What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the different water treatment processes?
Water treatment processesCoagulation/flocculation. During coagulation, liquid aluminium sulfate (alum) and/or polymer is added to untreated water (raw water). ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.
What are the 4 stages of water treatment in order?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is the first stage of water treatment?
Coagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. During coagulation, chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water.
What is the second stage of water treatment?
Secondary Treatment The secondary stage of treatment removes about 85 percent of the organic matter in sewage by making use of the bacteria in it. The principal secondary treatment techniques used in secondary treatment are the trickling filter and the activated sludge process.
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What are different methods of domestic water treatment?
There are several methods used in the water purification process, which include: (1) physical processes, such as filtration, sedimentation, or distillation; (2) biological processes, such as sand filters, active carbon; (3) chemical processes, such as flocculation, chlorination, the use of ultraviolet light.
How many types of water treatments are there?
There are four common types of household water treatment systems, and they are: Filtration System: This is a water filter device that will remove impurities by means of a physical barrier, chemical, or a biological process.Jul 6, 2017
What is fourth step of raw water treatment?
In the fourth step called ozonation, plant workers add a gas called ozone to destroy bacteria and other microorganisms as well as to improve taste. From there, the water is filtered using granular activated carbon to remove any fine particles.
What are stages of water?
There are four main stages in the water cycle. They are evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection. Let's look at each of these stages. Evaporation: This is when warmth from the sun causes water from oceans, lakes, streams, ice and soils to rise into the air and turn into water vapour (gas).
What is water treatment?
Water treatment is the process of removing all those substances, whether biological, chemical, or physical, that are potentially harmful to the water supply for human and domestic use. This treatment helps to produce water that is safe, palatable, clear, colorless, and odorless. Water also needs to be non-corrosive, meaning it will not cause damage to pipework.
How does aerated water work?
After screening, the water is aerated (supplied with air) by passing it over a series of steps to take in oxygen from the air. This process helps in expelling soluble gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide (both of which are acidic, so this process makes the water less corrosive) and expels any gas eous organic compounds an undesirable taste to the water. Aeration also removes iron or manganese by oxidation of these substances to their insoluble form. Iron and manganese can cause peculiar tastes and can stain clothing. Once in their insoluble forms, these substances can be removed by filtration.
What happens after aeration?
After aeration, coagulation occurs to remove the fine particles (less than 1 µm in size) suspended in the water . In this process, a chemical called a coagulant (with a positive electrical charge) is added to the water, which neutralizes the fine particles' negative electrical charge. The coagulant's addition takes place in a rapid mix tank where a high-speed impeller rapidly disperses the coagulant.
What is the process of separating solids from liquids?
Filtration is the process where solids are separated from a liquid. In water treatment, the solids that are not separated in the sedimentation tank are removed by passing the water through sand and gravel beds. With a flow rate of 4–8 cubic meters per square meter of filter surface per hour, rapid gravity filters are often used.
Is fluoride needed for dental decay?
Supplementary treatment may be needed for the benefit of the population . One such instance is the fluoridation of water, where fluoride is added to water. It has been stated by the World Health Organization that ‘fluoridation of water supplies, where possible, is the most effective public health measure for the prevention of dental decay. The optimum fluoride level is around 1 mg per liter of water (1 mg l –1 ).
What are the stages of wastewater treatment?
What Are the Three Stages of Wastewater Treatment? There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What is tertiary treatment?
In the case of water treated by municipalities, tertiary treatment also involves the removal of pathogens, which ensures that water is safe for drinking purposes.
Where is wastewater held?
During primary treatment, wastewater is temporarily held in a settling tank where heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids float to the surface. Once settled, these materials are held back while the remaining liquid is discharged or moved through to the more rigorous secondary phase of wastewater treatment.
How long does aeration last?
Aeration is a lengthy process which increases oxygen saturation by introducing air to wastewater. Typically, the aeration process can last for up to 30 hours, but it is very effective. 3.
