- Acne or oily skin.
- Mild fluid retention.
- Stimulation of prostate tissue, with perhaps some increased urination symptoms such as a decreased stream or frequency.
- Increased risk of developing prostate abnormalities.
- Breast enlargement.
- Increased risk of blood clots.
Top10homeremedies.com
1. Lose Weight...
2. Exercise...
3. Get Adequate Sleep...
4. Reduce Stress...
5. Eat Healthy Fats...
6. Optimize Your Vitamin D Levels...
7. Consume Plenty of Zinc...
8. Cut Back on the Booze...
Learn More...Homeremedyshop.com
1. Avoid Obesity...
2. Take More Zinc...
3. Check Alcohol Consumption...
4. Stay Away from Stress...
5. Regular Exercise...
6. Control Sexual Desire...
7. BCAA and Whey Proteins...
8. Eliminate Sugar...
Learn More...What are the negative effects of testosterone therapy?
The following changes may occur:
- Deepening of the voice and lengthening of the vocal chords
- Increase in body and facial hair
- Increase in libido with enlargement of the clitoris
- Change in body structure from rearrangement of fat cells
- Acne, and skin oiliness often increase--rougher skin not uncommon
- Male pattern baldness--will not regenerate if testosterone therapy stops
What effects do you get from taking testosterone?
These hormones are thought to have important effects on:
- Ovarian function
- Bone strength
- Sexual behavior, including normal libido (although evidence is not conclusive)
What are the risks of testosterone therapy?
UCLA-led meta-analysis may help guide treatment planning for patients with high-risk prostate cancer
- Journal
- DOI
- Method of Research
- Subject of Research
- Article Title
- Article Publication Date
- COI Statement. Dr. Kishan reported receiving personal fees from ViewRay, Inc., Varian Medical Systems, Inc., and Janssen Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work, as well as research funding from ViewRay.
What are the side effects of stopping testosterone injections?
- loss of bone mineral density and osteoporosis
- breast tenderness and gynecomastia
- sweating and hot flashes
- erectile dysfunction and infertility
- mood swings
- brain fog
- loss of muscle mass and strength
- loss of facial and body hair
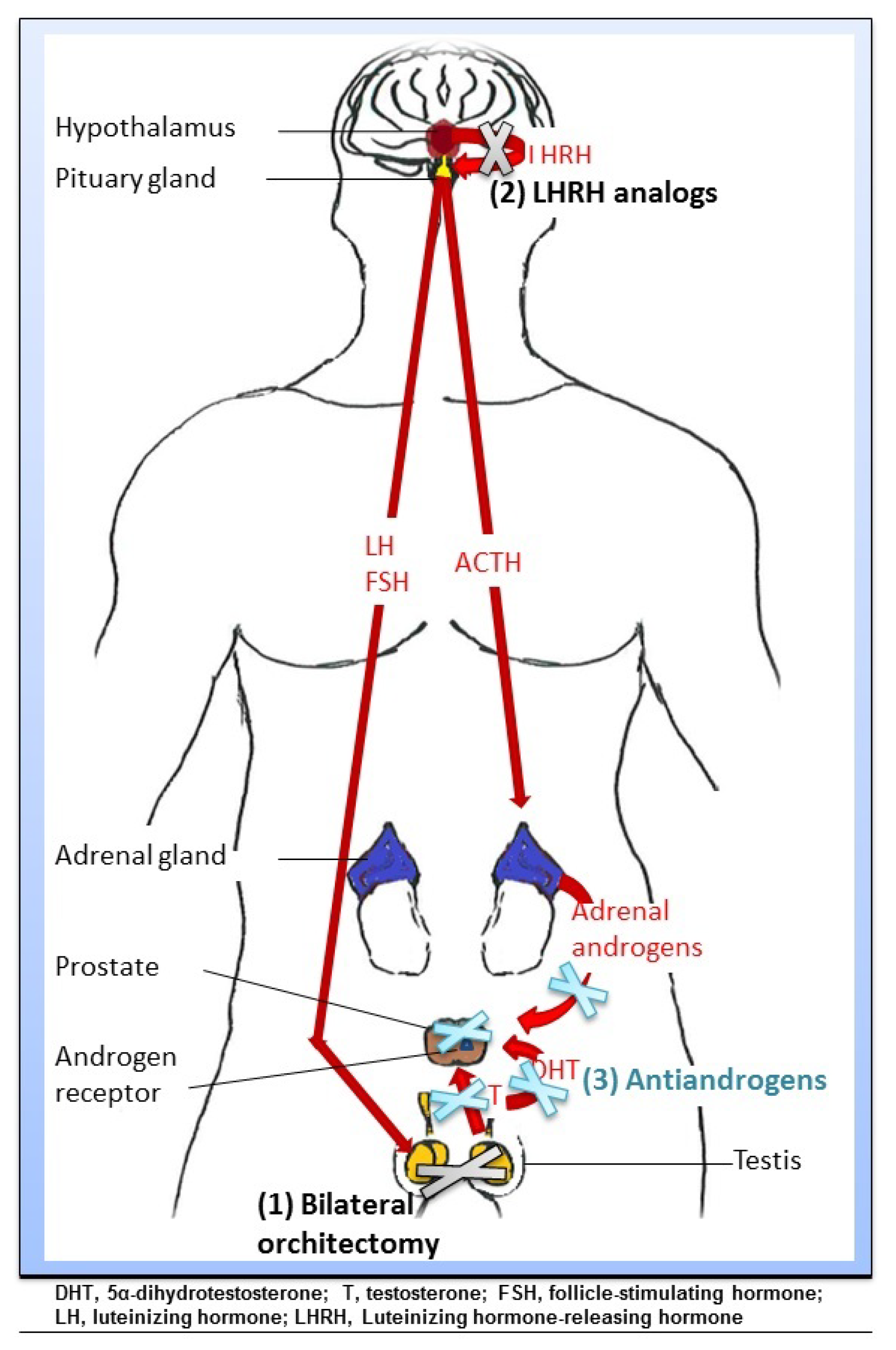
What does testosterone treatment do for you?
