
- medicines called anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs)
- surgery to remove a small part of the brain that's causing the seizures.
- a procedure to put a small electrical device inside the body that can help control seizures.
- a special diet (ketogenic diet) that can help control seizures.
Common Causes
Top 10 Tips On How To Treat Epilepsy Naturally
- Epsom Salt And Water Or Orange Juice. Many studies proved that Epsom salt is beneficial in easing seizures in patients with epilepsy. ...
- Garlic, Milk, And Water. The combination of garlic, milk and water is also an effective way on how to treat epilepsy. ...
- Winter Melon. ...
- Yoga. ...
- Acupuncture. ...
- Take Essential Vitamins. ...
- Do Exercise. ...
- Passionflower. ...
Related Conditions
- Calming brain protein is low in autism, leading to epilepsy
- No brakes on overactive brain because of mutation
- 30-50% of children with autism also have epilepsy
How to cure seizures naturally?
- First, ensure adequate ventilation and place patients on the floor on their left side
- Loosen clothing around the neck and ensure the airway is patent. ...
- Remove all items from the surrounding that can be hazardous. ...
- If the patient is confused and wandering, either gently guide him/her away and block access to outside areas
How do you cure seizures?
Treating seizures without medication is quite a controversial topic. This is because the causes of seizures may be different for different people and thus the treatment procedure may vary accordingly. For few people, medication work wonders while others may not even respond to medicated drugs.
What are the precautions for seizures?
Can you control seizures without medication?
What are the treatments for seizures?
The optimal goal in seizure treatment is to find the best possible therapy to stop seizures, with the fewest side effects.Medication. ... Dietary therapy. ... Surgery. ... Electrical stimulation. ... Pregnancy and seizures. ... Contraception and anti-seizure medications. ... Personal safety. ... Seizure first aid.More items...
What is the best medication to treat seizures?
Many medications are used in the treatment of epilepsy and seizures, including:Carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Tegretol, others)Phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek)Valproic acid (Depakene)Oxcarbazepine (Oxtellar, Trileptal)Lamotrigine (Lamictal)Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin)Topiramate (Topamax)Phenobarbital.More items...•
What is the first line treatment for seizure?
For generalised tonic-clonic seizures, sodium valproate is recommended as first-line treatment. If this is unsuitable, lamotrigine is recommended. Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine can be considered as alternatives.
What is the emergency treatment for seizures?
