Healthline.com
Mar 31, 2022 · Official Answer by Drugs.com From the 2015 Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) guidelines, the CDC recommends treatment for a gonorrhea-chlamydia coinfection with azithromycin ( Zithromax) 1 gram given orally in a single dose, plus ceftriaxone ( Rocephin) 250 mg given intramuscularly as first-line therapy.
Allremedies.com
Jan 02, 2022 · Azithromycin or doxycycline is recommended for the treatment of uncomplicated genitourinary chlamydial infection. When Can I Have Sex Again If you had doxycycline, you shouldn’t have sex including vaginal, oral or anal sex, even with a condom until both you and your partner have completed treatment.
Ehomeremedies.com
Jun 24, 2020 · The two most common antibiotics used for chlamydia are: azithromycin and doxycycline. While doxycycline is administered, two capsules a day for a week, azithromycin is normally prescribed as two or four tablets as a single dose. Antibiotics are the best treatment for chlamydia and when taken according to the docter's directions, the effectiveness is almost 100%.
Trueremedies.com
A randomized trial for the treatment of rectal chlamydia infection among MSM reported microbiologic cure was 100% with doxycycline and 74% with azithromycin (812). A published review reported that C. trachomatis was detected at the anorectal site among 33%–83% of women who had urogenital C. trachomatis infection, and its detection was not associated with …
What medications are used to treat chlamydia?
76 rows · Drugs used to treat Chlamydia Infection. The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition. Select drug class All drug classes quinolones (4) tetracyclines (11) aminopenicillins (3) miscellaneous antimalarials (7) …
How to cure Chlamydia without a doctor?
Feb 07, 2022 · Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are treated with an antibiotic called azithromycin. Youll usually be given a 1000mg dose in four tablets to be taken all at once. The infection/s will take a week to fully clear and you should avoid having sex during this time and until your partner has been tested and treated too.
Can Chlamydia be cured without antibiotics?
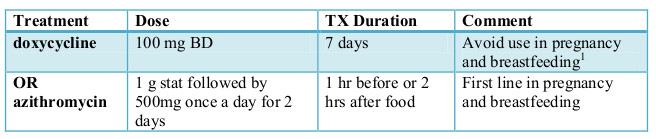
For people with uncomplicated genital chlamydia, the WHO STI guideline suggests one of the following options: azithromycin 1 g orally as a single oral dose doxycycline 100 mg …
Does azithromycin cure Chlamydia?
Apr 03, 2022 · But if you must use, then go for Amoxicillin, azithromycin, erythromycin, Doxycycline, levofloxacin, and ofloxacin. But always consult your doctor before taken the pills. How to use Over The Counter Antibiotics to safely treat Chlamydia?

Can any antibiotic treat chlamydia?
Can amoxicillin treat chlamydia?
Is 500mg of azithromycin enough to cure chlamydia?
Which is better for chlamydia azithromycin or doxycycline?
What is the strongest antibiotic for STD?
What is the best antibiotic for chlamydia and gonorrhea?
From the 2015 Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) guidelines, the CDC recommends treatment for a gonorrhea-chlamydia coinfection with azithromycin (Zithromax) 1 gram given orally in a single dose, plus ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 250 mg given intramuscularly as first-line therapy.Mar 31, 2022
Is 1000 mg of azithromycin too much?
Can I take 1000 mg of azithromycin at once?
How quickly does azithromycin work?
Are there any over the counter meds for chlamydia?
How can I treat chlamydia without going to the doctor?
Does azithromycin 500mg cure gonorrhea?
What is the most common STI in the UK?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can infect both men and women. It is one of the most common STIs in the UK and is most common in sexually active teenagers and young adults.
Can a pregnant woman pass chlamydia to her baby?
Pregnant women with chlamydia can pass on the infection to their unborn baby.
What is the best antibiotic for chlamydia?
Best antibiotics for treating chlamydia. The two most common antibiotics used for chlamydia are: azithromycin and doxycycline. While doxycycline is administered, two capsules a day for a week, azithromycin is normally prescribed as two or four tablets as a single dose.
Who has tested positive for chlamydia?
