
Risk Treatment Strategies
- Avoidance. : Action is taken to depart from the risk situation or remove the activities giving rise to the risk i.e. ...
- Reduction. : Action is taken to reduce the risk likelihood or consequence, or both, which may involve any of a myriad of everyday business and process control decisions, i.e. ...
- Sharing. ...
- Acceptance. ...
- Risk acceptance.
- Risk transference.
- Risk avoidance.
- Risk reduction.
What are the 5 types of risk treatment?
Apr 12, 2022 · You can break risk treatment options down in a number of types: Avoid: Risk avoidance is actually pretty self-explanatory. If a risk is deemed too high, then you simply avoid the... Transfer: In many instances, you can transfer the risk you take to another party. For instance, insurance companies... ...
What is a risk treatment?
Jul 19, 2015 · 7 Types of Risk Treatment 1. Avoidance. You can choose not to take on the risk by avoiding the actions that cause the risk. For example, if you... 2. Reduction. You can take mitigation actions that reduce the risk. For example, wearing a life jacket when you swim. 3. Transfer. You can transfer all ...
What should be included in a risk treatment plan?
Apr 18, 2013 · Here are the four key potential risk treatments to consider. Avoidance. Obviously one of the easiest ways to mitigate risk is to put a stop to any activities that might put your business in jeopardy. However it's important to remember that with nothing ventured comes nothing gained, and therefore this is often not a realistic option for many ...
What are the different types of risk management processes?
As explained in the sections above, there are usually four treatment options available for companies: decrease the risk, avoid the risk, share the risk, and retain the risk. According to ISO 27001, it is required to document the risk treatment results in the Risk Assessment Report, and those results are the main inputs for writing the Statement of Applicability.
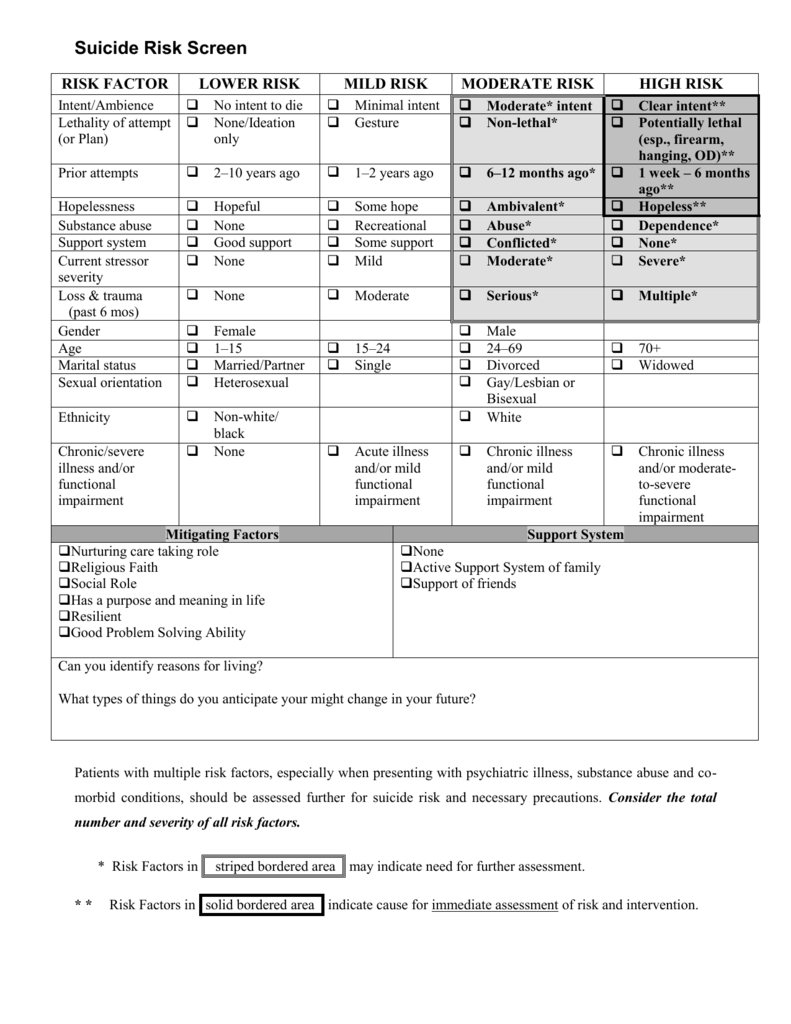
What are the 4 risk treatment options?
Risk treatment measures can include avoiding, optimizing, transferring or retaining risk. The measures (i.e. security measurements) can be selected out of sets of security measurements that are used within the Information Security Management System (ISMS) of the organization.
What are the 4 types of risk?
The main four types of risk are:strategic risk - eg a competitor coming on to the market.compliance and regulatory risk - eg introduction of new rules or legislation.financial risk - eg interest rate rise on your business loan or a non-paying customer.operational risk - eg the breakdown or theft of key equipment.
What are the risk treatment options?