What is treated wastewater?
Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow .#N#As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.#N#The water that flows from the secondary clarifier has substantially reduced organic material and should be approaching expected effluent specifications.
What is the process of removing large items from the influent?
Removal of large items from the influent to prevent damage to the facility’s pumps, valves and other equipment .#N#The process of treating and reclaiming water from wastewater (any water that has been used in homes, such as flushing toilets, washing dishes, or bathing, and some water from industrial use and storm sewers) starts with the expectation that after it is treated it will be clean enough to reenter the environment.#N#The quality of the water is dictated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Clean Water Act, and wastewater facilities operate to specified permits by National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES). According to the EPA, The Clean Water Act (CWA) establishes the basic structure for regulating discharges of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulating quality standards for surface waters. Under the CWA, EPA sets wastewater standards for industry. The EPA has also developed national water quality criteria recommendations for pollutants in surface waters. EPA's National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program controls discharges.#N#As an example of expected standards, the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of average wastewater effluent is 200 mg/L and the effluent after treatment is expected to be >30 mg/L. It is crucial a wastewater facility meets these expectations or risk stiff penalty.#N#The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill.
What is a bar screen in wastewater treatment?
A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from ...
What is activated sludge?
These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.
Why is chlorine added to water?
Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria in the contact chamber. With the enhanced concentration of bacteria as part of the aeration stage, there is a need to test the outgoing effluent for bacteria presence or absence and to disinfect the water.
What is the process of disinfecting water?
Chlorine or other disinfecting chemicals kill any remaining microorganisms or bacteria in the water and help keep the water clean until distribution. If a water treatment facility uses ground water as its only water source, disinfection may be the only step required to sufficiently treat the water. After it is disinfected, the purified water sits in the closed tank or reservoir until it flows through pipes to homes and businesses.
Why is water purification important?
Water purification plays a key role in ensuring access to safe drinking water. Safe drinking water positively impacts the health of the entire community. Systems are in place to ensure ongoing water quality, including water quality testing. The testing helps ensure the water treatment process results in a product that meets federal water quality ...
What is the purpose of a water screen?
When the water source is a lake or river, the screen serves an important function, keeping out large natural contaminants such as plants and wood, or fish.
How deep is the gravel layer in the ocean?
Water passes through layers of gravel, sand and perhaps charcoal, which serve to filter out any remaining particles. The gravel layer is often about 1 foot deep and the sand layer about 2½ feet deep.
What causes floc to form in water?
Treatment plant workers add alum and other chemicals to the water, which cause tiny sticky particles, or floc, to form. These floc attract dirt particles, making them eventually heavy enough to sink to the bottom of the water storage tank.
Who is Ann Wolters?
Ann Wolters has been a writer, consultant and writing coach since 2008. Her work has appeared in "The Saint Paul Almanac" and in magazines such as "Inventing Tomorrow" and "Frontiers." She earned a Master of Arts in English as a second language from the University of Minnesota.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
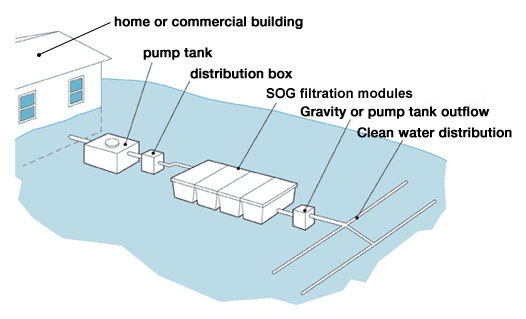
Household Water Treatment
- Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1. Remove specific contaminants 2. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3. Improve the taste of drinking water Household water treatment systems are composed of two categories: point-of-us…
The 6 Steps of Wastewater Treatment
- When we talk about wastewater treatment, it is inevitable that the first thing that comes to mind is the wastewater treatment plant. These plants treat the water before discharging it back into the natural cycle. Wastewater from populated areas is transported to the treatment plant via the sewage system. Here are the 6 stages of wastewater treatment.
