Laser treatment was started after completion of plaque therapy. LASERTHERAPY All photocoagulationwasperformed withanindirect ophthalmoscope argon laser (Coherent, Inc) set on the green wavelength. The first laser
Full Answer
Can plaque radiotherapy be used to treat a medium-size choroidal melanoma?
· Non-coagulative laser treatment techniques include low-power long-exposure treatment techniques making use of a conventional argon blue-green laser 4 or infrared laser. 5 Depending on the wavelength of the laser used the lesions are located deeper in the choroid when infrared or near infrared lasers are used and lesions created by argon blue-green lasers do not …
How is the course of radioactive plaque therapy planned?
Radiation plaque therapy may cause eventual blurring, dimming, or rarely a total loss of vision in the treated eye. Plaque radiation does not affect the vision in the other eye. The amount of vision loss depends on what your vision was before treatment, how close the tumor is to the area of central vision of the eye, and how sensitive your tissues are to radiation.
What are the side effects of radioactive plaque treatment?
Most choroidal melanomas are currently treated with plaque brachytherapy. However, the ensuing complications frequently compromise posttreatment vision. The purpose of this review is to …
What is the treatment for choroidal melanoma?
Treatment of choroidal melanoma has evolved from primary enucleation to local resection, laser photocoagulation, and, most commonly, eye- and vision-sparing radiation therapy. 3,4 More …
Does laser treatment cure retinopathy?
Laser photocoagulation may help slow or stop this disease. But laser treatment can't always be used for diabetic retinopathy. Sometimes you may need eye surgery or eye shots (injections).
Can laser treatment damage eyes?
Thermal, mechanical, and photochemical damage to ocular structures caused by lasers include corneal burns, uveitis, cataract formation, and retinal burns. Common patient symptoms are blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and conjunctival hyperemia.
What happens after brachytherapy plaque?
Most people eventually lose vision in the area of their eye where the plaque was placed. The amount of vision loss depends on where the plaque was placed. You may notice vision loss 12 to 18 months after your treatment. You can talk with your doctor about the possibility of vision loss in your eye.
What is the purpose of a laser in radiation therapy treatment?
Laser therapy uses an intense, narrow beam of light to remove or destroy cancer and abnormal cells that can turn into cancer. Tumor cells absorb light of different wavelengths (or colors) than normal cells do. So, tumor cells can be targeted by selecting the proper wavelength of the laser.
What is the side effect of laser treatment?
Pigment changes. Rarely, laser hair removal can cause blistering, crusting, scarring or other changes in skin texture. Other rare side effects include graying of treated hair or excessive hair growth around treated areas, particularly on darker skin.
How long does it take a laser to damage your eye?
Laser pointers can put out anywhere between 1 and 5 milliwatts of power, which is enough to damage the retina after 10 seconds of exposure. This can lead to permanent vision loss. That said, it can be very difficult to expose the retina to that much light for that long a time.
Is the eye plaque procedure is temporary?
The radiation is usually delivered to the tumor by placing a radioactive plaque on your eye, directly over the tumor in a procedure called brachytherapy. The plaque is held in place with temporary stitches. The plaque looks similar to a bottle cap and contains several radioactive seeds.
Does radiation hurt your eyes?
The main concern with radiation therapy is damage to parts of the eye, leading to problems such as blurry vision, dry eye, cataracts, retinal detachment, glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye), loss of eye lashes, problems with tear ducts, or bleeding into the eye.
What is the survival rate for ocular melanoma?
The 5-year survival rate for eye melanoma is 82%. When melanoma does not spread outside the eye, the 5-year relative survival rate is about 85%. The 5-year survival rate for those with disease that has spread to surrounding tissues or organs and/or the regional lymph nodes is 71%.
Is laser treatment safe?
Laser treatment is extremely safe. Technological and medical advances in recent years have significantly lowered the chances of serious side effects.
What are the benefits of laser treatment?
Laser treatment is safe and effective at treating:Sunspots.Uneven pigmentation.Red and brown spots.Fine lines & wrinkles.Skin laxity.Spider veins.Hair removal.
What are the advantages of laser surgery?
Use of the laser minimizes the risk of damage to adjacent tissues when compared to traditional surgical methods. Therefore, healing time is quicker and there is less post op discomfort than with traditional methods which require a scalpel and/or cauterizing procedure.
