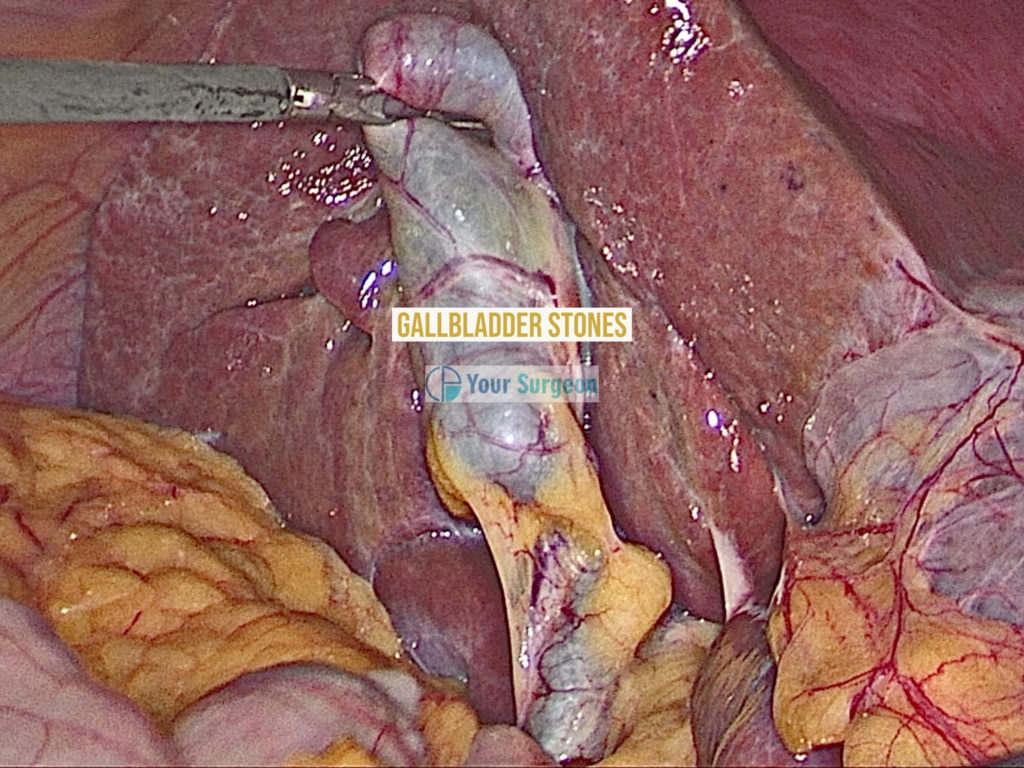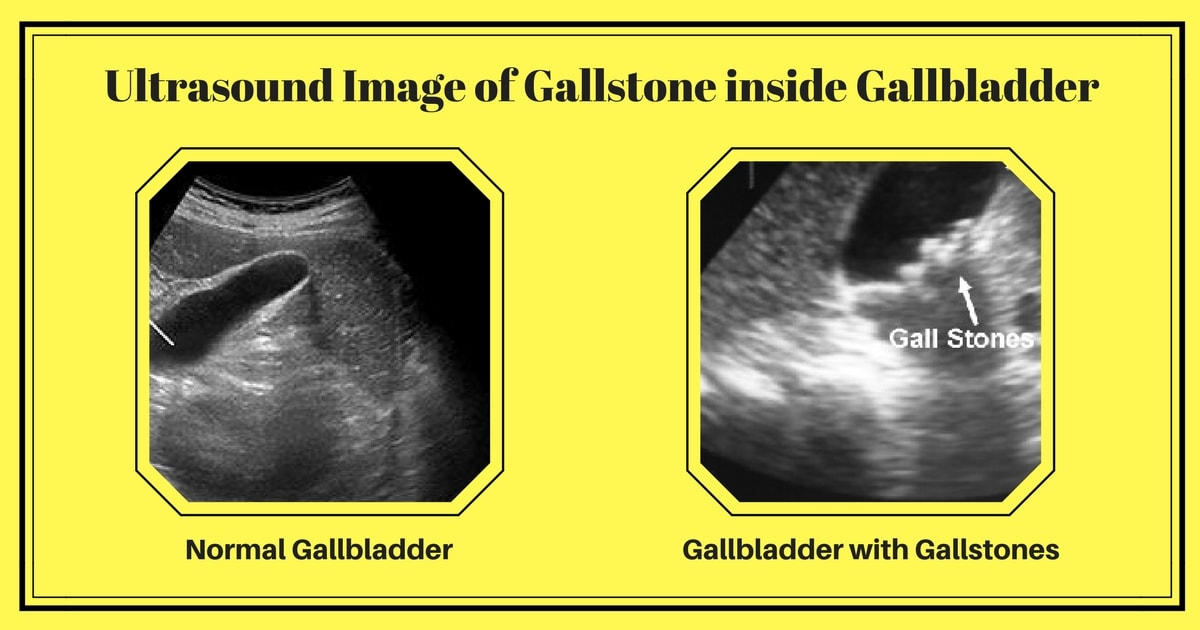
Medication
You can reduce your risk of gallstones if you:
- Don't skip meals. Try to stick to your usual mealtimes each day. ...