Screening
- Screening removes coarse waste such as wipes, rags, plastic or wood from the water. These wastes cannot degrade naturally over time, so they must be removed mechanically instead of being treated biologically or chemically. This is why JC France manufactures and supplies bar screensall over the world. Most of these machines are equipped with automatic cleaning syste…
Sand and Oil Removal
- The elimination of sediments is done by decantation, while greases are eliminated with the help of micro bubbles which help them to rise to the surface and to be evacuated by a scraping bridge. The collection of this waste is subject to a reprocessing and a revalorization of organic or sedimentary matter.
Biological Treatment
- This is the essential step of wastewater treatment which consists in reproducing the natural processes that exist in rivers. To accelerate this process, bacteria are used to digest impurities and transform them into sludge. Aerobic techniques, such as those of the active sanitation system (with oxygen), are the most widespread in France today, but anaerobic methods also hav…
Clarification
- The clarifier is a tank that separates the water from the sludge or secondary residues, resulting from the degradation of the organic matter. The impurities contained in this liquid are then controlled before being released into our natural environment. An analysis of the water is then carried out to control the respect of the discharge standards.
Tertiary Filtration
- As the discharge parameters can vary and not reach the standards, the interest of a filtration by drum filter is often necessary in order to further reduce the suspended matters as well as the BOD and COD but also the nitrates and phosphates associated with these floating particles. JC France Industrie manufactures and markets this type of filtration with a mesh size of up to 20 microns …
Sludge Treatment
- The secondary sludge is formed from the pollutant load dissolved during the periods of sand removal and oil recovery (recovered after the secondary treatment). Mixed” sludge is formed by combining primary or secondary treated wastewater with untreated raw sewage in an activated sludge process. This sludge is biologically stabilized before being composted for use on farms. …
Screening
Aeration
- After screening, the water is aerated (supplied with air) by passing it over a series of steps to take in oxygen from the air. This process helps in expelling soluble gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide (both of which are acidic, so this process makes the water less corrosive) and expels any gaseous organic compounds an undesirable taste to the water. Aeration also remove…
Coagulation and Flocculation
- After aeration, coagulation occurs to remove the fine particles (less than 1 µm in size) suspended in the water. In this process, a chemical called a coagulant (with a positive electrical charge) is added to the water, which neutralizes the fine particles' negative electrical charge. The coagulant's addition takes place in a rapid mix tank where a high-speed impeller rapidly disperses the coagul…
Sedimentation
- Once large flocs are formed, they need to be settled out, and this takes place in a process called sedimentation (when the particles fall to the floor of a settling tank). The water (after coagulation and flocculation) is kept in the tank for several hours for sedimentation to take place. The material accumulated at the bottom of the tank is called sludge; this is removed for disposal.
Filtration
- Filtration is the process where solids are separated from a liquid. In water treatment, the solids that are not separated in the sedimentation tank are removed by passing the water through sand and gravel beds. With a flow rate of 4–8 cubic meters per square meter of filter surface per hour, rapid gravity filters are often used. When the filters are full of trapped solids, they are back-wash…
Chlorination
- After sedimentation, the water is disinfected to eliminate any remaining pathogenic micro-organisms. The most commonly used disinfectant (the chemical used for disinfection) is chlorine, a liquid (such as sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl), or a gas. It is relatively cheap and simple to use. When chlorine is added to water, it reacts with any pollutants present, including micro-organism…
Supplementary Treatment
- Supplementary treatment may be needed for the benefit of the population. One such instance is the fluoridation of water, where fluoride is added to water. It has been stated by the World Health Organization that ‘fluoridation of water supplies, where possible, is the most effective public health measure for the prevention of dental decay. The optimum fluoride level is around 1 mg pe…