if I stop taking omeprazole?
Stopping omeprazole Usually, you can stop taking omeprazole without reducing your dose first. But if you've been taking omeprazole for a long time, speak to your doctor before you stop taking it. Stopping suddenly could make your stomach produce a lot more acid, and make your symptoms come back.
How long does it take for esophagus to heal from acid reflux?
It might take 1 to 3 weeks to heal. Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor or nurse call line if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How long is treatment for GERD?
Minor cases of GERD can heal in less than a month. More moderate cases can require 6 to 12 weeks of treatment. Some patients do not report good results even after treatment and require surgery. Some may prefer surgery over indefinite medication.
How to reduce GERD symptoms?
Bariatric surgery can help you lose weight and reduce GERD symptoms. Endoscopy. In a small number of cases, doctors may recommend procedures that use endoscopy to treat GERD. For endoscopy, doctors insert an endoscope—a small, flexible tube with a light and camera—through your mouth and into your esophagus.
What is the best way to reduce GERD?
In open fundoplication, surgeons make a larger cut in the abdomen. Bariatric surgery. If you have GERD and obesity, your doctor may recommend weight-loss surgery, also called bariatric surgery, most often gastric bypass surgery. Bariatric surgery can help you lose weight and reduce GERD symptoms. Endoscopy.
What is the most common surgery for GERD?
Fundoplication is the most common surgery for GERD. In most cases, it leads to long-term improvement of GERD symptoms. During the operation, a surgeon sews the top of your stomach around the end of your esophagus to add pressure to the lower esophageal sphincter and help prevent reflux.
What is the best medicine for GERD?
Your doctor may prescribe one or more medicines to treat GERD. Antacids. Doctors may recommend antacids to relieve mild heartburn and other mild GER and GERD symptoms. Antacids are available over the counter. Antacids can help relieve mild symptoms.
Can GERD be treated with surgery?
Your doctor may recommend surgery if your GERD symptoms don’t improve with lifestyle changes and medicines, or if you wish to stop taking long-term GERD medicines to manage symptoms. You’re more likely to develop complications from surgery than from medicines.
Can you buy GERD medication?
Over-the-counter and prescription medicines. You can buy many GERD medicines over the counter. However, if you have symptoms that will not go away with over-the-counter medicines, you should talk with your doctor. Your doctor may prescribe one or more medicines to treat GERD. Antacids.
Who develops guidelines for gastrointestinal surgery?
Guidelines are developed under the auspices of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons and its various committees, and approved by the Board of Governors. Each clinical practice guideline has been systematically researched, reviewed and revised by the guidelines committee, and reviewed by an appropriate multidisciplinary ...
What are guidelines in healthcare?
Guidelines are applicable to all physicians who address the clinical problem (s) without regard to specialty training or interests, and are intended to indicate the preferable, but not necessarily the only acceptable approaches due to the complexity of the healthcare environment. Guidelines are intended to be flexible.
What is the most common mechanism of reflux?
The most common mechanism for acid reflux is transient relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (≥ 90% of reflux episodes in normal subjects and 75% of episodes in patients with symptomatic GERD). Other mechanisms include breaching the lower esophageal sphincter because of increased intra-abdominal pressure (strain induced reflux) and a baseline low pressure at the lower esophageal sphincter. The latter two mechanisms increase in frequency with greater reflux severity. Other factors include delayed gastric emptying (co-factor in 20% of GERD patients), medication use (particularly calcium channel blockers), hiatal hernia (increased strain induced reflux and poor acid clearance from hernia sac), and poor esophageal acid clearance (eg, esophageal dysmotility, scleroderma, decreased salivary production).
Do GERD patients seek medical attention?
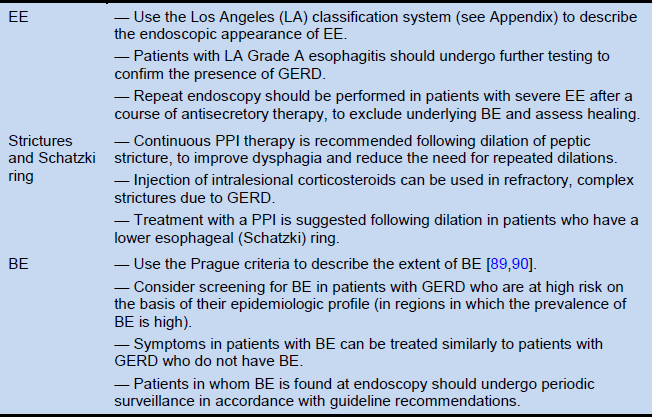
Most GERD patients (80-90%) do not seek medical attention and will self-medicate with OTC anti-secretory therapy (50%). In patients seeing physicians, most will have chronic symptoms that will occur off treatment. Patients with more severe esophagitis will have symptoms recur more quickly and almost allwill have recurrent symptoms and esophagitis if followed up for ≥ 1 year. Progression of disease can be seen in up to 25% of patients with esophagitis, but it is less likely to occur if esophagitis is not present or is mild. (Using the Los Angeles Classification for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, this would be LA grade A or B.) Complications such as Barrett’s esophagus, esophageal ulcers, esophageal stricture or adenocarcinoma of the esophagus are very rare unless the initial endoscopy shows esophagitis or Barrett’s esophagus. A normal endoscopy with symptomatic GERD presents a good prognosis, and does not need to be repeated for 10 years unless alarm or warning symptoms are present (Table 2). Long-term natural history studies are limited.
