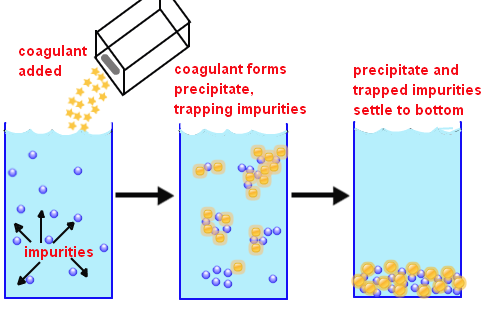
What is the purpose of the floc in water?
- Alginates (Brown seaweed extracts),
- Chitosan
- Isinglass
- Moringa oleifera seeds (Horseradish tree)
- Gelatin
- Strychnos potatorum seeds (Nirmali nut tree)
- Guar gum, etc.
What do flocculants do in water treatment?
- Water treatment plant is a generic term. ...
- Let me illustrate a few major water treatment plants.
- Municipal water treatment plants. ...
- They usually contain large filtration and sedimentation tanks to precipitate suspended and colloidal particles to deodorise and supply a clear colourless water. ...
What is flocculation water treatment?
The Hot Springs Board of Directors recently approved the purchase of motorized paddles that aid in the flocculation process at the Ouachita Water Treatment Plant, authorizing the city to acquire the equipment without soliciting bids. The two JDV Equipment ...
What is flocculation in a water treatment plant?
and accordingly will see improvements in treatment such as:
- Humic and fulvic molecules separate better with lower pH. Humic and fulvic acids are organic acids commonly found in raw water sources
- Less coagulant is required for treatment
- Flocculation improves at a lower pH
- Sulfuric Acid addition before coagulant is added preconditions organic matter

What is the purpose of FLoC?
Flocculants improve filtration, leading to an improved cleaning and disinfection of the water. This treatment method is recommended when the filtration system struggles to remove all the floating particles (murky/troubled water).
Why is FLoC important to the water treatment process?
Flocculants are used in many different types of processes, such as cheese-making and brewing. When it comes to water treatment processes, they are used to remove microscopic particles that can affect everything from taste to appearance, smell and texture.
What is the importance of flocculation?
Flocculation expedites sedimentation and ensures efficient solid/liquid separation. Large volumes of used water can be processed quickly, which minimizes the environmental impact in the sense of land needed for used water storage facilities.
What is the purpose of flocculation tank?
The flocculation tank has wooden paddle-type mixers that slowly rotate on a horizontal motor-driven shaft. After flocculation the water flows into the sedimentation tanks. Some small water-treatment plants combine coagulation and sedimentation in a single prefabricated steel unit called a solids-contact tank.
What is water flock?
Flocculation is a water treatment process where solids form larger clusters, or flocs, to be removed from water. This process can happen spontaneously, or with the help of chemical agents. It is a common method of stormwater treatment, wastewater treatment, and in the purification of drinking water.
What are CECs in water treatment?
CECs are items detected at low levels in surface water that are expected to cause harm. Contaminants include pharmaceuticals, pesticides, industrial effluents, and personal care products.
What is the difference between floc and clarifier?
Clarifier keeps the bounded matter at the top of the pool to be grabbed by the pool filter. Meanwhile, pool floc snags the particles, assembles them, and then sinks them to the bottom of the surface.
What is floc waste?
FLOC. Waste residue generated directly from the shredding of scrap metal (at a waste facility specified by the EPA by notice published in the Gazette). Soil (not contaminated or VENM) SOIL. Clay, sand or topsoil.
Do you need flocculant?
Conclusion. Flocculants are a great way to clear up your pool fast, but you should only use the chemical when you have time to vacuum really well after it has clumped everything together. If your pool is just a little cloudy, we recommend using a clarifier first to see if that does the trick.
What is floc formation?
Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
What is coagulant and flocculant?