How do I know if a laser damage my eye?
Symptoms of a laser burn in the eye include a headache shortly after exposure, excessive watering of the eyes, and sudden appearance of floaters in your vision. Floaters are those swirling distortions that occur randomly in normal vision most often after a blink or when eyes have been closed for a couple of seconds.
What laser power is eye safe?
Class 2 visible-light lasers are considered safe for unintentional eye exposure, because a person will normally turn away or blink to avoid the bright light. Do NOT deliberately stare into the beam -- this can cause injury to the retina in the back of the eye. Be aware of beam reflections off glass and shiny surfaces.
Can laser hair removal make you blind?
Resurfacing lasers pose a threat to the cornea and ocular surface. Ocular injuries associated with lasers include misshapen pupils, iritis and vision loss.
Can cold laser damage eyes?
Cold laser therapy should not be used over any suspicious cancerous lesions, or carcinoma, over the thyroid, on pregnant patients, and there should not be direct irradiation of the eyes, as the laser can cause permanent damage to the eyes.
How much tumor regression is needed for TTT?
When TTT was introduced in the treatment of choroidal melanoma, short-term follow-up data impressively showed that in appropriate cases tumor regression may be achieved in more than 90%. Tumors considered being appropriate for TTT included melanomas with a largest tumor diameter of <12 mm and not more than 4 mm thickness located posterior to the equator where the clinical diagnosis of a malignant melanoma was established. 8,15
What is TTT in medical terms?
The term “transpupillary thermotherapy” (TTT) was introduced by Journée-de Korver et al. 5 to describe a technique in which a near-infrared or infrared light source for long-term exposure laser treatment of uveal melanomas is used. There is controversy in the literature on whether the word “thermotherapy” is appropriate, or whether this treatment technique should be regarded as long-exposure subthreshold photocoagulation using a long wavelength light source, since a whitish-gray discoloration of the target tissue at the end of the procedure is recommended. 7 As published by Journée-de Korver et al. 5 thermotherapy is different from hyperthermia, which by definition is heating the tumor to a temperature of 42–44°C to enhance the cytotoxic effect of ionizing radiation on tumor cells. In TTT, temperatures of approximately 45–60°C within the tumor are reached with irreversible cytotoxic effects so that additional radiotherapy may be not required. 8
What is the best treatment for choroidal melanoma?
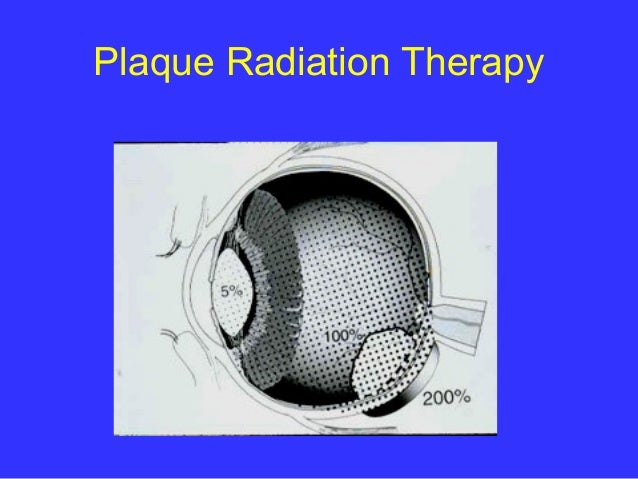
Radiation plaque therapy is the most commonly used “eye-sparing” treatment for choroidal melanoma.
How long does it take to remove a radioactive plaque from the eye?
The conjunctiva is then sewn back over the plaque. Patients remain in the hospital for about three to five days at which time the plaque is surgically removed.
How long does it take for a conjunctiva to heal after surgery?
The conjunctiva is then sewn back over the plaque. Patients remain in the hospital for about three to five days at which time the plaque is surgically removed. Most patients have no problems associated with plaque surgery.
Does radiation affect vision?
Plaque radiation does not affect the vision in the other eye. The amount of vision loss depends on what your vision was before treatment, how close the tumor is to the area of central vision of the eye, and how sensitive your tissues are to radiation.
What is plaque radiotherapy?