The two emergency medications used to prevent status in the community (outside of the hospital setting) are midazolam and diazepam: Buccal (oromucosal) midazolam – is given into the buccal cavity (the side of the mouth between the cheek and the gum). Rectal diazepam – is given rectally (into the bottom).
What is the most common seizure medication?
Below are 10 of the most common.Levetiracetam (Keppra, Spritam) ... Phenytoin (Dilantin) ... Zonisamide (Zonegran) ... Carbamazepine (Tegretol) ... Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) ... Valproic acid derivatives. ... Topiramate (Topamax) ... Phenobarbital. Phenobarbital is a barbiturate that can treat focal onset and generalized seizures.More items...•
What are 4 drugs to treat epilepsy?
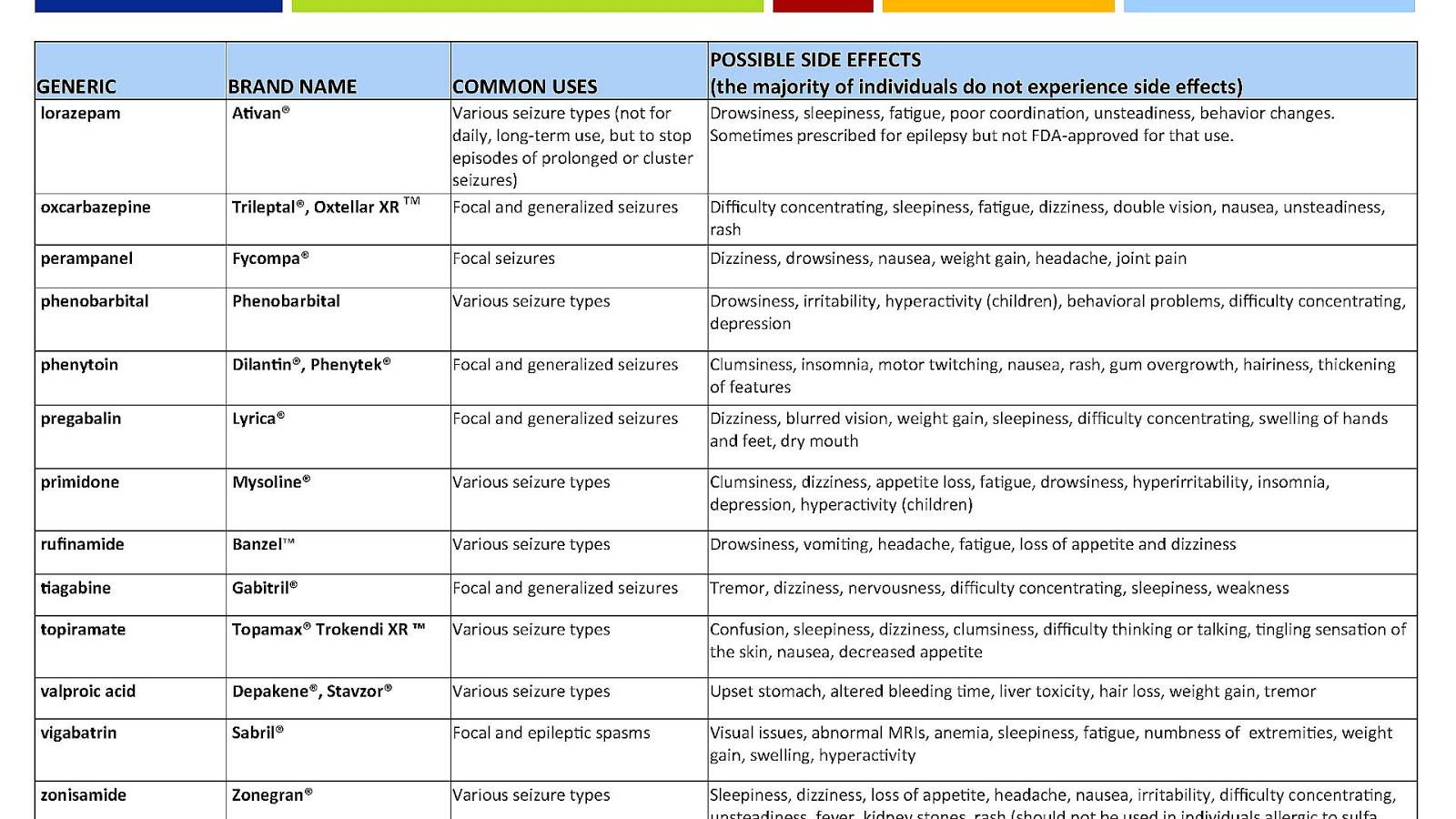
Medicines used to treat epilepsy Carbamazepine, clobazam, clonazepam, eslicarbazepine, ethosuximide, gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, pregabalin, primidone, rufinamide, sodium valproate, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin and zonisamide.
How do hospitals deal with seizures?
cushion their head if they're on the ground. loosen any tight clothing around their neck, such as a collar or tie, to aid breathing. turn them on to their side after their convulsions stop – read more about the recovery position. stay with them and talk to them calmly until they recover.
What is an epileptic seizure?
An epileptic seizure is an excessive, uncontrolled burst of electrical activity from nerve cells in the brain – essentially an electrical storm. There are many types of seizures that cause symptoms ranging from lightning-fast muscle jerks lasting less than a second ...
How long does a seizure last?
There are many types of seizures that cause symptoms ranging from lightning-fast muscle jerks lasting less than a second to full body convulsions lasting two or three minutes. Epilepsy, if not well-controlled, can greatly worsen a person’s quality of life and can cause severe injury or death.
What is epilepsy MRI?
Epilepsy is a neurologic disorder that causes unexpected and recurrent epileptic seizures. The diagnosis involves conducting a careful neurological history, a 30-minute brain wave study (electroencephalogram or EEG), and imaging of the brain (magnetic resonance imaging or MRI).
Where is the epilepsy focus located?
This is called intracranial EEG. The most common location in the brain for epilepsy surgery is the temporal lobe. About 60 percent to 80 percent of patients become seizure-free with this type of surgery.
How many treatments are there for a neurologist?
The medical community continually tests and approves new treatments. Here are 10 treatments, both basic and advanced, that I’ve tried to rank from least to most risk. However, almost all treatments involve some degree of risk. Discuss your options carefully with your neurologist to pick the best treatment for you.
Can you do aerobic exercise for epilepsy?
