
– Thus, there are always two possible explanations for the difference (or variance) that exists between treatments: • 1. Systematic Differences Caused by the Treatments • 2. Random, Unsystematic Differences – Two primary sources are usually id ifi d f h di blidentified for these unpredictable differences.
Full Answer
What is the within treatment variance?
-The differences represent random and unsystematic differences that occur when there are no treatment effects. -Thus, the within-treatments variance provides a measure of how big the differences are when H0 is true. The Logic and Process of Analysis of Variance(Cont'd)
What are variance components?
These contributions are called variance components. A company supplies a customer with a larger number of batches of raw materials. The customer makes three sample determinations from each of five randomly selected batches to control the quality of the incoming material.
Why do we compute between-treatments variance?
-Thus, when we compute the between-treatments variance, we are measuring differences that could be caused by a systematic treatment effect or could simply be random and unsystematic mean differences caused by sampling error. Within Treatments Variance Inside each treatment condition, we have a set of individuals who receive the same treatment.
What is factor in variance analysis?
• In the context of analysis of variance, an independent variable or a quasi- independent variable is called a factor. • Th i di id l di i l h The individual conditions or values that make up a factor are called the levels of the factor.
What is the variable that designates the groups being compared called?
What is the table called that organizes the results of the analysis?
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
Why do we need a notational system for ANOVA?
What is the final calculation for ANOVA?
What is the cut off value of a distribution?
Can differences in a sample be caused by different treatments?
See more
About this website
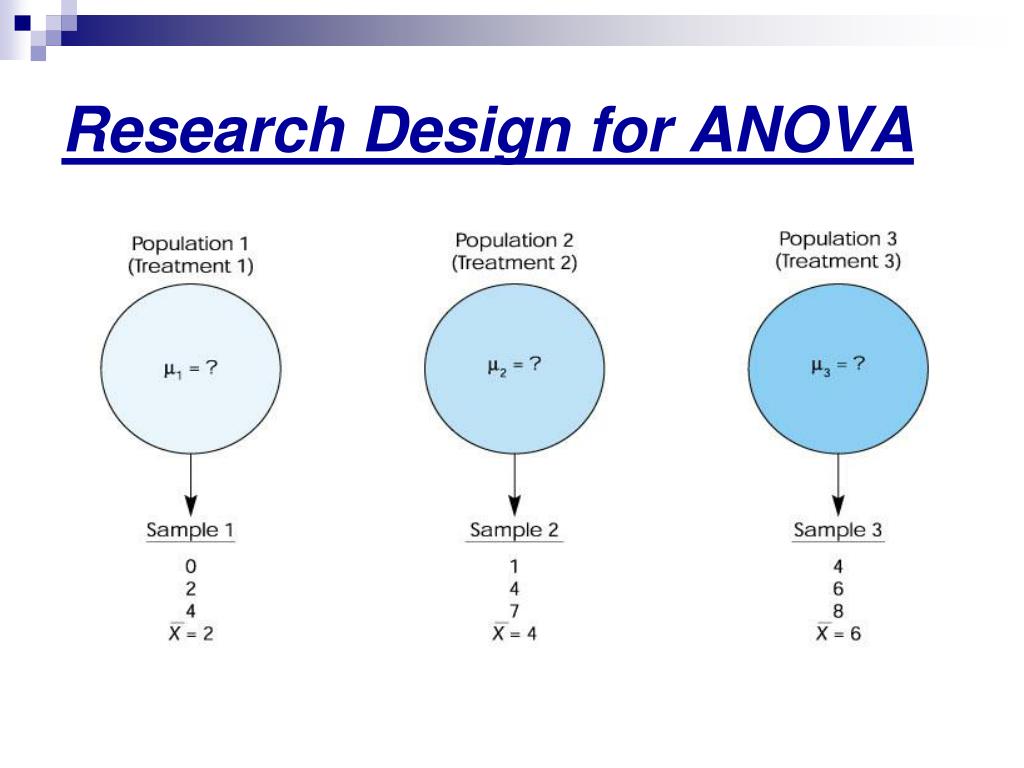
What contributes to between treatment variance?
