...
The ANOVA Procedure.
How do you find the error degrees of freedom?
Because n = 15, there are n −1 = 15−1 = 14 total degrees of freedom. Because m = 3, there are m −1 = 3−1 = 2 degrees of freedom associated with the factor. The degrees of freedom add up, so we can get the error degrees of freedom by subtracting the degrees of freedom associated with the factor from the total degrees of freedom.
How do you calculate degrees of freedom for lack of fit?
This can also be defined as the number of degrees-of-freedom for the replicate error. The remaining degrees-of-freedom for lack-of-fit error now become D = N − P − R. Any statistical design can be analysed for different sources of error or variability.
What is a degree of freedom (df)?
Degrees of freedom (df) refers to the number of independent values (variable) in a data sample used to find the missing piece of information (fixed) without violating any constraints imposed in a dynamic system. These nominal values have the freedom to vary, making it easier for users to find the unknown or missing value in a dataset.
What are the degrees of freedom for a 1 sample t test?
Consequently, for a 1-sample t test, the degrees of freedom equals n – 1. The DF define the shape of the t-distribution that your t-test uses to calculate the p-value. The graph below shows the t-distribution for several different degrees of freedom.

What is the degree of freedom for error?
The degrees of freedom add up, so we can get the error degrees of freedom by subtracting the degrees of freedom associated with the factor from the total degrees of freedom. That is, the error degrees of freedom is 14−2 = 12.
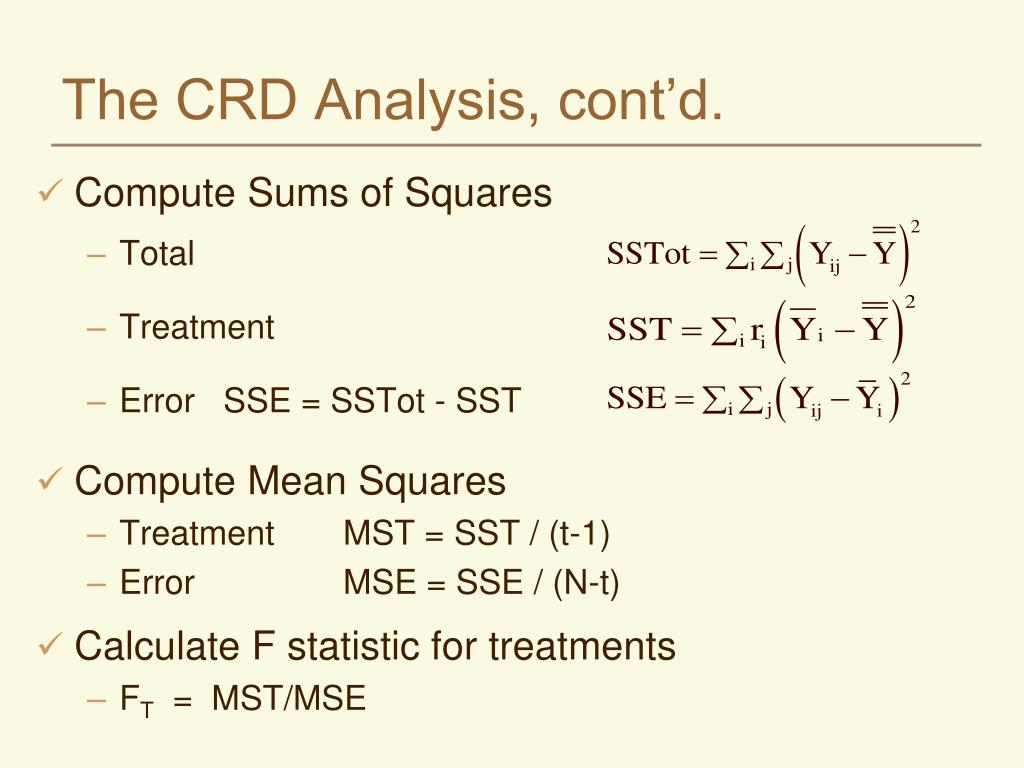
What are the degrees of freedom for the treatment and error sources of variation?