Testosterone is responsible for increased muscle mass. Leaner body mass helps control weight and increases energy. For men with low testosterone, studies show that treatment can decrease fat mass and increase muscle size and strength. Some men reported a change in lean body mass but no increase in strength.
How does testosterone therapy make you feel?
You might feel like you just don't have the energy that you're used to. Or you might be incredibly tired. These symptoms can add up to chronic low energy, and mental and physical fatigue. Studies have shown improvements in energy for men after they started TRT.
What are 3 effects of testosterone?
Testosterone is an important hormone. It can boost libido, increase muscle mass, sharpen memory, and bump up energy. Yet, most men lose testosterone with age. A reported 20 to 40 percent of older men have a medical condition called hypogonadism and need testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Are there any negative effects of testosterone?
Misuse of testosterone can cause dangerous or irreversible effects, such as enlarged breasts, small testicles, infertility, high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, liver disease, bone growth problems, addiction, and mental effects such as aggression and violence.
What happens when you start taking testosterone?
Soon after beginning hormone treatment, you will likely notice a change in your libido. Quite rapidly, your genitals, especially your clitoris, will begin to grow and become even larger when you are aroused. You may find that different sex acts or different parts of your body bring you erotic pleasure.
What happens after your first testosterone injection?
When you inject testosterone, you're putting a depot of oil into muscle tissue which is slowly dispersed into the bloodstream (for several days, or even weeks, depending on the ester). As a side effect of this, you might experience injection site soreness for a few days after the fact.
Why would a man take testosterone?
You may need testosterone therapy (TT) if you have Low-T. Both the FDA and the AUA suggest that TT be used to treat conditions you are born with, such as Klinefelter syndrome. You also may need TT if you harm or lose your testicles. If your testicles are removed because of a sickness such as cancer, you may need TT.
When should a man take testosterone?