– When you see the term variance, you can automatically translate it into the term differences. – Thus, the between-treatments variance simply measures how much difference exists between the di i treatment conditions. the differences have been caused by the treatment effects.
What are the components of variance?
Components of Variance (ANOVA)Source: source of variation.Var. Component: variance of the source of variation. ... % of Total: % of total variance due to the source of variation.Sqrt of Var: square root of the variance of the source of variation.EMS: the expected mean square.
What is treatment variance?
The treatment variance is based on the deviations of treatment means from the grand mean, the result being multiplied by the number of observations in each treatment to account for the difference between the variance of observations and the variance of means.
What does within-treatment variance measure?
Within-Treatment Variability: In addition to the between-treatments variability, there is variability within each treatment. The within treatments variability will provide a measure of the variability inside each treatment condition.
What do variance components tell us?
Variance components analysis would reveal if the between-stations random effect accounted for an important or a trivial amount of the variance in time-to-promotion, based on a model which included random-effects variables, fixed-effects variables, covariates, and interactions among them.
What are components in statistics?
Component analysis is the analysis of two or more independent variables which comprise a treatment modality. It is also known as a dismantling study. The chief purpose of the component analysis is to identify the component which is efficacious in changing behavior, if a singular component exists.
How do you calculate DF between treatments?
The between treatment degrees of freedom is df1 = k-1. The error degrees of freedom is df2 = N - k....The ANOVA Procedure= sample mean of the jth treatment (or group),= overall sample mean,k = the number of treatments or independent comparison groups, and.N = total number of observations or total sample size.
What are the two types of variance which can occur in your data?
'The two types of variance that can occur in our data are Independent and dependent One-way ANOVA and Two-way Anova Between and within groups MSTR and MSE Answer' We don't have your requested question, but here is a suggested video that might help.
How do you get the variance?
Steps for calculating the varianceStep 1: Find the mean. To find the mean, add up all the scores, then divide them by the number of scores. ... Step 2: Find each score's deviation from the mean. ... Step 3: Square each deviation from the mean. ... Step 4: Find the sum of squares. ... Step 5: Divide the sum of squares by n – 1 or N.
How do you calculate between and within variance?
Subtract each of the scores from the mean of the entire sample. Square each of those deviations. Add those up for each group, then add the two groups together. This is just like computing the variance.
What is between variance?
In layman's terms, the within variance is the variance within each dataset on the parameters being estimated, whereas the between variance is the variance across datasets in those parameters.
What is the difference between within group variance and between group variance?
Between Group Variation: The total variation between each group mean and the overall mean. Within-Group Variation: The total variation in the individual values in each group and their group mean.
Week 12 Practice quiz for exam #4 + exam #4 Flashcards | Quizlet
Start studying Week 12 Practice quiz for exam #4 + exam #4. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Chapter 12- ANOVA Flashcards | Quizlet
Start studying Chapter 12- ANOVA. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Solved The following data represent the means for each | Chegg.com
Math; Statistics and Probability; Statistics and Probability questions and answers; The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.
Definitions
Call the number of different treatments. For each of the treatments, let there be different measurements. There are then total measurements, where . We will label our input and output measurements with and , where is the kth measurement from the i th treatment. We will call the mean of the measurements at a single input setting , where
Underlying Assumptions
As mentioned above, with an analysis of variance for a single input, we assume that the measurements can be described using this simple model:
Graphs to Assess the Validity of the Assumptions
Several diagnostic graphs should be created to assess the data and determine if the assumptions are reasonable. If there are systematic patterns in the residuals, then it may be necessary to modify the model before proceeding.
Analysis Table
We will use the variance ratio, , to evaluate whether the variation between treatments is significantly larger than the variation within treatments.
Example Analyses
Two experiments will be analyzed, one in which the ANOVA indicates that the null hypothesis may be rejected, and one in which it does not. The first example involves three treatments with five measurements per treatment.
Example
The following example involves four treatments, one of which is a control. There are six measurements for each treatment level.
