What is the most effective antibiotic for MRSA?
- taking a bleach bath
- tea-tree oil
- Clorox® Pro Quaternary All-Purpose Disinfectant Cleaner
- Garlic
- hydrogen peroxide (35% or higher — OTC hydrogen peroxide is on the order of ~3%)
- possible: apple cider vinegar
- soap/alcohol (95–100%)
- dryer heat
What type of antibiotics are used to treat MRSA?
Top 10 List of Brand Name Antibiotics
- Augmentin
- Flagyl, Flagyl ER
- Amoxil
- Cipro
- Keflex
- Bactrim, Bactrim DS
- Levaquin
- Zithromax
- Avelox
- Cleocin
How has MRSA become resistant to the antibiotic?
What Causes MRSA Antibiotic Resistance?
- Overview. MRSA is the acronym used for all strains of Staph bacteria that have developed resistance to methicillin, and related antibiotics.
- More Antibiotics, More MRSA. ...
- Examples that Lead To Resistance. ...
- Mechanism for MRSA Antibiotic Resistance. ...
- Future Concerns. ...
How to treat a MRSA infection naturally?
How to Treat a MRSA Infection Naturally
- Warm Compresses. To treat the swollen, red, painful bumps on the skin caused by a CA-MRSA infection, it is important to apply a warm compress on the affected area.
- Turmeric. A natural spice, turmeric is an effective home treatment for a CA-MRSA infection. ...
- Aloe Vera. ...
- Garlic. ...
- Manuka Honey. ...
- Oil of Oregano. ...
- Colloidal Silver. ...
- Tea Tree Oil. ...
- Indian Lilac. ...

Which of the following antibiotics is most effective against MRSA?
Vancomycin continues to be the drug of choice for treating most MRSA infections caused by multi-drug resistant strains. Clindamycin, co-trimoxazole, fluoroquinolones or minocycline may be useful when patients do not have life-threatening infections caused by strains susceptible to these agents.
What is the first line treatment for MRSA?
Oral antibiotics. Some antibiotics available in oral formulations are treatment options for MRSA: First-line therapy: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX; Bactrim DS, Septra DS. Sulfamethoprim-DS). This agent has been shown to be 95% effective.
What oral antibiotics cover MRSA?
For the outpatient management of possible or proven MRSA infection, we suggest oral antibiotic therapy with clindamycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or a long acting tetracycline such as minocycline or doxycycline (Grade 2B).
Is doxycycline effective against MRSA?
Oral antibiotics belonging to the tetracycline family, including minocycline and doxycycline, provide an effective means of treating CA-MRSA infections. As stated above, incision and drainage remains the single most important intervention against CA-MRSA infections, which present as abscess-like lesions.
Linezolid (Brand Names: Zyvox, Zyvoxid Or Zyvoxam)
Approved for use in the year 2000, Linezolid is FDA approved for treating soft tissue and skin infections, including those caused by MRSA. It is of...
Mupirocin (Brand Name: Bactroban)
Commonly used as a topical cream for minor skin infections and skin lesions for Staph aureus, MRSA and Streptococcus infections. Mupirocin ointment...
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (Brand Name: Septra Or Bactrim)
It is not FDA-approved for the treatment of Staphylococcal infections (including MRSA). However, laboratory tests have shown most CA-MRSA strains a...
Tetracyclines (Doxycycline and Minocycline)
Data suggests these drugs are effective in treatment of soft tissue and skin infections, but not for deeper or more severe infections. 1. Side Effe...
Intravenous (IV) Vancomycin
Vancomycin is often called an antibiotic of last resort for MRSA, though resistance against it has been growing. Vancomycin requires IV administrat...
Intravenous (IV) Daptomycin
Daptomycin is FDA approved for adults with Staph aureus bacteremia, some forms of endocarditis and some skin and soft tissue infections. The safety...
Which antibiotic has the highest daily cost?
Antibiotics with once-daily dosing such as the quinolones have advantage in regard to compliance. Linezolid has the highest daily cost of treatment whereas the cost of the tetracyclines, erythromycin, and TMP-SMX is much lower.
Can you take antibiotics for MRSA?
Treatment options for MRSA infection are limited, complicated and expensive. Oral antibiotics have been used in the outpatient setting for less severe MRSA infections such as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), but their efficacy has not been well studied.
How to diagnose MRSA?
Doctors diagnose MRSA by checking a tissue sample or nasal secretions for signs of drug-resistant bacteria. The sample is sent to a lab where it's placed in a dish of nutrients that encourage bacterial growth. But because it takes about 48 hours for the bacteria to grow, newer tests that can detect staph DNA in a matter ...
Can antibiotics help with MRSA?
Treatment. Both health care-associated and community-associated strains of MRSA still respond to certain antibiotics. Doctors may need to perform emergency surgery to drain large boils (abscesses), in addition to giving antibiotics. In some cases, antibiotics may not be necessary.
What antibiotics are used for MRSA?