I don’t hesitate to recommend aerobic exercise and meditation for all my patients — both usually are win-win treatments! It’s rare that doctors would recommend only lifestyle changes or complementary/alternative treatments for epilepsy; however, these might work sometimes.
Can you add complementary therapies to your treatment plan?
The complementary and alternative therapies below can be added to your treatment plan. Because there is not a lot of medical research on their effectiveness for epilepsy, it’s important to discuss each treatment with your neurologist:
What are the two types of seizures?
Typically, seizures belong in one of two basic categories: primary generalized seizures and partial seizures. The difference between these types is in how they begin.
Why do people have seizures?
The reasons why epilepsy begins are different for people of different ages. But what is known is that the cause is undetermined for about half of all individuals with epilepsy, regardless of age. Children may be born with a defect in the structure of their brain or they may suffer a head injury or infection that causes their epilepsy. Severe head injury is the most common known cause in young adults. For middle-age individuals, strokes, tumors and injuries are more frequent catalysts. In people age 65 and older, stroke is the most common known cause, followed by degenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. Often, seizures do not begin immediately after a person has an injury to the brain. Instead, a seizure may occur many months later.
What is it called when seizures occur on both sides of the brain?
Epilepsy in which the seizures begin from both sides of the brain at the same time is called primary generalized epilepsy . Hereditary factors are important in partial generalized epilepsy, which is more likely to involve genetic factors than partial epilepsy — a condition in which the seizures arise from a limited area of the brain.
What percentage of epilepsy patients have intractable seizures?
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 20 percent of epilepsy patients have intractable seizures — seizures that do not respond to treatment. The reasons why epilepsy begins are different for people of different ages.
What is epilepsy disorder?
Check out the new videos at the bottom of the page. Epilepsy is a disorder of the brain characterized by repeated seizures. A seizure is usually defined as a sudden alteration of behavior due to a temporary change in the electrical functioning of the brain.
How does epilepsy affect the brain?
In epilepsy the brain's electrical rhythms have a tendency to become imbalanced, resulting in recurrent seizures.
What is the diagnosis of epilepsy?
A doctor makes his or her epilepsy diagnosis based on symptoms, physical signs and the results of such tests as an electroencephalogram (EEG), computed tomography (CT or CAT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is essential that the type of epilepsy and the type of seizures both are diagnosed properly.
What is the treatment for epilepsy?
Responsive neurostimulation . This treatment involves surgically implanting a small gadget called a neurostimulator. Your doctor puts it under your skull bone. It looks for patterns in your brain activity that can lead to a seizure. When the neurostimulator sees one of these patterns, it sends out a little pulse to interrupt it. Not every person is able to have this device, it is based on the type of epilepsy
What is the procedure to remove a part of the brain that causes seizures?
There are two main kinds: Resective surgery. The surgeon will remove the part of your brain that causes the seizures. This surgery is most often done when the part of the brain causing the seizures is very small, has very good boundaries, and doesn’t control things like your speech, movement, sight, or hearing.
What is the medication called that changes the way the brain works?
Epilepsy medications, sometimes called anti-seizure or anticonvulsant medications, change the way your brain cells work and send messages to each other. The kind of medication your doctor suggests depends on a few things: The type of seizures you have. How likely it is you’ll have more seizures. Your age. Your sex.
How often do you need epilepsy pills?
How often you need them depends on your type of epilepsy medication, other drugs you take, and any health conditions you might have.
Can a teenager have seizures?
Some types of seizures only happen in children and younger teenagers. If you’re an older teenager or young adult, your doctor might think it’s safe for you to stop your medication. This diet is high in fats and low in carbohydrates. Your doctor may suggest it, depending on the type of seizures you have.
Can you take more than one medication for epilepsy?
Drugs that work for one person might not work for another. You might have to try more than one. Most people who take medication for epilepsy find a good fit on the first or second try. You might have to start with a low dose and slowly add more. It depends which medication you take.
What is the procedure for seizures?
When medications fail to provide adequate control over seizures, surgery may be an option. With epilepsy surgery, a surgeon removes the area of your brain that's causing seizures. Doctors usually perform surgery when tests show that: Your seizures originate in a small, well-defined area of your brain.
How to get rid of seizures in epilepsy?
Medication. Most people with epilepsy can become seizure-free by taking one anti-seizure medication, which is also called anti-epileptic medication. Others may be able to decrease the frequency and intensity of their seizures by taking a combination of medications.