Example
The exposure time is varied for a UV-cured adhesive, and the resulting bond strength is evaluated. The control is the manufacturer's recommended setting of 15 seconds. Treatments A, B, and C are exposed to the UV source for 5 sec, 30 sec, and 90 sec, respectively.
What is the variable that designates the groups being compared called?
In analysis of variance, the variable (independent or quasi-independent) that designates the groups being compared is called a factor.
What is the table called that organizes the results of the analysis?
It is useful to organize the results of the analysis in one table called an ANOVA summary table.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a hypothesis-testing procedure that is used to evaluate mean differences between two or more treatments (or populations).#N#-As with all inferential procedures, ANOVA uses sample data as the basis for drawing general conclusions about populations.#N#-The major advantage of ANOVA is that it can be used to compare two or more treatments.
Why do we need a notational system for ANOVA?
Because ANOVA typically is used to examine data from more than two treatment conditions (and more than two samples), we need a notational system to keep track of all the individual scores and totals.
What is the final calculation for ANOVA?
The final calculation for ANOVA is the F-ratio, which is composed of two variances:
What is the cut off value of a distribution?
The distribution is cut off at zero (all positive values), piles up around 1.00, and then tapers off to the right.
Can differences in a sample be caused by different treatments?
Because all the individuals in a sample receive exactly the same treatment, any differences (or variance) within a sample cannot be caused by different treatments.
What is the variable that designates the groups being compared called?
In analysis of variance, the variable (independent or quasi-independent) that designates the groups being compared is called a factor.
What is the table called that organizes the results of the analysis?
It is useful to organize the results of the analysis in one table called an ANOVA summary table.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a hypothesis-testing procedure that is used to evaluate mean differences between two or more treatments (or populations).#N#-As with all inferential procedures, ANOVA uses sample data as the basis for drawing general conclusions about populations.#N#-The major advantage of ANOVA is that it can be used to compare two or more treatments.
Why do we need a notational system for ANOVA?
Because ANOVA typically is used to examine data from more than two treatment conditions (and more than two samples), we need a notational system to keep track of all the individual scores and totals.
What is the final calculation for ANOVA?
The final calculation for ANOVA is the F-ratio, which is composed of two variances:
What is the cut off value of a distribution?
The distribution is cut off at zero (all positive values), piles up around 1.00, and then tapers off to the right.
Can differences in a sample be caused by different treatments?
Because all the individuals in a sample receive exactly the same treatment, any differences (or variance) within a sample cannot be caused by different treatments.

Definitions
Underlying Assumptions
- As mentioned above, with an analysis of variance for a single input, we assume that the measurements can be described using this simple model: where is the kth measurement from the ith treatment as before, is the mean for the ith treatment, and is the experimental error for the kth measurement from the ithtreatment. The literature sometimes separates the treatement means…
Graphs to Assess The Validity of The Assumptions
- Several diagnostic graphs should be created to assess the data and determine if the assumptions are reasonable. If there are systematic patterns in the residuals, then it may be necessary to modify the model before proceeding. A box and whisker plot of the data for each treament should be used to check for outliers. A histogram, dot diagram, or stem-and-leaf chart should be create…
Analysis Table
- We will use the variance ratio, , to evaluate whether the variation between treatments is significantly larger than the variation within treatments. This is the same analysis we conducted when investigating inferences for the variance, but now the result of the test indicates whether we can reject our null hypothesis that the treatments have no eff...
Example Analyses
- Two experiments will be analyzed, one in which the ANOVA indicates that the null hypothesis may be rejected, and one in which it does not. The first example involves three treatments with five measurements per treatment. The following example involves four treatments, one of which is a control. There are six measurements for each treatment level. Our analysis for the example abov…
Anova in Excel
- The Analysis Toolpak in Microsoft Excel includes an automated ANOVA solver. To install the add-in, open the Add-In popup in Excel, and select Excel Analysis ToolPak. This should create a [Data Analysis] button on the Data section of the header. The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA: Single-Factor)is the first option of all the available analyses. An example of the output of the Exc…