Since everyone's body operates a little differently, TRT could be something you consider anywhere from your mid-20s to your late 40s or so. Ultimately, the best age for TRT is whatever age that you personally need it.
Who should not take testosterone?
Who Shouldn't Take Testosterone Replacement Therapy? Men who have prostate cancer or breast cancer should not take testosterone replacement therapy. Nor should men who have severe urinary tract problems, untreated severe sleep apnea or uncontrolled heart failure.
Are testosterone injections safe?
Testosterone injections may be safe for many people when they follow a doctor's instructions. However, research has also linked testosterone therapy with several side effects and possible complications. Possible negative effects of testosterone therapy may include: an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
What Happens to Testosterone Levels With Age?
Testosterone levels generally peak during adolescence and early adulthood. As you get older, your testosterone level gradually declines — typically...
Does A Naturally Declining Testosterone Level Cause The Signs and Symptoms of Aging?
Not necessarily. Men can experience many signs and symptoms as they age. Some may occur as a result of lower testosterone levels and can include: 1...
Can Testosterone Therapy Promote Youth and Vitality?
Testosterone therapy can help reverse the effects of hypogonadism, but it's unclear whether testosterone therapy would have any benefit for older m...
What Are The Risks of Testosterone Therapy For Normal Aging?
Testosterone therapy has various risks. For example, testosterone therapy may: 1. Contribute to sleep apnea — a potentially serious sleep disorder...
Should You Talk to Your Doctor About Testosterone Therapy?
If you wonder whether testosterone therapy might be right for you, talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits. Your doctor will likely meas...
What is the effect of testosterone on the body?
The Effects of Testosterone on the Body. Testosterone is a vital male hormone that is responsible for the development and maintenance of male attributes. Women also have testosterone, but in much smaller amounts.
How does testosterone affect men?
Testosterone levels affect everything in men from the reproductive system and sexuality to muscle mass and bone density. It also plays a role in certain behaviors.
How long does it take for testosterone to rise?
The Effects of Testosterone on the Body. Testosterone is an important male hormone. A male begins to produce testosterone as early as seven weeks after conception. Testosterone levels rise during puberty, peak during the late teen years, and then level off. After age 30 or so, it’s normal for a man’s testosterone levels to decrease slightly every ...
How to know if you have testosterone?
Testosterone travels around the body in the bloodstream. The only way to know your testosterone level for sure is to have it measured. This usually requires a blood test.
How does testosterone help build muscle?
It also interacts with nuclear receptors in DNA, which causes protein synthesis. Testosterone increases levels of growth hormone. That makes exercise more likely to build muscle .
What is testosterone responsible for?
During puberty, testosterone is responsible for the development of male attributes like a deeper voice, beard, and body hair. It also promotes muscle mass and sex drive.
Where does testosterone come from?
Most testosterone is produced in the testicles, but small amounts come from the adrenal glands, which are located just above the kidneys. In women, the adrenal glands and ovaries produce small amounts of testosterone. Before a boy is even born, testosterone is working to form male genitals. During puberty, testosterone is responsible for ...
Why is testosterone good for you?
Jed Kaminetsky, M.D., a clinical assistant professor in the department of urology at NYU Langone Medical Center also notes that this may be partially because testosterone improves overall motivation to get up and sweat it out, so if you're motivated to put in the work again, you'll see results.
What happens when you take testosterone outside?
When you take outside testosterone, the pituitary gland gets the memo that there's enough T in your bloodstream, so it stops sending these signals. This essentially puts the testicles to sleep (read: little or no sperm and testosterone production), says Dr. Kaminetsky.
What happens if you don't have enough testosterone?
If there’s not enough testosterone to go around, those androgen receptors all over your body and brain stay silent, leading to symptoms like low libido, weak erections and orgasms, inability to build muscle mass, low energy, or just feeling a little blue.
What hormones are produced when there is no testosterone in the blood?
Normally, when your pituitary gland senses that there's not enough testosterone in the bloodstream, it sends down a hormone called luteinizing hormone (LH) to signal your testicles to start producing more testosterone, and a hormone called follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) to signal sperm production.