Coagulation is the destabilization of colloidal particles brought about by the addition of a chemical reagent called as coagulant. Flocculation is the agglomeration of destabilized particles into microfloc and after into bulky floccules which can be settled called floc.
Why are organic flocculants used?
Organic polymeric flocculants are most widely used today, due to their ability to promote flocculation with a relatively low dosage. Although, their lack of biodegradability and the associated dispersion of potentially harmful monomers into water supplies is causing the focus to shift to biopolymers, which are more environmentally friendly. The problem with these is they have a shorter shelf-life, and require a higher dosage than organic polymeric flocculants. To combat this, combined solutions are being developed, where synthetic polymers are grafted onto natural polymers, to create tailored flocculants for water treatment that deliver the optimum benefits of both.
What is flocculation?
Flocculation is the separation of a solution, commonly the removal of sediment from a fluid. The term is derived from floc, which means flakes of material; and when a solution has been flocculated, the sediment has formed into larger aggregated flakes, making them easier to see and remove. This process occurs naturally, or it can also be forced using flocculants and/or physical processes.
What are the differences between flocculants and coagulants?
While both coagulation and flocculation are both common processes used in the treatment and purification of water , they are in fact very different. Coagulation is a chemical process, whereby the chemical properties of the solution are altered to promote coagulation. Coagulate means to curdle, and coagulants initiate the same process that naturally occurs in milk, when the pH of the liquid changes and the milk solids clump together. Coagulants are usually salts, which break down to release positive or negative charges. Flocculation, on the other hand, is a physical process that causes particles to floc together, first forming a cloud and then a precipitate. Flocculants are often polymers, which induce the settling of particles into larger and larger flakes or flocs. Physical agitation or other techniques are often required to promote flocculation, while coagulation will occur as soon as the coagulant has been added to the solution, without any physical processes being required.
How do coagulants work?
Coagulants work by destabilising particles present in a stable solution, causing them to aggregate, and allowing them to be bonded together by flocculants . The flocculants join the particles together into flocs, which are then separated from the solution, once they have either fallen as sediment or floated to the surface.
What is the purpose of coagulation in water?
Water can contain colloidal solids, like clay particles, bacteria, plankton, decaying plant material or other organic matter; and using coagulation and flocculation to purify water has been an active practice since as early as 2000BC, when the ancient Egyptians used almonds smeared around vessels to purify river water.
What is the process of coagulation?
Coagulation is a chemical process, whereby the chemical properties of the solution are altered to promote coagulation. Coagulate means to curdle, and coagulants initiate the same process that naturally occurs in milk, when the pH of the liquid changes and the milk solids clump together.
What is floculant in chemistry?
Flocculants are substances that promote the agglomeration of fine particles present in a solution, creating a floc, which then floats to the surface (flotation) or settles to the bottom (sedimentation). This can then be more easily removed from the liquid.
Inorganic flocculants
Inorganic compounds are comprised of molecules that do not contain carbon. These compounds make up some of the most widely used flocculation agents on the market.
Organic flocculants
Organic flocculants include carbon-based molecules and may be biological in nature. The following agents may represent a more efficient alternative to inorganic flocculants in some cases.
What happens when a floc is added to wastewater?
Once floc is beginning to form, a polymer chemical is added to the wastewater. Polymers bridge the flocculant from micro to macro flocculant, meaning that the mass of particles collecting together gets bigger. This chemical also binds the collected mass together so that it does not easily disintegrate even when the water is slightly agitated.
What is floculation in water?
Flocculation is a water treatment process where solids form larger clusters, or flocs, to be removed from water. This process can happen spontaneously, or with the help of chemical agents. It is a common method of stormwater treatment, wastewater treatment, and in the purification of drinking water. One of the requirements for treated water leaving ...
Where is flocculation used in waste water?
Sydney Water is one of the water authorities in the Australian context that uses flocculation for wastewater treatment. Their specific focus is on removing phosphate in the final stages of treatment. Sydney Water uses sand filters for removing the floc from treated wastewater. They backwash the filters every 24 hours to remove the accumulated floc. Backwash water is returned to the primary treatment section of the plant where the floc is removed with other solids.