- Lose weight slowly. If you need to lose weight, go slow. ...
- Eat more high-fiber foods. Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity and being overweight increase the risk of gallstones. ...
Procedures
- Flatulence
- Bloating or having chronic digestive problems after consuming high-fat diets
- Severe and sudden pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Pain that radiates to right shoulder or back (between shoulder blades)
- Nausea and vomitting (mainly from cholecystitis or inflammation of gallbladder)
- High fever and chills
Self-care
Psyllium
- Add 1 tablespoon of psyllium powder to a glass of water.
- Mix well and drink it 2 times a day.
- Repeat daily until your gallstones are gone.
Nutrition
Surgical intervention is not always necessary when gallstones are present. When gallstones cause you chronic pain or when one of your bile ducts becomes obstructed, surgery is recommended. We refer to gallstone blockages as gallbladder attacks. You’ll know them by a sensation in your belly that mimics being stabbed.
What are gallstones and how to treat them?
How dangerous is untreated gallstones?
How to remove gallstones with home remedies?
Is surgery always necessary for gallstones?

What are 3 treatments for gallstones?
Treatment options for gallstones include:Surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove your gallbladder, since gallstones frequently recur. ... Medications to dissolve gallstones. Medications you take by mouth may help dissolve gallstones.
Can gallstones disappear without surgery?
Most cases of gallstones clear up without surgery. Some stones are tiny and would not cause long-term discomfort. There are times where doctors can clear gallstones with medication or non-surgical treatments. Large stones, infections, or those that cause severe, chronic pain will require surgery.
How do you treat gallstones without surgery?
How to treat gallstones without surgeryGallbladder cleanse. There are several reasons why gallstones may form: ... Apple juice. Some people use apple juice to treat gallstones. ... Apple cider vinegar. ... Yoga. ... Milk thistle. ... Artichoke. ... Gold coin grass. ... Castor oil pack.More items...
What is the main cause of gallstones?
Gallstones form when bile stored in the gallbladder hardens into stone-like material. Too much cholesterol, bile salts, or bilirubin (bile pigment) can cause gallstones.
What happens if gallstones are left untreated?
If gallstones lodge in a bile duct and cause a blockage, it eventually results in severe life-threatening complications such as bile duct inflammation and infection, pancreatitis or cholecystitis (an inflammation of gallbladder). In addition, if left untreated, it might increase risk of “gallbladder cancer”.
Are gallstones serious?
Most gallstones are not dangerous, but gallstones can become dangerous. Gallstones can pose a danger if they block the gallbladder and the flow of bile through it. In this instance, you can get an infection within the gallbladder. This is what is known as cholecystitis which can be acute or chronic (long-standing).
What foods cause gallstones?
The gallbladder produces bile that helps the body digest fats. A high intake of fats, and especially saturated and trans fats, may put extra strain on this process. Researchers have found that people who consume red, processed meats, and egg as part of an overall unhealthful diet have a higher risk of gallstones.
What foods should be avoided with gallbladder stones?
Foods to Avoid With Gallbladder ProblemsFried foods.Highly processed foods (doughnuts, pie, cookies)Whole-milk dairy products (cheese, ice cream, butter)Fatty red meat.
What dissolves gallbladder stones fast?
Ursodiol is used to dissolve gallstones in people who do not want surgery or cannot have surgery to remove gallstones. Ursodiol is also used to prevent the formation of gallstones in overweight people who are losing weight very quickly.
What are the warning signs of gallstones?
SymptomsSudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen.Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center of your abdomen, just below your breastbone.Back pain between your shoulder blades.Pain in your right shoulder.Nausea or vomiting.
What is the most common treatment for gallstones?
