Medication
Lifestyle Tips To Cure Meningitis
- Maintain a healthy diet. One of the most important things to consider while fighting meningitis is to follow a healthy diet. ...
- Get plenty of rest. Refrain from your busy lifestyle filled with activities and take rest as often as you can. ...
- Use cold packs. ...
- Try a neutral bath. ...
- Hydrate yourself. ...
Self-care
There is no specific treatment for viral meningitis, which is often mild. Most of the time, people recover from viral meningitis in 7 to 10 days with little more than rest, over-the-counter fever reducers or pain medication, and proper fluid intake.
Nutrition
What is the incubation period of Bacterial Meningitis and how long is it contagious? Symptoms generally develop 1-10 days after exposure, but usually less than 4 days. Meningitis is contagious until at least 24 hours after treatment with antibiotics the bacteria is sensitive to. What should I do if I think I have a Bacterial Meningitis infection?
How to treat meningitis naturally at home?
Individual cases of meningitis and encephalitis can vary greatly depending on their cause and severity. Therefore, it is not clear which is more serious and dangerous overall. Viral encephalitis and bacterial meningitis tend to be especially dangerous. All cases of meningitis and encephalitis are serious and need emergent treatment.
Can you cure meningitis?
Is meningitis contagious after antibiotic treatment?
Which meningitis is worse?
What is the best treatment for meningitis?
How to treat viral meningitis?
How to diagnose meningitis?
How to stop a fever from a fever?
What test is used to determine if a child has a bacterial infection?
What is the best way to diagnose meningitis?
Can antibiotics treat tuberculous meningitis?
See more
About this website
What is the best antibiotic for bacterial meningitis?
In most cases of bacterial meningitis a broad spectrum cephalosporin (cefotaxime or ceftriaxone) is the most appropriate empirical choice in children over 3 months old. These cover Neisseria meningitides, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae, and penetrate CSF well.
What are 3 of the main antibiotics used to treat bacterial meningitis?
Commonly used meningitis treatments include a class of antibiotics called cephalosporins, especially Claforan (cefotaxime) and Rocephin (ceftriaxone). Various penicillin-type antibiotics, aminoglycoside drugs such as gentamicin, and others, are also used.
What is the most common bacterial meningitis?
Several strains of bacteria can cause acute bacterial meningitis, most commonly: Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). This bacterium is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in infants, young children and adults in the United States.
What is the first aid treatment for meningitis?
Emergency advice Treat the fever. Do the glass test. If spots don't fade, call 999 immediately. Reassure them and keep them cool.
Can Oral antibiotics treat meningitis?
Antibiotics treat bacterial meningitis in both adults and children. Those with a known or suspected exposure to bacterial meningitis may also take antibiotics to avoid developing the infection.
WHO guidelines meningitis treatment?
Since 1996, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the use in peripheral health centres of oily chloramphenicol (OC) for the presumptive treatment of meningococcal epidemics. Subsequently, studies have demonstrated that a single dose of ceftriaxone (100 mg/kg) cures meningitis due to N. meningitidis.
What are the 3 most common causes of bacterial meningitis?
Bacterial Meningitis is the most common type of meningitis. Three types of bacteria are responsible for 80% of all Bacterial Meningitis. These are: 1) Hemophilus influenzae (type B), 2) Streptococcus pneumoniae (Pneumococcus), and 3) Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus).
What vaccine is for bacterial meningitis?
Meningococcal vaccine (MenACWY) is highly effective at protecting against four strains of the meningococcal bacteria. Three strains are common in the United States and the fourth strain protects travelers to certain countries where the disease is more common.
What are the 5 types of meningitis?
MeningitisBacterial Meningitis. Meningitis caused by bacteria can be deadly and requires immediate medical attention. ... Viral Meningitis. Meningitis caused by viruses is serious but often is less severe than bacterial meningitis. ... Fungal Meningitis. ... Parasitic Meningitis. ... Amebic Meningitis. ... Non-Infectious Meningitis.
Can meningitis be cured without treatment?
Most people who get mild viral meningitis usually recover completely in 7 to 10 days without treatment. Antiviral medicine may help people with meningitis caused by viruses such as herpesvirus and influenza. Antibiotics do not help viral infections, so they are not useful in the treatment of viral meningitis.
Is bacterial meningitis curable?
Bacterial meningitis is serious. Some people with the infection die and death can occur in as little as a few hours. However, most people recover from bacterial meningitis.
How do you know if meningitis is bacterial or viral?
The clues that the doctor uses are the levels of white cells, protein and glucose in the CSF. Typically in bacterial meningitis the white cell count is much higher than in viral meningitis (and is a different type of white cell), the protein is much higher and the glucose is much lower than in viral meningitis.
What Is Bacterial Meningitis?
Acute bacterial meningitis is the most common form of meningitis. Approximately 80% of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis. Bacterial meningit...
Who Gets Bacterial Meningitis?
Children between the ages of 1 month and 2 years are the most susceptible to bacterial meningitis.Adults with certain risk factors are also suscept...
What Causes Bacterial Meningitis?
The bacteria most often responsible for bacterial meningitis are common in the environment and can also be found in your nose and respiratory syste...