People who have tested positive for chlamydia. Newborn babies of mothers who tested positive for chlamydia. Sexual partners of those who have tested positive for chlamydia. Persons who are experiencing the symptoms of chlamydia and have engaged in unprotected sexual intercourse not long ago. The use of antibiotics differs based on the level ...
What is doxycycline used for?
Doxycycline is used to treat numerous types of bacteria. Doxycycline is an antibiotic in the group of tetracyclines. Doxycycline, like the previous described azithromycin also binds to a specific part of the bateria's ribosomes, preventing bacterial growth.
How does azithromycin stop bacterial growth?
Azithromycin stops the bacterial growth in the body by binding to a specific part of the bacteria's ribosomes. If not properly administered, azithromycin may be less or totally ineffective. In other words, strict adherence must be given to the instructions issued by medical personnel.
Why are pregnant women given antibiotics?
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are given different types of antibiotics because of the effect it might have on the fetus or newborn. Examples of such antibiotics are erythromycin and amoxicillin. Extra care is taken when treating pregnant and lactating women to avoid complications.
Why is it important to consult a qualified medical personnel before taking antibiotics?
This is why it is advisable to consult a qualified medical personnel and not resort to self-medication. Wrong administration of antibiotics may lead to the bacteria to become resistant , or causing other opportunistic pathogens to cause a new infection.
Can you take antibiotics without a prescription?
Antibiotics should not be taken without a prescription and medical advice. Always take the recommended dosage and do not stop with the antibiotic course. A test should be done to confirm the infection before taking antibiotics. A test can be done at your local GP, a hospital/clinic or by the use of a rapid test kit.
When should a chlamydial etiology be considered?
A chlamydial etiology should be considered for all infants aged ≤30 days who experience conjunctivitis, especially if the mother has a history of chlamydial infection. These infants should receive evaluation and age-appropriate care and treatment.
Where to collect chlamydial specimens?
Specimens for chlamydial testing should be collected from the nasopharynx. Tissue culture is the definitive standard diagnostic test for chlamydial pneumonia. Nonculture tests (e.g., DFA and NAAT) can be used. DFA is the only nonculture FDA-cleared test for detecting C. trachomatis from nasopharyngeal specimens; however, DFA of nasopharyngeal specimens has a lower sensitivity and specificity than culture. NAATs are not cleared by FDA for detecting chlamydia from nasopharyngeal specimens, and clinical laboratories should verify the procedure according to CLIA regulations ( 553 ). Tracheal aspirates and lung biopsy specimens, if collected, should be tested for C. trachomatis.
Can azithromycin be used for neonatal chlamydia?
Although data regarding use of azithromycin for treating neonatal chlamydial infection are limited, available data demonstrate that a short therapy course might be effective ( 834 ). Topical antibiotic therapy alone is inadequate for treating ophthalmia neonatorum caused by chlamydia and is unnecessary when systemic treatment is administered.
Is doxycycline effective for urogenital chlamydia?
Available evidence supports that doxycycline is efficacious for C. trachomatis infections of urogenital, rectal, and oropha ryngeal sites. Although azithromycin maintains high efficacy for urogenital C. trachomatis infection among women, concern exists regarding effectiveness of azithromycin for concomitant rectal C. trachomatis infection, which can occur commonly among women and cannot be predicted by reported sexual activity. Inadequately treated rectal C. trachomatis infection among women who have urogenital chlamydia can increase the risk for transmission and place women at risk for repeat urogenital C. trachomatis infection through autoinoculation from the anorectal site ( 816 ). Doxycycline is also available in a delayed-release 200-mg tablet formulation, which requires once-daily dosing for 7 days and is as effective as doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days for treating urogenital C. trachomatis infection in men and women. It is more costly but also has lower frequency of gastrointestinal side effects ( 817 ). Levofloxacin is an effective treatment alternative but is more expensive. Erythromycin is no longer recommended because of the frequency of gastrointestinal side effects, which can result in nonadherence. When nonadherence to doxycycline regimen is a substantial concern, azithromycin 1 g regimen is an alternative treatment option but might require posttreatment evaluation and testing because it has demonstrated lower treatment efficacy among persons with rectal infection.