How does an EEG work?
An EEG records the electrical activity of your brain via electrodes affixed to your scalp. EEG results show changes in brain activity that may be useful in diagnosing brain conditions, especially epilepsy and other seizure disorders. CT scanner. Open pop-up dialog box. Close.
What is the best treatment for epilepsy?
For some types of epilepsy, minimally invasive approaches such as MRI -guided stereotactic laser ablation may provide effective treatment when an open procedure may be too risky. In these procedures, doctors direct a thermal laser probe at the specific area in the brain causing seizures to destroy that tissue in an effort to better control the seizures.
What to do if you have a migraine?
Tell your doctor if you have migraines. Doctors may prescribe one of the anti-epileptic medications that can prevent your migraines and treat epilepsy.
What test is used to diagnose epilepsy?
Your doctor may also suggest tests to detect brain abnormalities, such as: Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. In this test, electrodes are attached to your scalp with a paste-like substance or cap. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.
Can you take fewer medications after epilepsy surgery?
Although many people continue to need some medication to help prevent seizures after successful surgery, you may be able to take fewer drugs and reduce your dosages. In a small number of cases, surgery for epilepsy can cause complications such as permanently altering your thinking (cognitive) abilities.
What are the two types of seizures?
Seizures are classified into two groups. Generalized seizures affect both sides of the brain. Absence seizures, sometimes called petit mal seizures, can cause rapid blinking or a few seconds of staring into space. Tonic-clonic seizures, also called grand mal seizures, can make a person. Cry out.
What are the words used to describe seizures?
These words are used to describe generalized seizures: Tonic: Muscles in the body become stiff. Atonic: Muscles in the body relax. Myoclonic: Short jerking in parts of the body. Clonic: Periods of shaking or jerking parts on the body.
What is a tonic clonic seizure?
Tonic-clonic seizures, also called grand mal seizures, can make a person. Cry out. Lose consciousness. Fall to the ground. Have muscle jerks or spasms. The person may feel tired after a tonic-clonic seizure. Focal seizures are located in just one area of the brain. These seizures are also called partial seizures.
How do you know if you have a seizure?
A person having a seizure may seem confused or look like they are staring at something that isn’t there. Other seizures can cause a person to fall, shake, and become unaware of what’s going on around them.
Where do secondary seizures occur?
Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, but then spread to both sides of the brain. In other words, the person first has a focal seizure, followed by a generalized seizure.
Can epilepsy cause a strange taste?
These seizures can cause twitching or a change in sensation, such as a strange taste or smell. Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confused or dazed. The person will be unable to respond to questions or direction for up to a few minutes.
What is the most common treatment for seizures?
Medication is the most common treatment for controlling seizures, and is (in most cases) the first trial of therapy.
Can you stop AED therapy without talking to your doctor?
It is important to discuss all of your AED therapy options with your doctor. A person should not stop or change their seizure medicine without talking to their doctor, as this could cause serious complications. Side effects to medications should be reported to your doctor immediately.
Does CBD oil help with seizures?
People living with uncontrolled seizures who have previously attempted other forms of treatment have reported beneficial effects and reduced seizure activity, especially with cannabis-derived Cannabidiol (CBD) oil .
How to stop a seizure from hurting?
This can prevent injury. Put something soft and flat, like a folded jacket, under his or her head. Remove eyeglasses. Loosen ties or anything around the neck that may make it hard to breathe. Time the seizure.
How long should you stay with a seizure patient?
Stay with the person until the seizure ends and he or she is fully awake.
What happens if you have a seizure in water?
The person has another seizure soon after the first one. The person is hurt during the seizure. The seizure happens in water. The person has a health condition like diabetes, heart disease, or is pregnant.
How to help someone after a syringe?
Once they are alert and able to communicate, tell them what happened in very simple terms. Comfort the person and speak calmly. Check to see if the person is wearing a medical bracelet or other emergency information. Keep yourself and other people calm.
What is the name of the seizure that causes a person to cry out?
First aid for generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures. When most people think of a seizure, they think of a generalized tonic-clonic seizure, also called a grand mal seizure. In this type of seizure, the person may cry out, fall, shake or jerk, and become unaware of what’s going on around them.
How many people have a seizure?
About 1 out of 10 people may have a seizure during his or her lifetime. That means seizures are common, and one day you might need to help someone during or after a seizure.
Do you call 911 for a seizure?