The usual treatment for gallstones is surgery to remove the gallbladder. Doctors sometimes can use nonsurgical treatments to treat cholesterol stones, but pigment stones usually require surgery.
What is gallstone pain like?
Gallstones can cause sudden, severe abdominal pain that usually lasts 1 to 5 hours, although it can sometimes last just a few minutes. The pain can be felt: in the centre of your abdomen (tummy) just under the ribs on your right-hand side – it may spread from here to your side or shoulder blade.
What is the best treatment for gallstones?
Your doctor may refer to you a gastroenterologist or surgeon for treatment. The usual treatment for gallstones is surgery to remove the gallbladder. Doctors sometimes can use nonsurgical treatments to treat cholesterol stones, but pigment stones usually require surgery.
What is the procedure to remove the gallbladder?
Surgery. Surgery to remove the gallbladder, called cholecystectomy, is one of the most common operations performed on adults in the United States. The gallbladder is not an essential organ, which means you can live normally without a gallbladder. A health care professional will usually give you general anesthesia.
Where does bile go after gallbladder removal?
Once the surgeon removes your gallbladder, bile flows out of your liver through the hepatic duct and common bile duct and directly into the duodenum , instead of being stored in the gallbladder. Surgeons perform two types of cholecystectomy: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
How long do you have to stay in the hospital after cholecystectomy?
After the surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for up to a week. You will probably be able to return to normal physical activity after about a month.
Can gallbladder surgery cause infection?
All surgeries come with a possible risk of complications; however, gallbladder surgery complications are very rare. The most common complication is injury to the bile ducts, which can cause infection.
Can gallstones return after surgery?
Doctors use nonsurgical treatments for gallstones only in special situations, like if you have cholesterol stones and you have a serious medical condition that prevents surgery. Even with treatment, gallstones can return. Therefore, you may have to be regularly treated for gallstones for a very long time, or even for the rest of your life.
What is the best treatment for gallstones?
Gallstone Disease Treatment: Surgery. Cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your gallbladder. It is the only treatment option to cure symptomatic gallstones. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most common procedure instead of a traditional, open procedure. During a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, your surgeon:
How to treat gallstones?
Gallstone Disease Treatment: Percutaneous Therapy. In certain high-risk patients, surgery may be too dangerous. A percutaneous (through the skin) treatment approach may be used. During this procedure, your doctor opens the gallbladder, dilates the tract and removes any gallstones using a device called a cholecystoscope.
What is the best treatment for gallbladder resection?
Usually, a cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) is the best treatment. Choledocholithiasis: This occurs when gallstones become displaced to the common bile duct rather than to the gallbladder. Choledocholithiasis can cause life-threatening conditions.
What is the procedure to remove gallstones?
Endoscopic gallbladder stenting is another nonsurgical approach to treat gallstones. It is useful in treating high-risk patients who cannot undergo surgery, usually due to an illness. During this procedure, your doctor performs an ERCP and inserts a stent from the gallbladder to the duodenum. The stent relieves biliary symptoms and complications.
How long does it take for gallstones to dissolve?
Dissolve the stones. These medications are only useful in patients who have small, non-calcified cholesterol stones and whose gallbladder is functioning normally. Therapy takes at least six to 12 months. There is a chance that the gallstones will recur within five years.
What are the complications of gallbladder disease?
Certain complications may arise in patients with gallbladder disease. Your doctor will discuss with you the risks of complications. Acute cholecystitis: This is the most common complication, and it occurs when the gallstone becomes impacted in the cystic duct.
What is ESWL in a gallbladder?
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is a nonsurgical alternative to manage gallstones. You can receive this treatment as long as your gallbladder is functioning normally and your stones are small. You do not need anesthesia for ESWL, and the procedure may be performed as an outpatient.
What is the purpose of gallstones?
Gallstones. The gallbladder stores and releases bile to help digest fats. Gallstones, stone-like objects often made of cholesterol or bilirubin, can develop in the gallbladder or bile ducts. These stones can cause pain and other complications. Treatment options often involve minimally invasive surgery to remove the gallstones, ...
What is a gallstone?
Gallstones are stone-like objects that develop in the gallbladder or bile ducts ( the pipe-like system within the liver). Gallstones can range dramatically in size, from tiny grains of sand to golf ball-sized objects. Interestingly, small stones can often cause the most trouble. These are stones that can leave the gallbladder and get stuck.
What is the bile in the gallbladder?
Bile is a mixture of cholesterol, bilirubin, bile salts and lecithin. The gallbladder is connected to other parts of the digestive system through a series of ducts, or tunnels. These ducts help to carry bile and aid in the entire process of breaking down food.