Can C. trachomatis be transmitted to genital sites?
Although the clinical significance of oropharyngeal C. trachomatis infection is unclear and routine oropharyngeal screening is not recommended, oropharyngeal C. trachomatis can be sexually transmitted to genital sites ( 211, 814 ); therefore, if C. trachomatis is identified from an oropharyngeal specimen while screening for pharyngeal gonorrhea, it should be treated. Evidence is limited regarding the efficacy of antimicrobial regimens for oropharyngeal chlamydia; however, a recently published observational study indicates doxycycline might be more efficacious than azithromycin for oropharyngeal chlamydia ( 815 ).
Is azithromycin better than doxycycline?
A meta-analysis and a Cochrane systematic review evaluated data from randomized clinical trials of azithromycin versus doxycycline for treating urogenital chlamydial infection determined that microbiologic treatment failure among men was higher for azithromycin than for doxycycline ( 748, 749 ). Observational studies have also demonstrated that doxycycline is more efficacious for rectal C. trachomatis infection for men and women than azithromycin ( 748, 811 ). A randomized trial for the treatment of rectal chlamydia infection among MSM reported microbiologic cure was 100% with doxycycline and 74% with azithromycin ( 812 ). A published review reported that C. trachomatis was detected at the anorectal site among 33%–83% of women who had urogenital C. trachomatis infection, and its detection was not associated with report of receptive anorectal sexual activity ( 813 ).
Does chlamydia reduce PID?
Chlamydia screening programs have been demonstrated to reduce PID rates among women ( 786, 787 ). Although evidence is insufficient to recommend routine screening for C. trachomatis among sexually active young men because of certain factors (i.e., feasibility, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness), screening of sexually active young men should be considered in clinical settings with a high prevalence of chlamydia (e.g., adolescent clinics, correctional facilities, or STD specialty clinics) or for populations with a high burden of infection (e.g., MSM) ( 149, 788 ). Among women, the primary focus of chlamydia screening should be to detect and treat chlamydia, prevent complications, and test and treat their partners, whereas targeted chlamydia screening for men should be considered only when resources permit, prevalence is high, and such screening does not hinder chlamydia screening efforts for women ( 789 – 791 ). More frequent screening than annual for certain women (e.g., adolescents) or certain men (e.g., MSM) might be indicated on the basis of risk behaviors.
One Of The Most Common Sexually Transmitted Disease
Gonorrhea is an extremely usual sexually transmitted infection, especially for teenagers and individuals in their 20s. Gonorrhea is sometimes called the clap or the drip. Gonorrhea is spread out via vaginal, rectal, and oral sex.
Related Questions Answered On Yanswers
Is Gonorrhea and Chlamydia curable diseases, and lets say you have been experiencing the symptons for 5 days.?
Preventing The Spread Of Gonorrhea
To minimize the risk of transmitting gonorrhea to others, avoid having sexual intercourse for at least seven days after completion of treatment. Also encourage any sexual partners from within the past 60 days to see their own doctors for evaluation.
What Is The Difference Between Gonorrhea And Chlamydia
Both STIs are caused by bacteria and can cause similar symptoms. Gonorrhea is caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria and Chlamydia trachomatis is the bacteria which causes chlamydia. Chlamydia is more common and is less likely to produce symptoms, especially in women.
How Are Chlamydia And Gonorrhea Treated
Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are treated with an antibiotic called azithromycin. Youll usually be given a 1000mg dose in four tablets to be taken all at once. The infection/s will take a week to fully clear and you should avoid having sex during this time and until your partner has been tested and treated too.
Best Over The Counter Antibiotics For Chlamydia
In order to get best over the counter antibiotics for chlamydia, you should onsult your doctor, your doctor will not turn his back on you, often time you might not get rid of Chlamydia by going to counter medication. Sometime you may have false positive chlamydia test result, so it is better to consult doctor.
Put Sex On Hold During And After Chlamydia Treatment
If you were given a single dose of antibiotics to treat your chlamydia, you should not have any kind of sex for a full seven days after the day you took the medicine. If youre taking antibiotics for a week, wait another seven days after the last day of your treatment. Be sure to take all of the medicine that is prescribed for you.