The ANOVA ProcedureSource of VariationSums of Squares (SS)Degrees of Freedom (df)Between Treatmenst75.84-1=3Error (or Residual)47.420-4=16Total123.220-1=19
How do you find degrees of freedom in treatment?
3:246:05Degrees of Freedom in One Factor ANOVA (Module 2 2 7) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo every time we estimate a population parameter. We lose a degree of freedom a final way toMoreSo every time we estimate a population parameter. We lose a degree of freedom a final way to calculate degrees of freedom for air is taking the total number of observations. We have minus the degrees
What is degree of freedom total?
Degrees of freedom refers to the maximum number of logically independent values, which are values that have the freedom to vary, in the data sample. Degrees of freedom are commonly discussed in relation to various forms of hypothesis testing in statistics, such as a chi-square.
What is degree freedom formula?
The most commonly encountered equation to determine degrees of freedom in statistics is df = N-1. Use this number to look up the critical values for an equation using a critical value table, which in turn determines the statistical significance of the results.
What are the degrees of freedom for the denominator df error?
The denominator degrees of freedom is the bottom portion of the F distribution ratio and is often called the degrees of freedom error. You can calculate the denominator degrees of freedom by subtracting the number of sample groups from the total number of samples tested.
Why is the degree of freedom n 1?
In the data processing, freedom degree is the number of independent data, but always, there is one dependent data which can obtain from other data. So , freedom degree=n-1.
What is the value of DF?
df = N₁ + N₂ - 2 , where: N₁ - Number of values from the first sample; and. N₂ - Number of values from the second sample.
What is degree of freedom with examples?
Example – Degrees of freedom for calculating mean To calculate the mean of the sample data, the degrees of freedom is equal to count of the data in the sample that are free to vary. For example, in the example given below, the degrees of freedom is 5. This means that all 5 data is equally independent to vary.
Understanding Degrees Of Freedom
Degrees of freedom first appeared in the works of German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss in early 1821. However, English statistician William Sealy Gosse first defined it in his paper “The Probable Error of a Mean,” published in Biometrika in 1908.
Degree of Freedom Formula & Calculations
As exemplified in the above section, the df can result by finding out the difference between the sample size and 1.
Example
Let us move ahead with the abovementioned example to find out the df. The set of observations obtained by the medical center is as follows:
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Degrees of Freedom and its definition. Here we discuss the formula to calculate degrees of freedom along with examples. You can learn more from the following articles –
What is degree of freedom?
Degrees of freedom encompasses the notion that the amount of independent information you have limits the number of parameters that you can estimate. Typically, the degrees of freedom equal your samplesize minus the number of parameters you need to calculate during an analysis. It is usually a positive whole number.
What does DF mean in statistics?
In statistics, the degrees of freedom (DF) indicate the number of independent values that can vary in an analysis without breaking any constraints. It is an essential idea that appears in many contexts throughout statistics including hypothesis tests, probability distributions, and regression analysis. Learn how this fundamental concept affects the ...
TWO MODELS
Consider a very simple experiment of two observations, where a y variable (which may be peak heights in the presence of a baseline or constant interferent) is measured as an x variable is varied (eg, concentrations).
RESIDUAL ERRORS
Using each model, we can estimate the values of y from x or . These estimates are presented in Table 1 .
DEGREES-OF-FREEDOM
For both models, we have performed the same experiment and used the same observations.
ADDITIONAL TERMS
Models do not need to be restricted to linear terms, for example, a series of 3 observations can be used to obtain a linear model with no intercept with D = 2 degrees-of-freedom for lack-of-fit, a linear model with an intercept with D = 1, or a model including intercept, linear, and quadratic terms with D = 0.
REPLICATES
However, the measurement of residuals alone does not always tell us enough to be able to decide whether any model is significant. Imagine being told that the error in modelling a process is 0.1 AU (its response may be measured spectroscopically). On its own, this probably does not convey much, and it is a good idea to compare this to a yardstick.
SOURCES OF ERROR
Any statistical design can be analysed for different sources of error or variability.