Why is the gallbladder green?
The gallbladder’s job is to store and dispense bile —a fluid that helps digest fats in the food you eat. Similarly to a pea pod, the gallbladder is green. This is due to the bile inside the gallbladder. Bile is a mixture of cholesterol, bilirubin, bile salts and lecithin.
How long does it take to get home after gallbladder removal?
If you have a laparoscopic cholecystectomy (minimally invasive procedure to remove the gallbladder) without any complications, you may be home within 24 hours. If there are complicating factors—swelling of the gallbladder, infection, a blocked duct or other medical conditions may need to have an open surgery.
Where are gallstones found?
Gallstones are most commonly found in the gallbladder, as cholesterol stones. Gallstones can also travel from the gallbladder to the common bile duct, which is the largest of the ducts (pipes) in the liver. Common bile duct stones are much less common than gallstones.
How long does it take for gallstones to dissolve?
However, as minimally invasive methods have advanced, these drugs haven’t been used as often. Dissolving medications can take months—or possibly even years— to get rid of the gallstones. By contrast, a procedure resolves the issue quickly.
What is the procedure to remove gallbladder?
Removing the gallbladder is usually done with a minimally invasive ("keyhole) operation known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
How long does it take for gallstones to go away?
Even when gallstone symptoms go away on their own, they return within two years in about two of three people. Most people whose gallstones cause symptoms will continue to have symptoms until the gallbladder is removed, although medications or procedures to break up the stones may also be used.
Why does my gallbladder hurt after eating?
It can be very painful if the gallbladder squeezes against a gallstone, or if a gallstone blocks bile from being released into the intestines.
How do you know if you have gallstones?
Eighty percent of people with gallstones do not have any symptoms and do not need treatment. When gallstones do cause symptoms, they include: 1 abdominal pain, usually high in the abdomen and often on the right side (where the gallbladder is located). The pain can spread to the back. Pain from gallstones can be steady or come and go. It can last between 15 minutes and several hours each time it occurs. 2 sensitivity to high fat meals. Fats trigger the gallbladder to contract and can worsen pain. 3 unexplained belching, gas, nausea, or a general decrease in appetite.
How long does gallstone pain last?
Pain from gallstones can be steady or come and go. It can last between 15 minutes and several hours each time it occurs. sensitivity to high fat meals. Fats trigger the gallbladder to contract and can worsen pain. unexplained belching, gas, nausea, or a general decrease in appetite.
What is the camera called for gallbladder surgery?
A camera, called a laparoscope, is placed into the abdomen through one of these openings. It lets the surgeon see what he or she is doing during the operation. Using small instruments inserted into the abdomen through other small openings, the surgeon removes fluid and stones from the gallbladder to deflate it.
How many women have gallstones?
About 1 in 5 women and 1 in 10 men have a gallstone by age 60. They are more likely to happen to older people, those who are overweight, and those who suddenly lose weight. Women who have had multiple pregnancies, taken birth control pills, or took estrogen after menopause are also more likely to develop gallstones.
How to treat gallstones?
Acupuncture. Acupuncture may help relieve some of the pain from gallstones by reducing spasms, easing bile flow, and restoring proper function. Acupuncture has been reported to treat gallstones, but more research is needed. One small study.
How to treat gallstones with castor oil?
Castor oil packs are another folk remedy, and some people choose to use this method instead of a gallbladder cleanse. Warm cloths are oaked in castor oil, which you then place on your abdomen. The packs are supposed to relieve pain and help treat your gallstones. There are no scientific studies to support claims that this treatment is effective.
What does it feel like to have gallstones on your back?
Gallstones can cause sharp, intense pain in the upper right part of the abdomen. This pain may radiate to your back and up to your shoulder blade. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, light-colored or gray stool, and diarrhea. Talk with your doctor before trying to treat gallstones on your own. Your doctor can help you receive ...
What is gold coin grass used for?
Gold coin grass, or Lysimachiae herba, is used in traditional Chinese medicine#N#Trusted Source#N#to treat gallstones. It’s been linked to reduced gallstone formation. Some people recommend taking gold coin grass before beginning a gallstone cleanse to help soften the stones.
What foods can help with gallbladder removal?
A 2006 study reported that women who ate more fruits and vegetables had a lower risk for gallbladder removal surgery than women who ate the least fruits and vegetables. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables may help support a healthy gallbladder and reduce your risk for gallstones.