How to raise testosterone levels?
That’s where testosterone replacement therapy—a treatment that raises your low testosterone levels—comes in. Testosterone can be supplemented in the form of an injection, a gel, a suction cup on your gums, and even a deodorant. It comes down to personal preference and what your insurance covers, says Dr. Tamler.
How long does it take for depression to go away after testosterone?
In fact, a 2012 study published in The Aging Male found that after 12 months of testosterone therapy, the percentages of guys with moderately severe to severe depression symptoms decreased from 17 percent to 2 percent.
Does testosterone stimulate growth?
This is because androgen receptors are found in muscle tissue, so testosterone activates them to stimulate growth. Of course, to make the most of this benefit, you’ll need to be doing your part by strength training as well.
The Benefits of Testosterone Treatment
When you look at the many well documented benefits of testosterone treatments, it is easy to see that the benefits of testosterone therapy, far outweigh the minimal risk of any potential side effects. We have also found that the safest and most effective form of testosterone treatment, is prescription testosterone injections.
Testosterone Treatment and the Risk of Heart Disease and Cancer
Despite testosterone therapy being generally regarded as safe, there remains a lot of misinformation out there about the risks of testosterone treatment.
Benefits of Testosterone Treatment Vs the Side Effects
By now, we hope you have come to realize that the many benefits of testosterone treatment far outweigh the possible side effects of testosterone replacement. As you now know, the potential dangers of testosterone treatment have been largely exaggerated, and the risk of side effects can be kept to a minimum. Weigh that against the advantages of:
How to Avoid Testosterone Treatment Side Effects
When it comes to avoiding any potential side effects of testosterone replacement therapy, who you get your testosterone injections from can make a big difference.
What are the side effects of testosterone?
General. The most frequently reported side effects with this drug are edema, acne, site pain, injection site erythema, cough or dyspnea during or immediately after injection. The most frequently reported side effects with testosterone topical are skin reaction (16.1%) and allergic contact dermatitis (up to 37%). [ Ref]
What are the symptoms of overdose on testosterone?
Get emergency help immediately if any of the following symptoms of overdose occur while taking testosterone: Symptoms of overdose. Blurred vision. headache. seizures. slurred speech. sudden and severe inability to speak. temporary blindness. weakness in the arm or leg on one side of the body, sudden and severe.
Does testosterone go away?
Some side effects of testosterone may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Does testosterone undecanoate increase blood pressure?
Warning: Blood Pressure IncreasesTestosterone undecanoate can cause blood pressure (BP) increases that can increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke and cardiovascular death. Before initiating testosterone undecanoate, consider the patient’s baseline cardiovascular risk and ensure blood pressure is adequately controlled. Periodically monitor for and treat new-onset hypertension or exacerbations of pre-existing hypertension and re-evaluate whether the benefits of testosterone undecanoate outweigh its risks in patients who develop cardiovascular risk factors or cardiovascular disease on treatment. Due to this risk, use testosterone undecanoate only for the treatment of men with hypogonadal conditions associated with structural or genetic etiologies.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
severe or sudden headache. slurred speech. temporary blindness. weakness in the arm or leg on one side of the body, sudden and severe. Some side effects may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.
Can medicine cause side effects?
Side Effects. Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
Why is testosterone deficiency important?
Testosterone deficiency (TD) in men has garnered substantial attention over the last decade due to an increased awareness by medical providers, increased direct-to-consumer advertising in the media, and the increasing age of the male population. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) has been used in millions of men worldwide to treat diminished libido and erectile dysfunction, and to improve strength and physical function [Shabsigh 2003; Page et al.2005]. Between 2001 and 2011, prescriptions for TRT among men 40 years of age or older in the US increased more than threefold, from 0.81% in 2001 to 2.91% in 2011 [Baillargeon et al. 2013].
What is TRT therapy?