In general, there are four types of risk treatment:Avoidance. You can choose not to take on the risk by avoiding the actions that cause the risk. ... Reduction. You can take mitigation actions that reduce the risk. ... Transfer. You can transfer all or part of the risk to a third party. ... Acceptance. ... Sharing.May 10, 2021
What are the 3 types of risk management?
There are different types of risks that a firm might face and needs to overcome. Widely, risks can be classified into three types: Business Risk, Non-Business Risk, and Financial Risk.Mar 3, 2022
What are the risk risk types?
Systematic Risk – The overall impact of the market. Unsystematic Risk – Asset-specific or company-specific uncertainty. Political/Regulatory Risk – The impact of political decisions and changes in regulation. Financial Risk – The capital structure of a company (degree of financial leverage or debt burden)
What is risk treatment?
A risk treatment is an action that is taken to manage a risk. Risk management processes all include steps to identify, assesses and then treat risks. In general, there are four types of risk treatment:
How to choose not to take on the risk?
You can choose not to take on the risk by avoiding the actions that cause the risk. For example, if you feel that swimming is too dangerous you can avoid the risk by not swimming.
What is risk acceptance?
Risk acceptance, also known as risk retention, is choosing to face a risk. In general, it is impossible to profit in business or enjoy an active life without choosing to take on risk. For example, an investor may accept the risk that a company will go bankrupt when they purchase its bonds. 5. Sharing.
What is secondary risk?
Secondary Risk. It's common for your efforts to reduce risk to have risks of their own. These are known as secondary risks. For example, if you outsource a project you will assume a number of secondary risks such as the risk that the outsourcing company will fail to deliver.
Can you transfer all of your risk to a third party?
You can transfer all or part of the risk to a third party. The two main types of transfer are insurance and outsourcing. For example, a company may choose to transfer a collection of project risks by outsourcing the project.
What is risk reduction strategy?
Risk reduction strategies need to be weighed up in terms of their potential return on investment. If the cost of risk reduction outweighs the potential cost of an incident occurring, you will need to decide whether it is really worthwhile. Transfer. One of the best methods of risk management is transferring that risk to another party.
How to mitigate risk?
Avoidance. Obviously one of the easiest ways to mitigate risk is to put a stop to any activities that might put your business in jeopardy. However it's important to remember that with nothing ventured comes nothing gained, and therefore this is often not a realistic option for many businesses. Reduction.
What is the first step in risk management?
The first stage is to determine exactly what the risks facing your business are, in order to assess the likely and potential impact of each incident occurring. Once this process has been completed, you can get down to evaluating the technique which will best suit your business and maximise your risk management moving forward.
What is risk transfer?
Risk transfer is a realistic approach to risk management as it accepts that sometimes incidents do occur, yet ensures that your business will be prepared to cope with the impact of that eventuality. Acceptance. Finally, risk acceptance involves 'taking it on the chin', so to speak, and weathering the impact of an event.
What is Elders Insurance?
Elders Insurance is a leader in providing business interruption insurance and business liability insurance, and can help you determine the right risk management policy for your enterprise.
What is risk reduction action?
Risk reduction, actions are taken for: o Changing likelihood (mitigating actions): action taken to reduce the likelihood of negative outcomes and/or to increase opportunity, in order to enhance good outcomes.
What are the response actions?
These response action categories are: 1. TOLERATE. The exposure may be tolerable without any further action being taken or even if not tolerable, the ability to do anything may be limited ( or the cost of taking any action may be dis proportionate to the potential benefit). In these cases the response may be to tolerate the existing level of risk. ...
Is risk treatment mutually exclusive?
Risk treatment options are not necessarily mutually exclusive, or appropriate in all circumstances. Often a risk response may combine two or more of these strategies to achieve the desired results. An organization can normally benefit from adopting a combination of treatment options.
What is risk treatment?
The risk treatment of moderate or higher risks is taken to the department’s management team for approval. The treatment is assigned to a person responsible for implementing the treatment as a part of normal operations or if that is not possible a separate implementation plan is to be prepared”.
Is risk treatment of most significant risks assigned to managers?
R1. “Yes. risk treatment of most significant risks is assigned to managers, and followed up (annually or bi-annually by the board of directors). The less significant risks are treated as a part of normal operations. The risk treatment of moderate or higher risks is taken to the department’s management team for approval. The treatment is assigned to a person responsible for implementing the treatment as a part of normal operations or if that is not possible a separate implementation plan is to be prepared”.
What is enterprise risk management?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) has been a developing area of practice for actuaries for over 10 years. In 2001, the Casualty Actuarial Society (CAS) Advisory Committee on Enterprise Risk Management produced a report that recommended areas of research and education that were needed by actuaries entering this emerging field. In 2002, the Society of Actuaries (SOA) formed a Risk Management Task Force that wrote guides to Economic Capital and Enterprise Risk Management practice as well as initiating several research projects. In 2004, the task force evolved into a new Risk Management Section of the Society of Actuaries and became the first and largest joint activity in 2005 when it became the Joint Risk Management Section co-sponsored by the SOA, CAS, and the Canadian Institute of Actuaries (CIA). The Joint Risk Management Section has been tightly linked with an annual ERM Symposium event that is a joint activity of the SOA, CAS, CIA, and the Professional Risk Managers’ International Association (PRMIA), a non-actuarial risk management organization.