DEGREES-OF-FREEDOM TREE
Sometimes, the degrees-of-freedom can be represented by a “degrees-of-freedom tree.” In our case, it is represented in Figure 2 and is a good way of summarising a design. Sometimes, degrees-of-freedom trees can be more elaborate, for example, if errors are viewed as coming from different sources.
What does error mean in statistics?
Error means "the variability within the groups" or "unexplained random error.". Sometimes, the row heading is labeled as Within to make it clear that the row concerns the variation within the groups. Total means "the total variation in the data from the grand mean" (that is, ignoring the factor of interest).
What does DF mean in learning?
In the learning study, the factor is the learning method. DF means "the degrees of freedom in the source.". SS means "the sum of squares due to the source.". MS means "the mean sum of squares due to the source.".
What does error mean in statistics?
Error means "the variability within the groups" or "unexplained random error.". Sometimes, the row heading is labeled as Within to make it clear that the row concerns the variation within the groups. Total means "the total variation in the data from the grand mean" (that is, ignoring the factor of interest).
What does DF mean in learning?
In the learning study, the factor is the learning method. DF means "the degrees of freedom in the source.". SS means "the sum of squares due to the source.". MS means "the mean sum of squares due to the source.". F means "the F -statistic.".

What Are Degrees of Freedom?
Degrees of Freedom Definition
- What are degrees of freedom in statistics? Degrees of freedom are the number of independent values that a statistical analysis can estimate. You can also think of it as the number of values that are free to vary as you estimate parameters. I know, it’s starting to sound a bit murky! DF encompasses the notion that the amount of independent information you have limits the numbe…
Independent Information and Constraints on Values
- The degrees of freedom definitions talk about independent information. You might think this refers to the sample size, but it’s a little more complicated than that. To understand why, we need to talk about the freedom to vary. The best way to illustrate this concept is with an example. Suppose we collect the random sample of observations shown below. Now, imagine we know th…
How to Find The Degrees of Freedom in Statistics
- As you can see, that last number has no freedom to vary. It is not an independent piece of information because it cannot be any other value. Estimating the parameter, the mean in this case, imposes a constraint on the freedom to vary. The last value and the mean are entirely dependent on each other. Consequently, after estimating the mean, we have only 9 independent …
Degrees of Freedom Formula
- The degrees of freedom formula is straightforward. Calculating the degrees of freedom is often the sample size minus the number of parameters you’re estimating: DF = N – P Where: 1. N = sample size 2. P = the number of parameters or relationships For example, the degrees of freedom formula for a 1-sample t test equals N – 1 because you’re estimating one parameter, th…
Df and Probability Distributions
- Degrees of freedom also define the probability distributions for the test statistics of various hypothesis tests. For example, hypothesis tests use the t-distribution, F-distribution, and the chi-square distribution to determine statistical significance. Each of these probability distributions is a family of distributions where the DF define the shape. Hypothesis tests use these distribution…
Degrees of Freedom For T Tests
- T tests are hypothesis tests for the mean and use the t-distribution to determine statistical significance. A 1-sample t test determines whether the difference between the sample mean and the null hypothesis value is statistically significant. Let’s go back to our example of the mean above. We know that when you have a sample and estimate the mean, you have n – 1 degrees o…
Degrees of Freedom Table
- You’ll often find degrees of freedom in statistical tables along with their critical values. Statisticians use the DF in these tables to determine whether the test statisticfor their hypothesis test falls in the critical region, indicating statistical significance. For example, in a t-table, you’ll find the degrees of freedom in the first column of the table. You must know the degrees of freed…
How to Find Degrees of Freedom For Tables in Chi-Square Tests
- The chi-square test of independence determines whether there is a statistically significant relationship between categorical variablesin a table. Just like other hypothesis tests, this test incorporates DF. To find the chi-square DF for a table with r rows and c columns, use this formula to calculate degrees of freedom: (r-1) (c-1). However, we can create tables to understand how t…
Linear Regression Degrees of Freedom
- Calculating degrees of freedom in linear regression is a bit more complicated, and I’ll keep it on the simple side. In a linear regression model, each term is an estimated parameter that uses one degree of freedom. In the regression output below, you can see how each linear regression term requires a DF. There are n = 29 observations, and the two independent variables use a total of tw…