Testosterone replacement therapy ( TRT) has been used in millions of men worldwide to treat diminished libido and erectile dysfunction, and to improve strength and physical function. The estimated likelihood of adverse effects of long-term TRT is still essentially unknown, as overall high-quality evidence based upon prospective randomized trials ...
How long after TRT can you get prostate cancer?
A prospective trial followed 81 men (mean age 57 years) for a mean (range) of 33.8 (6–144) months after starting TRT [Coward et al. 2008]. Only four men were found to develop prostate cancer over 5 years of observation, which is not greater than the incidence in the general population. The baseline PSA of men in this study was 1.32 ng/mL and among those not diagnosed with prostate cancer, there was no significant difference either at any 12-month interval or at 5 years relative to baseline (1.43 ng/ml, p= 0.82). However, among men diagnosed with prostate cancer, there was a significant increase in PSA from baseline by a mean value of 3.2 ng/ml (p < 0.05). This finding led the authors to conclude that prostate cancer can be effectively diagnosed and treated while receiving TRT. These findings are consistent with prior data that demonstrated no influence of either T or other androgens on prostate cancer development [Morgentaler 2011].
Does TRT increase prostate cancer risk?
The theoretical relationship between an increased risk of prostate cancer development and TRT has been a robust debate for decades. It has been demonstrated in several trials that TRT increases serum PSA levels in some men, while androgen deprivation therapy can be used in the successful treatment of prostate cancer. The supportive argument posits that by treating men with TRT, thereby increasing PSA levels and administering T to a steroid responsive cancer, a man’s risk of development of prostate cancer is significantly increased. However, prior literature has failed to definitively demonstrate an increased risk in a cause-and-effect relationship. A meta-analysis, looking at the adverse events associated with TRT in older men, found that men receiving TRT were 11 times more likely to undergo biopsy than the placebo group; however, there was no difference in the number of men diagnosed with prostate cancer between the two groups [Calof et al. 2005].
Does TRT increase PSA?
While TRT for treatment of TD may cause elevations in serum PSA in some men within safe parameters (as outlined in the Endocrine Society Guidelines), it has not been definitively shown to lead to a significantly increased risk of prostate cancer [Bhasin et al. 2010]. The Saturation Model postulates that the androgen receptors on the prostate are saturated at physiologic and even subphysiologic levels of T, such that there is minimal response of the prostatic tissue to TRT. This model also explains how castration results in dramatic regression of prostate cancer, as there is no longer an available substrate for the androgen receptors [Morgentaler and Traisch, 2008].
Does TRT increase cardiovascular risk?
To date, the literature has been conflicting, suggesting TRT has either no beneficial effect on reduction of cardiovascular morbidity or mortality, or even a detrimental effect. Two meta-analyses found no differences in cardiovascular events between TRT and placebo groups [Fernandez-Balsells et al.2010; Calof et al.2005], while a more recent meta-analysis found that TRT increased the risk of cardiovascular events, although the data seemed to vary by source of research trial funding. The authors concluded that overall, and particularly in trials not funded by the pharmaceutical industry, exogenous T increased the risk of cardiovascular-related events [Xu et al.2013]. It should be noted that trials that were not supported directly by the pharmaceutical industry [Basaria et al. 2010] commonly used T doses of 100–150 mg in older and frail men.
Is TRT safe for long term?
The estimated likelihood of adverse effects of long-term TRT is still essentially unknown, as overall high-quality evidence to recommend against its use in most men with TD is lacking. The highlighted studies addressed in this paper can be used to guide the clinician in how to best monitor patients on TRT, especially those with the comorbid conditions detailed below.
How long does testosterone affect bone?
Effects on inflammation occur within 3–12 weeks. Effects on bone are detectable already after 6 months while continuing at least for 3 years. Conclusion. The time-course of the spectrum of effects of testosterone shows considerable variation, probably related to pharmacodynamics of the testosterone preparation.
How long does it take for cholesterol to decrease?