What Are The Symptoms of Bacterial Meningitis?
You want to watch for high fever, headaches, and an inability to lower your chin to your chest due to stiffness in the neck.In older children and a...
National Center for Biotechnology Information
National Center for Biotechnology Information
Bacterial Meningitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
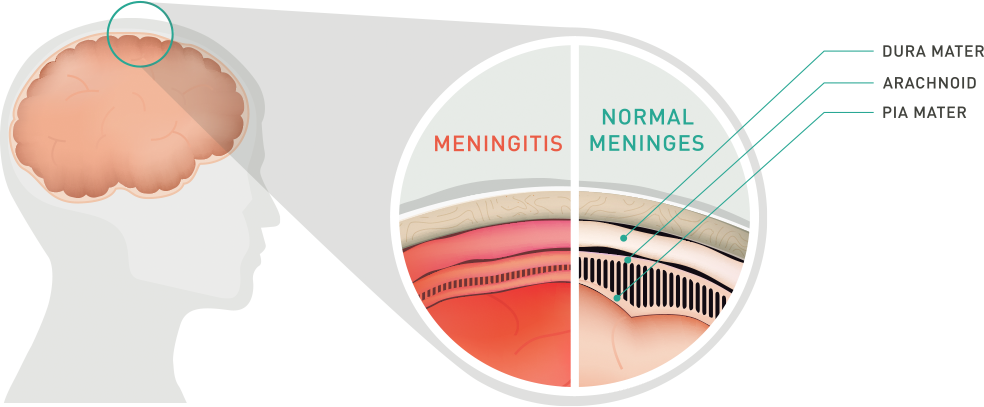
Overview What is meningitis? Meningitis is an infection of the membranes (meninges) surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis can be caused by a bacterial, fungal or viral infection. Meningitis can be acute, with a quick onset of symptoms, it can be chronic, lasting a month or more, or it can be mild or aseptic.
How to treat meningitis?
Bacterial meningitis is treated with antibiotics. A general intravenous antibiotic with a corticosteroid to bring down the inflammation may be prescribed even before all the test results are in. When the specific bacteria are identified, your doctor may decide to change antibiotics. In addition to antibiotics, it will be important to replenish fluids lost from loss of appetite, sweating, vomiting and diarrhea.
What is meningitis caused by?
Meningitis can be caused by a bacterial, fungal or viral infection. Meningitis can be acute, with a quick onset of symptoms, it can be chronic, lasting a month or more, or it can be mild or aseptic.
What is the most common form of meningitis?
Acute bacterial meningitis is the most common form of meningitis. Approximately 80 percent of all cases are acute bacterial meningitis. Bacterial mening itis can be life threatening. The infection can cause the tissues around the brain to swell. This in turn interferes with blood flow and can result in paralysis or even stroke.
How old are you when you get bacterial meningitis?
Who gets bacterial meningitis? Children between the ages of 1 month and 2 years are the most susceptible to bacterial meningitis. Adults with certain risk factors are also susceptible. You are at higher risk if you abuse alcohol, have chronic nose and ear infections, sustain a head injury or get pneumococcal pneumonia.
How long does it take for bacterial meningitis to show symptoms?
The onset of symptoms is fast, within 24 hours. If allowed to progress, you can die from bacterial meningitis.
What is the best treatment for bacterial meningitis?
Prophylaxis. When someone has bacterial meningitis, a doctor may recommend antibiotics to help prevent people around the patient from getting sick. Doctors call this prophylaxis. CDC recommends prophylaxis for: Close contacts of someone with meningitis caused by N. meningitidis.
What are the risks of meningitis?
Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, medications, and surgical procedures put people at increased risk for meningitis. For example, having an HIV infection or a cerebrospinal fluid leak, or not having a spleen can increase a person’s risk for several types of bacterial meningitis. Working with meningitis-causing pathogens: ...
How does meningitis spread?
How It Spreads. Certain germs that cause bacterial meningitis, such as L. monocytogenes, can spread through food. But most of these germs spread from one person to another. How people spread the germs often depends on the type of bacteria.
How do you spread N. meningitidis?
N. meningitidis: People spread these bacteria by sharing respiratory or throat secretions (saliva or spit). This typically occurs during close (coughing or kissing) or lengthy (living together) contact.
What to do when you cough and sneeze?
Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze (use your upper sleeve or elbow if a tissue isn’t available)
Can microbiologists work with meningitis-causing pathogens?
Working with meningitis-causing pathogens: Microbiologists routinely exposed to meningitis-causing bacteria are at increased risk for meningitis.
Do meningitis shots work?
Like with any vaccine, these vaccines do not work 100% of the time. The vaccines also do not protect against infections from all the types (strains) of each of these bacteria. For these reasons, there is still a chance vaccinated people can develop bacterial meningitis.
Why do people get meningitis?
Experts don't always know why meningitis happens. Some people get it when their immune system is weak or they've recently been sick. A head injury may also increase risk. Bacterial meningitis is more common in infants under 1 year of age and people ages 16 to 21.
How long does it take for meningitis to come on?