How long should I take doxycycline for chlamydia?
In people with anorectal chlamydial infection, the WHO STI guideline suggests using doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 7 days over azithromycin 1 g orally single dose.
How often should I take azithromycin for genital chlamydia?
For people with uncomplicated genital chlamydia, the WHO STI guideline suggests one of the following options: azithromycin 1 g orally as a single oral dose. doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 7 days. or one of these alternatives: tetracycline 500 mg orally four times a day for 7 days.
How often should I take azithromycin for chlamydial conjunctivitis?
In neonates with chlamydial conjunctivitis, the WHO STI guideline recommends using oral azithromycin 20 mg/kg/day orally, one dose daily for 3 days, over erythromycin 50 mg/kg/day orally, in four divided doses daily for 14 days.
How often should I take doxycycline for LGV?
In adults and adolescents with LGV, the WHO STI guideline suggests using doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 21 days over azithromycin 1 g orally, weekly for 3 weeks.
Is doxycycline better than azithromycin?
In summary, doxycycline may result in more cures, but although it is less expensive than azithromycin, azithromycin may be better accepted due to the single-dose treatment.
Is azithromycin a single dose?
The GDG agreed that equity may vary between the medicines depending on the population: in some populations, azithromycin may be more acceptable since it is a single-dose treatment, and some people may experience stigma related to visibility of a multi-dose regimen with doxycycline.
Is azithromycin a good treatment for chlamydial infection?
When high value is placed on reducing costs, doxycycline in a standard dose may be the best choice; when high value is placed on convenience, azithromycin in a single dose may be the best choice. A delayed-release formulation of doxycycline may be an alternative to twice daily dosing of doxycycline, but the high cost of the delayed-release formulation may prohibit its use. Note that doxycycline, tetracycline and ofloxacin are contraindicated in pregnant women (see recommendations 3a–3c).
How to get rid of chlamydia over the counter?
In order to get best over the counter antibiotics for chlamydia, you should onsult your doctor, your doctor will not turn his back on you, often time you might not get rid of Chlamydia by going to counter medication . Sometime you may have false positive chlamydia test result, so it is better to consult doctor. Moreover if you fail to treat this disease you might end up with PID which is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and then you will also consult your doctor and by that time things will be worse. So the best thing is to go to a doctor if you notice the symptoms. But if you must use, then go for Amoxicillin, azithromycin, erythromycin, Doxycycline, levofloxacin, and ofloxacin. But always consult your doctor before taken the pills.
Why are antibiotics used?
Antibiotics are been used in a clinical practice which has allowed or helps in saving millions of lives, that is if been prescribed by a medical expert who knows the pros and cons of the disease. Although antibiotics are been prescribed and are always taken to preventive measures without further considerations.
What is the best medicine to take for a swollen ear?
But if you must use, then go for Amoxicillin, azithromycin, erythromycin, Doxycycline, levofloxacin, and ofloxacin. But always consult your doctor before taken the pills.
Can you have a false positive chlamydia test?
Sometime you may have false positive chlamydia test result, so it is better to consult doctor . Moreover if you fail to treat this disease you might end up with PID which is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and then you will also consult your doctor and by that time things will be worse.
Is it a sin to take antibiotics for chlamydia?
It is not a sin or wrong to go for Chlamydia over the counter antibiotics but our major concern is your safety and using it more effectively. Do not ignore your doctor’s instructions when using your prescribe drug. Always go for the label if you must buy from the counter. Make sure you check.
Do pharmacists prescribe antibiotics?
Well, all these antibiotics have their various functions. They are just prescription, prescribe by your doctors and each and every one of them has what is does. They are all important, do not neglect anyone. All you have to do is to know the one that is needed for your problem. The most medical pharmacist can prescribe fully well than others.
Does antibiotics help with chlamydia?
So with over the counter antibiotics, it has helped so far by in various ways: Identifying those that have positive Chlamydia tests and treating them with immediate effect. With good prescriptions, it has helped to eradicate Chlamydia from newly delivered babies who was infected during by their mother during delivery.