What is the most common gallstone?
cholesterol gallstones, which are most common and made up of excess cholesterol. pigment gallstones, which are made up of excess bilirubin. Surgery is a common treatment for gallstones, but you may be able to treat them with natural remedies.
Can gallstones form again after cholecystectomy?
Surgery, known as cholecystectomy, involves removing the gallbladder, so gallstones are not able to form again following this treatment. A gallbladder is not needed for survival, and in most people, the body is able to compensate for the loss of the gallbladder with minimal side effects.
How many people with gallstones need surgery?
However, about 80 percent of people with gallstone symptoms will need surgery. Anyone experiencing symptoms of gallstone attack is advised to see their GP, or to present to the nearest hospital if the pain doesn’t disappear after a few hours.
Where are gallstones found?
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder, a small organ on the right side of your abdomen, beneath your liver. 1. . You’re more at risk of gallstones if you’re female, aged over 40, overweight or obese, are pregnant or have recently been pregnant.
What is the condition where the gallbladder becomes inflamed and infected?
This causes severe pain and is often accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms, as cholecystitis can lead on to other more severe complications.
Can you eat fatty foods with gallstones?
If you have gallstone symptoms, eating fatty foods can lead to pain. Foods that are high in fat include butter, cream, oils, fried foods, fatty meats, pastries, and pies.
Can gallstones cause pain?
Most people who have gallstones will not experience symptoms and may not be aware of their presence. However, in about 30 percent of cases, gallstones will cause complications that can be incredibly painful.
Can you have gallstones without surgery?
Medical treatment for gallstones isn’t generally necessary until you experience symptoms. In the early stages of experiencing biliary colic, you may be advised to avoid fatty foods to reduce your symptoms. However, about 80 percent of people with gallstone symptoms will need surgery.
How to reduce the risk of gallstones?
To help improve your condition and reduce your risk of gallstones, try these tips: Reduce your intake of fats and choose low-fat foods whenever possible. Avoid high-fat, greasy, and fried foods. Add fiber to your diet to make your bowel movements more solid.
How to remove gallbladder?
Removing a gallbladder involves rerouting the bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile no longer goes through the gallbladder and it becomes less concentrated. The result is a laxative effect that causes diarrhea. To treat this, eat a diet lower in fats so that you release less bile.
What happens if you have gallstones?
Untreated gallstones may cause complications such as: 1 jaundice, a yellowish tint to your skin or eyes 2 cholecystitis, a gallbladder infection 3 cholangitis, a bile duct infection 4 sepsis, a blood infection 5 pancreas inflammation 6 gallbladder cancer
What is the condition where bile moves from the gallbladder?
Acute cholecystitis. When a gallstone blocks the duct where bile moves from the gallbladder, it can cause inflammation and infection in the gallbladder. This is known as acute cholecystitis. It is a medical emergency. The risk of developing acute cholecystitis from symptomatic gallstones is 1 to 3 percent.
Why does my gallbladder have stones?
Your gallbladder needs to empty its bile to be healthy and to function properly. If it fails to empty its bile content, the bile becomes overly concentrated, which causes stones to form.
What percentage of gallstones are cholesterol?
According to Harvard Health Publications, 80 percent of gallstones are made of cholesterol. The other 20 percent of gallstones are made of calcium salts and bilirubin. It’s not known exactly what causes gallstones to form, though there are some theories.
Where is the gallbladder located?
Your gallbladder is a small organ below the liver in the upper right abdomen. It’s a pouch that stores bile, a green-yellow liquid that helps with digestion. Most gallstones form when there’s too much cholesterol in the bile.
How to prevent gallstones?
Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity and being overweight increase the risk of gallstones.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
Seek immediate care if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious gallstone complication, such as: Abdominal pain so intense that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position. Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice) High fever with chills.
What is the fluid in the gallbladder called?
The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine. Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
What is the name of the fluid that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder?
Gallstones. Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder. When you eat, your gallbladder contracts and empties bile into your small intestine (duodenum).
What are the different types of gallstones?
Types of gallstones. Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include: Cholesterol gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
How long does gallstone pain last?
Back pain between your shoulder blades. Pain in your right shoulder. Nausea or vomiting. Gallstone pain may last several minutes to a few hours.
Can gallstones cause fever?
A gallstone that becomes lodged in the neck of the gallbladder can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Cholecystitis can cause severe pain and fever. Blockage of the common bile duct. Gallstones can block the tubes (ducts) through which bile flows from your gallbladder or liver to your small intestine.