Seizures do not usually require emergency medical attention. Only call 911 if one or more of these are true: The person has never had a seizure before. The person has difficulty breathing or waking after the seizure. The seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes. The person has another seizure soon after the first one.
What are the different types of seizures?
. A person with epilepsy can experience one or multiple types of seizure. The three primary seizure types are: generalized seizures. focal seizures. unknown seizures. The four different types of epilepsy are defined by the type of seizure a person experiences.
Who should seek medical attention for a seizure?
Anyone who suspects they have had a seizure should seek medical attention. A doctor can determine what caused the seizure, the type of seizure it was, and discuss appropriate next steps.
How do seizures affect the brain?
Different types of seizures affect the brain in different ways. For example, focal seizures affect only one part of the brain, whereas generalized seizures affect the entire brain. To be categorized as having epilepsy, a person must experience two or more unprovoked seizures.
What side of the brain does epilepsy affect?
Generalized epilepsy. People with this type of epilepsy have generalized seizures. These affect both the left and right sides of the brain. Additionally, these seizures may be either motor, which involve physical movement, or non-motor, which do not.
What is the primary identifying factor of epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder. Its primary identifying factor is recurrent, unprovoked seizures. Abnormal electrical activity in the brain causes seizures. This brain activity affects how a person feels, acts, and behaves. Depending on the seizure type and severity, a person may or may not lose consciousness.
How long do seizures last?
These seizures usually last 1–3 minutes. If they last more than 5 minutes, call emergency services immediately.
When does epilepsy start?
Generalized epilepsy usually starts during childhood. However, it can also affect adults.
What is a seizure?
A seizure is a burst of uncontrolled electrical activity between brain cells (also called neurons or nerve cells) that causes temporary abnormalities in muscle tone or movements ( stiffness, twitching or limpness), behaviors, sensations or states of awareness. Seizures are not all alike. A seizure can be a single event due to an acute cause, ...
Why is it important to get a seizure diagnosis?
It is important for the doctor to get an accurate seizure diagnosis in order to implement the most appropriate kind of treatment. Focal and generalized onset seizures usually have different causes and accurately diagnosing seizure types often helps identify the cause for the seizures.
What is a myoclonic seizure?
Myoclonic seizures consist of sudden body or limb jerks that can involve the arms, head and neck. The spasms occur on both sides of the body in clusters, especially in the morning. When these seizures develop in adolescence along with tonic-clonic seizures, they are part of a syndrome called juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. People can also have myoclonic seizures as part of other epilepsy related-conditions.
Why are focal seizures important?
These seizures are important to treat and prevent since they can cause respiratory problems and injuries.
Why do people have focal seizures?
Focal seizures are also called partial seizures since they begin in one area of the brain. They can be caused by any type of focal injury that leaves scar tangles. Medical history or MRI will identify a cause (such as trauma, stroke or meningitis) in about half of the people who have focal seizures. Developmental scars — ones that occur as part of fetal and early growth of the brain — are common causes of focal seizures in children.
Where do focal onset seizures start?
Focal onset seizures start in one area and can spread across the brain and cause mild or severe symptoms, depending on how the electrical discharges spread.
What is generalized onset seizures?
Generalized-onset Seizures. Generalized-onset seizures are surges of abnormal nerve discharges throughout the cortex of the brain more or less at the same time. The most common cause is an imbalance in the “brakes” (inhibitory circuits) and “accelerator” (excitatory circuits) of electrical activity in the brain.

Diagnosis
Sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain which can cause changes in behavior, movements, feelings, and consciousness.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Not everyone who has one seizure will have another one, and because a seizure can be an isolated incident, your doctor may not decide to start treatment until you've had more than one. The optimal goal in seizure treatment is to find the best possible therapy to stop seizures, with the fewest side effects.
Diagnosis
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Treatment
- If you're living with a seizure disorder, you may feel anxious or stressed about what your future holds. Stress can affect your mental health, so it's important to talk with your health care professional about your feelings and seek ways you can find help.
Clinical Trials
- In some cases, seizures need immediate medical attention, and there's not always time to prepare for an appointment. In other cases, your first appointment to evaluate a seizure may be with your family doctor. Or you may be referred to a specialist, such as a doctor trained in brain and nervous system conditions (neurologist) or a neurologist trained in epilepsy (epileptologist). To prepare f…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Doctors generally begin by treating epilepsy with medication. If medications don't treat the condition, doctors may propose surgery or another type of treatment.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.