Can a pregnant woman get GERD?
New onset GERD symptoms are common during pregnancy due mainly to the mechanical pressure placed on the stomach and intestinal tract as the uterus enlarges. Therapy for GERD during pregnancy usually takes a step-wise approach, starting with lifestyle modifications often combined with a trial of calcium containing antacids. If this does not sufficiently treat the symptoms, H2RAs (eg, cimetidine, famotidine, and nizatidine) are considered safe in pregnancy and can be taken to alleviate symptoms. If symptoms persist despite these efforts, PPIs can be considered (caution advised during pregnancy; possible risk of teratogenicity based on conflicting human data).
Does baclofen help with GERD?
While not considered to be first-line therapy, baclofen has been shown to offer symptomatic relief for patients with GERD. This approach is aimed at decreasing the number of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations and increasing lower esophageal sphincter tone. These effects have been observed most significantly after eating a meal.
Is antacid better than placebo for GERD?
Antacids (Tums, Rolaids, Maalox) and combined antacid with alginic acid (Gaviscon) have been shown to be more effective than placebo in the relief of daytime GERD symptoms . Two long-term studies suggest that approximately 20% of patients experience some relief from over-the-counter agents.
Is a barium esophagram necessary for GERD?
perfusion testing (also called Bernstein testing), esophageal sensory testing, and barium esophagram are not indicated for the diagnosis of GERD. Barium esophagram may be helpful in the preoperative phase of anti-reflux surgery or in the evaluation of major motor disorders (eg, achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm) after a normal endoscopy.
Does GERD cause chest pain?
As noted in Table 1, GERD may manifest atypically as pulmonary (asthma, chronic cough), laryngeal (laryngitis, hoarseness, sore throat, globus, throat clearing), or cardiac (chest pain ) symptoms , often without symptoms of heartburn and regurgitation. Mechanisms include direct contact and microaspiration of small amounts of noxious gastric contents into the larynx and upper bronchial tree triggering local irritation, and cough, and acid stimulation of vagal afferent neurons in the distal esophagus causing non-cardiac chest 8 pain and vagally-mediated bronchospasm or asthma. Laryngeal neuropathy has been implicated as a cause for laryngitis symptoms and cough.
Lifestyle Changes
Over-The-Counter and Prescription Medicines
Surgery and Other Medical Procedures
Authors
Specialist to consult
Abstract
- Lifestyle changes may reduce your symptoms. Your doctor may recommend 1. losing weight if you’re overweight or have obesity 2. elevating your head during sleep by placing a foam wedge or extra pillows under your head and upper back to incline your body and raise your head off your bed 6 to 8 inches 3. quitting smoking External link, if you smoke 4....
Executive Summary
- You can buy many GERD medicines over the counter. However, if you have symptoms that will not go away with over-the-counter medicines, you should talk with your doctor. Your doctor may prescribe one or more medicines to treat GERD. Antacids. Doctors may recommend antacids to relieve mild heartburn and other mild GER and GERD symptoms. Antacids are available over the …
Recommendations
- Your doctor may recommend surgery if your GERD symptoms don’t improve with lifestyle changes and medicines, or if you wish to stop taking long-term GERD medicines to manage symptoms. You’re more likely to develop complications from surgery than from medicines. Fundoplication. Fundoplication is the most common surgery for GERD. In most cases, it leads to long-term impr…
Introduction
Key Questions
Discussion
Disclaimer
Supplemental Information
- Aim of these guidelines and specific objectives The purpose of these guidelines is to provide evidence-based recommendations from a surgeon and patient perspective regarding the surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux (GERD). This review assessed outcomes of antireflux surgery versus medical management of GERD in adults and children, robotic ...
Acknowledgements