Lack of appetite. Seizures (sometimes also seen in adults if the meningitis is advanced) Symptoms typically come on quickly, in as little as a couple of hours or up to a day or two. If you think you or your child may have meningitis, go to an emergency room right away.
What is the term for an infection of the membranes that protect the spinal cord and brain?
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes (meninges) that protect the spinal cord and brain. When the membranes become infected, they swell and press on the spinal cord or brain. This can cause life-threatening problems. Meningitis symptoms strike suddenly and worsen quickly.
Can meningitis cause stroke?
It can lead to brain damage, paralysis, or stroke. In some cases, it can be fatal. Many different types of bacteria can cause meningitis. Vaccines are available that target many of these bacteria. For this reason, it's important to know what's causing meningitis.
Is meningitis contagious?
Bacterial meningitis is contagious. If you’ve been around someone who has it, call your healthcare provider to talk about how to keep from getting sick.
What is the best medicine for meningitis?
But if you have meningitis caused by a herpes virus or influenza, your doctor may prescribe an antiviral medication, such as: 1 Cytovene (ganciclovir) or Foscavir (foscarnet), which are sometimes used to treat cytomegalovirus meningitis (CMV meningitis) in people with weakened immune systems 2 Zovirax (cyclovir), which may be used to treat meningitis from the herpes simplex virus
What is the best treatment for cryptococcal meningitis?
For example, amphotericin B (AmBisome, Amphotec) is one of the most common treatments for cryptococcal meningitis, caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. Amphotericin B may also be used to treat a rare type of parasitic meningitis caused by Naegleria fowleri.
How many serogroups are there in Meningitidis?
At least 12 different serogroups, or strains, of N. meningitidis have been identified so far, with five of them (A, B, C, W-135, and Y) causing the majority of meningococcal disease cases in the world. ( 1)
How long does it take to recover from viral meningitis?
There is no specific treatment for viral meningitis, which is often mild. Most of the time, people recover from viral meningitis in 7 to 10 days with little more than rest, over-the-counter fever reducers or pain medication, and proper fluid intake. But if you have meningitis caused by a herpes virus or influenza, ...
What antibiotics are used for fungus?
Alternatively, the antifungal agent miconazole and the antibiotic rifampin may be used.
What is the name of the drug that treats yeast infections?
These medicines are often part of the azole class of antifungal drugs, such as Diflucan ( fluconazole), which is used to treat infections from Candida albicans, the fungus behind yeast infections. Depending on the type of infection, other antifungals may also be used.
Can meningitis be treated with medication?
Medication is available to treat some forms of meningitis, but not all.
Antibiotics for adults
While there’s overlap between antibiotics used to treat children and adults, some are only prescribed for adult use. This is because antibiotics can be hard on your body while trying to resolve a serious infection.
Antibiotics for children
Infants and children are at particular risk for bacterial meningitis. Their immune systems are less developed and more vulnerable to infections.
Antibiotics for exposure to bacterial meningitis
Bacterial meningitis spreads through bodily fluids, including saliva. It can be transmitted if someone close to you coughs.
What is the best treatment for meningitis?
Acute bacterial meningitis must be treated immediately with intravenous antibiotics and sometimes corticosteroids. This helps to ensure recovery and reduce the risk of complications, such as brain swelling and seizures. The antibiotic or combination of antibiotics depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection.
How to treat viral meningitis?
Treatment of mild cases of viral meningitis usually includes: Bed rest. Plenty of fluids. Over-the-counter pain medications to help reduce fever and relieve body aches. Your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids to reduce swelling in the brain, and an anticonvulsant medication to control seizures.
How to diagnose meningitis?
Your family doctor or pediatrician can diagnose meningitis based on a medical history, a physical exam and certain diagnostic tests. During the exam, your doctor may check for signs of infection around the head, ears, throat and skin along the spine.
How to stop a fever from a fever?
Drink plenty of fluids and take acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) to reduce your fever and body aches. Also avoid any medications that may make you less alert. Don't go to work or school. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What test is used to determine if a child has a bacterial infection?
You or your child may undergo the following diagnostic tests: Blood cultures. A blood sample is placed in a special dish to see if it grows microorganisms, particularly bacteria. A sample may also be placed on a slide and stained (Gram's stain), then studied under a microscope to see whether bacteria are present. Imaging.
What is the best way to diagnose meningitis?
Imaging. Computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the head may show swelling or inflammation. X-rays or CT scans of the chest or sinuses also may show infection that may be associated with meningitis.
Can antibiotics treat tuberculous meningitis?
Treatment for chronic meningitis is based on the underlying cause. Antifungal medications treat fungal meningitis, and a combination of specific antibiotics can treat tuberculous meningitis. However, these medications can have serious side effects, so treatment may be deferred until a laboratory can confirm that the cause is fungal.

Causes
Risk Factors
How It Spreads
Signs and Symptoms
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
- Certain germs that cause bacterial meningitis, such as L. monocytogenes, can spread through food. But most of these germs spread from one person to another. How people spread the germs often depends on the type of bacteria. It is also important to know that people can have these bacteria in or on their bodies without being sick. These people are “carriers.” Most carriers neve…