The decrease in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol seems somewhat slower: after 3 months (35), after 40–44 weeks, (44)or after 12 months (42)with a maximum observed after 24 months (32). Studies have found both an increase and decrease in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Does testosterone increase muscle mass?
In a series of studies, Bhasin et al. (8)have demonstrated that upon testosterone administration, there is a positive correlation between blood testosterone concentrations and leg press strength, thigh, and quadriceps muscle volume, and, further, levels of hemoglobin and IGF1. In a later study, the same group of authors concluded that the anabolic response to testosterone can largely be predicted by the dose administered (9). If the dose administered is too low, no effects may be demonstrable (10). Recent studies of the effects of testosterone on muscle mass/strength are mostly short term. In a study that combined testosterone with GH, total lean body mass increased, as did appendicular lean tissue. Composite maximum voluntary strength of upper and lower body muscles had increased after 16 weeks (11). A study investigating the effect of a 12-week long-acting testosterone administration on maximal exercise capacity and muscle strength found an increase in quadriceps isometric strength, maximal voluntary contraction, and isokinetic strength (peak torque) (12). Testosterone administration for 20 weeks was associated with dose-dependent increases in skeletal muscle mass, leg strength, and power (13). In a study of 180 days of treatment with a 1% testosterone gel preparation (50 or 100 mg/day, contained in 5 or 10 g gel), mean muscle strength in the leg press exercise increased by 90 days and had not improved further at 180 days (14). A study similar in design found an increase in lean body mass and an improvement of lower limb muscle strength after 6 months (15). Another study using high doses of testosterone gel (starting dose 100 mg/day with possible up-titration to 150 mg/day) observed significant increases in leg press strength, chest press strength, and stair climbing power with a load within 6 months (16). A study administering testosterone enanthate, 200 mg/2 weeks observed major effects to occur over the first 12 months of testosterone administration, thereafter minor increases could be observed (17). It can be concluded that the effects of testosterone on muscle strength are demonstrable after 12–20 weeks and that depending on the achieved testosterone levels, the maximum effects are attained after 6 or 12 months. The data are summarized in Fig. 1.
Is testosterone deficiency related to depression?
There is now evidence that the spectrum of complaints of testosterone deficiency cannot be related to a specific threshold of testosterone concentrations, but that thresholds vary with the various symptoms of testosterone deficien cy (2). In a cohort of men, androgen-related loss of libido or vigor became more prevalent when testosterone concentrations fell below 15 nmol/l, while depression and diabetes mellitus type 2 (also in non-obese men) were significantly more present in men with testosterone concentrations below 10 nmol/l. Symptoms related to androgen deficiency in this study could be subdivided into three independent groups: psychosomatic complaints, metabolic disorders, and sexual health problems. Patients suffering from one of these three groups exhibit distinct features in terms of androgen levels, age, and body mass index. So, complaints are not only linked to androgen levels but age and body mass index carried weight as well in the manifestation of signs and symptoms of androgen deficiency (2). To further complicate the matter of the relationship between testosterone levels on the one hand and symptoms of testosterone deficiency on the other hand, there is the multifactorial impact on certain androgen-related functions (2). Erectile dysfunction may serve as an example of a composite dysfunctionality in which arterial endothelial function, neuronal integrity, testosterone concentrations, and psychological factors play pivotal roles (3, 4), almost precluding establishing a straightforward relationship between testosterone levels and erectile dysfunction. In a study only testosterone concentrations below 8 nmol/l contributed to the symptom of erectile dysfunction (2).
Does testosterone affect the male body?
Testosterone has a spectrum of effects on the male organism. This review attempts to determine, from published studies, the time-course of the effects induced by testosterone replacement therapy from their first manifestation until maximum effects are attained.
Does testosterone deficiency occur at a threshold?