What is the role of an actuary?
Actuaries often have a central role in the operation of the control cycle for individual risks including insurance risk, equity risk, credit risk, interest rate risk, operational risk and liquidity risk. Within those control cycles, actuaries may use tools and processes such as reinsurance, hedging and duration/convexity matching as well as the more general risk mitigation processes such as underwriting, risk selection, and risk avoidance. In many organizations, actuaries are not the only risk managers. Actuaries might be a part of a multi-disciplinary team or may be managing one risk while other teams, including non-actuaries, manage other risks.
What Is Risk Treatment?
Risk treatment follows risk analysis in the risk management process and its goal is to select one or more option for addressing the risk and then implementing the option (s).
Brainstorming and Selecting Risk Treatment Options
Your risk treatment option (s) may lead you in any of the following directions:
Planning and Implementing Risk Treatments
Next, create a plan for implementing the risk treatment. The risk treatment plan spells out how the risk treatment will be implemented. This helps all involved have the same understanding and helps you measure progress toward implementation.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Implemented Risk Treatments
Once you’ve implemented your risk treatment (s), you’ll want to monitor and review them to evaluate their effectiveness. Remember, this is something you should have prepared to do when creating your risk treatment plan, as described above.
Recording and Reporting on Risk Treatments
Always document all phases of the risk management process, including of course risk treatment and risk treatment evaluation.
Where to Learn More About Risk Management
Of course, you can hang tight for the next article (s) in our Risk Management Basic Series, but here are some additional resources for you if you want to kickstart your risk management awareness.
Conclusion: Risk Treatment is an Essential Phase of the Risk Management Process
We hope you enjoyed and learned from this installment of our Risk Management Basics series.
What is risk treatment?
According to its definition, Risk Treatment is the process of selecting and implementing of measures to modify risk. Risk treatment measures can include avoiding, optimizing, transferring or retaining risk. The measures (i.e. security measurements) can be selected out of sets of security measurements that are used within ...
What is risk management plan?
The Risk Management plan should define how Risk Management is to be conducted throughout the organization. It must be developed in a way that will ensure that Risk Management is embedded in all the organization’s important practices and business processes so that it will become relevant, effective and efficient.
What is the purpose of sharing risk?
trying to manipulate possible consequences, to increase the expected gains; sharing the risk with other parties that may contribute by providing additional resources which could increase the likelihood of the opportunity or the expected gains ; retaining the residual risk .
What is the responsibility of the top management?
Last but not least, an important responsibility of the top management is to identify requirements and allocate necessary resources for Risk Management. This should include people and skills, processes and procedures, information systems and databases, money and other resources for specific risk treatment activities.
What is residual risk?
Residual risk is a risk that remains after Risk Management options have been identified and action plans have been implemented. It also includes all initially unidentified risks as well as all risks previously identified and evaluated but not designated for treatment at that time.
What is the next step in identifying and evaluating the risks?
Having identified and evaluated the risks, the next step involves the identification of alternative appropriate actions for managing these risks, the evaluation and assessment of their results or impact and the specification and implementation of treatment plans.
Is initial approval necessary for a risk management process?
As with all relevant management processes, initial approval is not sufficient to ensure the effective implementation of the process. Top management support is critical throughout the entire life-cycle of the process. For this reason, it is the responsibility of the Risk Management Process Owner to keep the organization’s executive management continuously and properly informed and updated, through comprehensive and regular reporting
What is information security risk treatment?
Information security risk treatment is that the overall process of choosing risk treatment options, determining appropriate controls to implement such options, formulating a risk treatment plan and obtaining approval of the Risk treatment plan by the Risk owner (s).All steps of the knowledge security risk treatment process also because the results of its application are retained by the organization as documented information.
How to avoid risk?
Avoiding the Risk by deciding to not start or continue with the activity that provides rise to the Risk or by removing the Risk source (e.g. closing an e-commerce portal);
What is special attention in information security?
Special attention should tend to the determination of the required information security controls. Any control should be determined supported information security risks previously assessed. If a corporation features a poor information security risk assessment, it’s a poor foundation for its choice of data security controls.
What is risk owner?
Risk owner (s); Expected residual risk after the implementation of actions. If any action is required by the Risk treatment plan, then it should be planned indicating responsibilities and deadlines such an action plans are often represented by an inventory of those actions.
What is ISO/IEC 27001:2013?
Annex A ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Annex A contains a comprehensive list of control objectives and controls. Users of this document are directed to the generic representation of controls in ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Annex A to make sure that no necessary controls are overlooked. Comparison with ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Annex A also can identify alternative controls to those determined in which may be simpler at modifying information security risk. Control objectives are implicitly included within the controls chosen. The control objectives and controls listed in ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Annex A aren’t exhaustive and extra control objectives and controls should be added as required.