Why is high energy mixing required in wastewater?
The wastewater must be agitated with mixers. High energy mixing is required initially to ensure that the coagulant spreads throughout the water. When flocculation is in progress the mixing energy is reduced to prevent the mass of particles from separating again.
What is the charge of suspended solid particles in wastewater?
Suspended solid particles in wastewater are negatively charged. In the first stage of flocculation, a coagulant like aluminium sulphate is added to the wastewater. The positively charged coagulant molecules neutralize the negatively charged solid particles suspended in the water.
Why is phosphorus limited in wastewater?
Phosphorus content must also be limited in wastewater as a release of phosphorus into rivers promotes algae growth. Uncontrolled releases of phosphorus have been known to cause mass die-offs of fish and other aquatic life.
What is Cleanawater wastewater?
Cleanawater is an Australian company that specialises in wastewater treatment equipment and solutions. Our track record and experience over more than 20 years means that we have the expertise to help you solve your wastewater problems. Our technical experts can help you evaluate your application and advise you on the optimum solutions for your needs.
What is the purpose of coagulation and flocculation?
The primary purpose of the coagulation and flocculation is to destabilize the charged colloidal particles in water and make them to settle so as to remove turbidity from the water. In addition to removing turbidity from the water, coagulation and flocculation process removes many bacteria which are suspended ...
Why do we add coagulants to water?
The purpose of addition of coagulant chemicals is to neutralize the negative charges on the colloidal particles to prevent those particles from repelling each other . Coagulants due to their positive charge attract negatively charged particles in the water.
What is the process of adding coagulant to water?
Coagulation is a unit process of addition of coagulant chemicals to water and rapid mixing so as to neutralize the electrical charges of the colloidal particles in the water, and allow them to come closer and form fine clumps or micro flocs. No related topics.
What is Flocculant?
Flocculant (Floc) is used to clear cloudy water by helping to remove microscopic contaminants such as pollen, dust, oils, or any number of other particles that find their way into your water and aren’t heavy enough to sink or that are too small to filter.
What is the difference between a clarifier and a flocculant?
A key difference between clarifiers and flocculants is that clarifiers can be used with cartridge filters whereas flocculants can not. Additionally, clarifiers require circulation to be effective and as a result, they take longer to work.
What is the purpose of Sutro app?
With Sutro you’ll save time, cost and effort while keeping your pool chemicals in balance, even if you don’t know what you are doing , the Sutro app will help you out telling you what to do.
How to store pool chemicals?
You should always read and follow all safety precautions on the product labels. Keeping your pool (or spa) safe means keeping yourself and others around you safe while maintaining your chemistry and your equipment. Some common recommendations include: 1 Wearing protective gear such as gloves and eye protection. 2 Store chemicals in ventilated areas and separate from one another to avoid chemical reactions from leaks. 3 As with any pool chemicals: do not mix them, unless you know what you are doing.
Can you mix pool chemicals?
As with any pool chemicals: do not mix them, unless you know what you are doing.
Can you use flocculant with a cartridge filtration system?
You want to circulate the flocculant initially, but then you want to turn off the pump and allow the particles to clump and fall to the bottom so that they can be vacuumed to waste. Note that you can not use flocculant with a cartridge filtration system.
What is floc water treatment?
Flocculation water treatment is the process of bringing together the destabilized, or “coagulated,” particles to form a larger agglomeration, or “floc.”
What is poly floc?
PolyFloc products are high molecular weight water-soluble polymers. They are designed to function in a variety of industrial water and wastewater treatment applications. Depending on customer preference, they are available in concentrated powder form, cost-effective emulsion liquids and convenient, easy-to-feed liquid solutions.
What is the purpose of clarification aids in wastewater treatment?
In influent water and effluent wastewater treatment, clarification aids like coagulants and flocculants help remove suspended solids, including oil, organics (TOC and color) and hardness. In turn, this allows our customers to prepare their influent raw water for efficient use as process water, meet wastewater discharge regulations reliably, all while allowing for cost-effective water reuse.