Given that the clinical manifestations of testosterone deficiency do not occur at a definitive threshold value of circulating testosterone, but vary with the target organ, associated symptoms and underlying conditions, it is even more complicated to establish a time-course since a reversal of these symptoms of deficiency is not only dependent on restoring serum testosterone to normal. In fact, at least two new variables are to be entered into the model: pharmacodynamics of the testosterone preparation and pharmacogenomics of the treated subject. Indeed, if replacement therapy fails to restore idiosyncratic ‘adequate’ androgen levels, it also will fail to ‘reverse’ its clinical manifestations. The issue is that defining ‘adequate’ replacement will necessarily have a certain range of serum testosterone values.
Is testosterone good for hypogonadal men?
Treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone is rewarding, for the patients as well as the physician. The patient experiences, to his satisfaction, profound changes in his physical appearance and his mental makeup. The attending physician observes the changes the patient undergoes and rarely fails to be fascinated by the multitude of functions testosterone appears to have in the process of masculinization in the broadest sense (1).
What happens if you are allergic to testosterone?
Get emergency medical help if you have any signs of an allergic reaction to testosterone: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Why do men inject testosterone?
Testosterone injection is used in men and boys to treat conditions caused by a lack of this hormone, such as delayed puberty or growth.
Why do women get testosterone injections?
Testosterone injection is also used in women to treat certain types of breast cancer that have spread to other parts of the body.
How often is testosterone given?
Testosterone is injected into a muscle. The injection is usually given every 2 to 4 weeks.
What to do if you miss your appointment for testosterone injection?
Call your doctor for instructions if you miss an appointment for your testosterone injection.
How do you know if you have excess testosterone?
Call your doctor at once if you notice any of these signs of excess testosterone: acne; changes in menstrual periods; male-pattern hair growth (such as on the chin or chest); hoarse or deepened voice; or. enlarged clitoris. Common testosterone side effects (in men or women) may include: breast swelling;
Is testosterone safe for pregnancy?
if you are pregnant or may become pregnant. To make sure testosterone is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have: heart disease or coronary artery disease; a history of heart attack, stroke, or blood clot; diabetes; enlarged prostate; high cholesterol or triglycerides (a type of fat in the blood);
Why is the number of men taking testosterone dropping?
The number of men who take testosterone has dropped dramatically in the past few years, in part because of growing awareness of the risks that may accompany it. Should you avoid it?
How much testosterone does a man lose in a year?
Beginning in their mid-30s, men lose testosterone at an average of just under 2% per year. Testosterone replacement treatment (TRT)aims to boost those low levels.
Does TRT improve symptoms linked to low testosterone?
And there are other concerns. Does TRT improve symptoms linked to low testosterone? In January of this year, the American College of Physicians released new practice guidelines that outlined the limited benefits men are likely to get from TRT. The doctors’ group found that TRT offered slight improvements to sexual and erectile function; they found no other benefits.
Is testosterone safe for aging?
FDA: “FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions about using testosterone products for low testosterone due to aging; requires labeling change to inform of possible increased risk of heart attack and stroke with use.”
Does physical activity increase testosterone?
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition: “Increased physical activity has a greater effect than reduced energy intake on lifestyle modification-induced increases in testosterone.”
Can low libido cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes. Low libido and erectile dysfunction, for example, have many contributing factors to rule out, including heart disease and psychological issues.
Does TRT cause heart attacks?
In 2014, the FDA ordered that a warning label must accompany TRT prescriptions, alerting men to the possibility that TRT increases the chances of heart attack and stroke . More recently, a study linked TRT to higher chances of venous thromboembolism, a potentially fatal type of blood clot. And there are other concerns.
Function
Risks
Symptoms
Reproduction
Effects
Causes
Mechanism
Behavior
Biology
Side effects
- A man with shrinking levels of testosterone actually may lose some body hair. Testosterone replacement therapy comes with a few potential side effects, including acne and breast enlargement. Testosterone patches may cause minor skin irritation. Topical gels may be easier to use, but great care must be taken to avoid transferring testosterone to som...
Health
Diagnosis
in Summary
- More frequently reported side effects include:deep vein thrombosis. See below for a comprehensive list of adverse effects.
For The Consumer
For Healthcare Professionals
Frequently Asked Questions
Further Information