Common antibiotics for treatment of MRSA include sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim, clindamycin, vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, tedizolid, doxycycline, minocycline, omadacycline, and delafloxacin. Your treatment may vary due to the nature of a MRSA infection, your medical history, and other prescriptions you may be taking.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Antibiotics. Depending on your specific antibiotic resistance with a MRSA infection, you may be given one or more antibiotic treatments to try. Antibiotics are the most commonly used and accepted form of treatment for MRSA patients because the condition is caused by bacteria.
What does the R in MRSA stand for?
By definition, MRSA is a condition that involves antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In fact, the R in MRSA stands for resistant. This makes it difficult to find the appropriate treatment because MRSA may not respond to dozens of antibiotics which are usually used for similar types of infections.
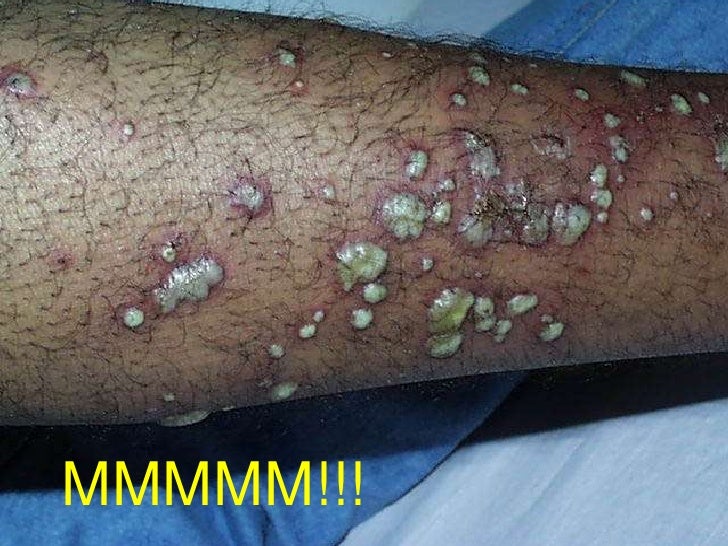
What are the symptoms of MRSA?
You may notice a skin infection that resembles a spider bite, large pimple, or a red and painful bump.
What is the most common type of bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is a specific type of bacteria, also called staph, which can cause infection and has become resistant to common antibiotic treatments, such as methicillin. CDC.gov estimates that 5% of patients in United States hospitals are carriers for MRSA via their skin or nose.
How does MRSA spread?
The spread of MRSA in the general community is typically through the sharing of personal items such as razors, washcloths, towels, or other items that may have come into contact with the infected skin.
How long does MRSA treatment last?
This will depend on the type of treatment and the location of the MRSA. Typically, you can expect treatment to last for 7 to 14 days, although you may notice it clear up before you finish your antibiotic treatment. It’s critical to complete your entire course of prescribed antibiotics.
Do you need antibiotics for boils?
Antibiotics, however, aren't always necessary. If you have a small skin boil caused by MRSA, your doctor may just make an incision and drain it. If you are prescribed antibiotics, follow your health care provider's instructions precisely. Never stop taking your medicine, even if you're feeling better.
Can you take antibiotics for MRSA?
By definition, MRSA is resistant to some antibiotics. But other kinds of antibiotics still work. If you have a severe infection, or MRSA in the bloodstream, you will need intravenous antibiotics. Unfortunately, there is emerging antibiotic resistance being seen with some of these medications.
Can MSRA be diagnosed without a test?
Often skin infections caused by MRSA are diagnosed clinically, without any tests. Since MSRA is now so prevalent, if staph is suspected, your doctor, as a course will; treat for MRSA. If tests are run, they will likely do a culture of an open sore for MRSA.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Vancomycin or daptomycin are the agents of choice for treatment of invasive MRSA infections [1]. Alternative agents that may be used for second-line or salvage therapy include telavancin, ceftaroline, and linezolid. Recent studies of treatment of MRSA bacteremia are reviewed. Vancomycin.
How much daptomycin should I take for MRSA?
This is reflected in the Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for treatment of MRSA infections, where daptomycin dosing is recommended at 8 to 10 mg/kg for complicated bacteremia and in combination with other agents if there has been prior vancomycin treatment failure [1].
What is the fifth generation of cephalosporin?
Ceftaroline. Ceftaroline is a fifth-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity against MRSA and VISA as well as Gram-negative pathogens [14]. Ceftaroline fosamil, the pro-drug of ceftaroline, received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2010.
When was telavancin approved?
Telavancin was approved in November 2009 in the United States for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), and in June 2013 in US for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) caused by gram-positive pathogens including MRSA where alternative treatments are not suitable.
Is daptomycin a good substitute for vancomycin?
Daptomycin is an acceptable alternative to vancomycin for treatment of MRSA bacteremia. Historically, daptomycin has been used as salvage therapy in patients failing vancomycin therapy, particularly with high vancomycin MIC infections, but increasingly it is being used as initial therapy in high inoculum MRSA infections.
Is telavancin effective for MRSA?
Telavancin may prove effective for treatment of MRSA bacteremia. In a phase 2 trial of telavancin for treatment of bacteremia including 17 patients, cure rates were comparable for telavancin and standard therapy (88 vs 89%) [8].
Is vancomycin bactericidal?
aureus. Furthermore, vancomycin is slowly bactericidal, which may be partly responsible for reported clinical failures in treatment of bacteremia and endocarditis.