What is Klaraid used for?
They are designed to function in a variety of industrial water and wastewater treatment applications , including use as a primary coagulant for removal of colloidal turbidity and color for raw water clarification, as a demulsifier to facilitate liquid solids separation in dissolved gas flotation units for primary wastewater treatment, and settling and filter aids used separately or in conjunction with organic flocculants.
What is the process of destabilization of water?
Coagulation water treatment is the process of particle destabilization by charge neutralization. Once neutralized, the particles no longer repel each other and can be brought together. Coagulation is necessary for the removal of the colloidal-sized suspended matter in wastewater.
How does coagulation occur?
Coagulation can be accomplished through the addition of inorganic salts of aluminum or iron. These inorganic salts neutralize the particles' charge and hydrolyze to form insoluble precipitates, which entrap particles. Coagulation can also be affected by the addition of water-soluble organic polymers with numerous ionized sites for particle charge neutralization.
Why do particles in water repel each other?
Finely divided particles suspended in surface water repel each other because most of the surfaces are negatively charged. These colloids can be said to be stabilized and can stay in suspension for a long time. The goal of clarification is to make them bigger so that they settle faster. The following steps in clarification are necessary for particle agglomeration:
What is coagulation and how is it used in water treatment?
Coagulation is the process of adding specific chemicals to untreated water in order to destabilize the particles within the water. In most cases, aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride is added to achieve this. These particles have positive charges that are opposite to the negative charges of suspended particles within the water.
What is flocculation and how is it used in water treatment?
Flocculation is the process of encouraging the formation of flocs, or small clumps, from solids in the water. The water is mixed and activated slowly, allowing movement of particles and micro solid throughout the waste water treatment chamber.
Deploying coagulation and flocculation together in sequence
Where coagulation is found to be lacking — i.e., in creating large macro flocs that can be easily filtered and removed — flocculation can help. In areas where flocculation is inadequate by itself — for example, in targeting the particles that are suspended within the untreated water — coagulation is useful.
What is the treatment for drinking water?
Treatment for drinking water production involves the removal of contaminants and/or inactivation of any potentially harmful microbes from raw water to produce water that is pure enough for human consumption without any short term or long term risk of any adverse health effect. In general terms, the greatest microbial risks are associated with ingestion of water that is contaminated with human or animal (including bird) faeces. Faeces can be a source of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa and helminths. The removal or destruction of microbial pathogens is essential, and commonly involves the use of reactive chemical agents such as suspended solids, to remove bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi, and minerals including iron and manganese. Research including Professor Linda Lawton 's group at Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen is working to improve detection of cyanobacteria. These substances continue to cause great harm to several less developed countries who do not have access to effective water purification systems.
Why is water treatment important?
This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
What causes water contamination?
Water contamination is primarily caused by the discharge of untreated wastewater from enterprises . The effluent from various enterprises, which contains varying levels of contaminants, is dumped into rivers or other water resources. The wastewater may have a high proportion of organic and inorganic contaminants at the initial discharge. Industries generate wastewater as a result of fabrication processes, processes dealing with paper and pulp, textiles, chemicals, and from various streams such as cooling towers, boilers, and production lines .
Why is it important to keep disinfectants in water?
It is therefore common practice to keep residual disinfectants in the treated water to kill bacteriological contamination during distribution and to keep the pipes clean.
How does filtration remove particles from water?
Filtration removes particles from water either by passage through a layer of sand, such as a rapid gravity filter, or in a mechanical filter .
How is saline water treated?
Saline water can be treated to yield fresh water. Two main processes are used, reverse osmosis or distillation. Both methods require more energy than water treatment of local surface waters, and are usually only used in coastal areas or where water such as groundwater has high salinity.
What is the solution to water scarcity?
To address water scarcity issues, it is required to recover water from current wastewater or develop alternate water sources for human consumption