Plaque radiotherapy is now the first line of treatment for patients with medium-size melanomas. In the natural history study of small melanomas (1 to 3 mm in apical height and at least 5 mm in diameter), delay or refusal of treatment was associated with an increased incidence of metastatic disease and/or early death when compared ...
What are the factors that determine the management of choroidal melanoma?
Management of choroidal melanoma depends on several factors including patient age, tumor size and location, systemic health of the patient, and the status of the other eye.
When did choroidal melanomas start?
The treatment of choroidal melanomas with radiation began in 1929 with the use of radon seeds, 10 and later with cobalt 60. 11 Plaque radiotherapy remains the gold standard for the treatment of medium-size choroidal melanomas, as in the current case.
Is enucleation a treatment for melanoma?
Before the 1970s , enucleation was the most common management of malignant melanoma. However, in a landmark paper, Zimmerman and colleagues 4 suggested that enucleation itself might be associated with increased risk of metastatic disease. Controversy over the effectiveness of enucleation for the treatment of uveal melanoma prompted the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study (COMS) in 1986. 5 The trial included 3 substudies: a large-size tumor trial comparing enucleation vs enucleation preceded by external radiation; a medium-size tumor trial comparing enucleation and brachytherapy; and a natural history study of small melanomas. 6 In the first arm of the study, patients with large-size melanomas (more than 8 mm in thickness and/or greater than 16 mm in longest base diameter) were randomized between enucleation alone and enucleation preceded by external radiation (2000 centigrays). 7 At 5- and 8-year follow-ups, radiation neither favorably nor unfavorably influenced outcomes in terms of local orbital complications or 5-year survival. Adjunct radiation therapy for large-size tumors has subsequently fallen out of favor.
Why is choroidal melanoma treated?
In general, choroidal melanoma treatment is performed to prevent metastatic disease, to maximize visual acuity, and to preserve the eye.
What causes vision loss after radiation?
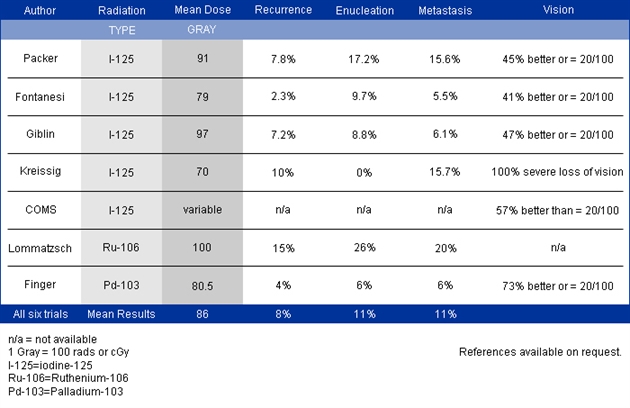
In a 1997 review, more than 50% of patients were noted to have less than 20/200 vision at or before 5 years after radiation therapy.3 Although this was allcause visual morbidity, the most common causes of severe irreversible loss of vision were radiation maculopathy and radiation optic neuropathy.
What is the procedure for a melanoma?
Enucleation. Enucleation surgery is typically performed when the melanoma is considered too large for eye-sparing techniques, there is no vision, there is extensive extrascleral tumor extension, and in painful, glaucomatous eyes. 3,4 Additionally, in developing countries it may be performed when eye- and vision-sparing radiation techniques are not available.
How does Cole Eye Institute remove radioactive plaque?
The implantation and removal of the radioactive plaque is generally performed under local anesthesia with sedation by specialists from Cole Eye Institute. This requires one or more injections around the eye to numb it. There is likely to be a moderate amount of pain on the day of surgery after the anesthesia wears off.
What is a radioactive plaque?
Contact Us. A radioactive plaque is a sealed device that delivers a high dose of radiation to a tumor. The plaque is positioned on the surface of the eyeball directly over the tumor inside the eye. The plaque gives off radiation constantly while in place on the wall of the eyeball.
How long does it take for a tumor to shrink?
It may be three to six months before definite signs of tumor shrinkage can be established. Occasionally, a tumor appears to enlarge minimally during the initial months after treatment before it begins to shrink. A treated tumor almost never disappears completely, leaving behind a residual lump that may persist indefinitely.
How long does pain killer last in Cleveland Clinic?
Pain killers are provided during the hospital stay. Most of the severe discomfort is gone within the first 24 to 48 hours. Patients typically stay at Cleveland Clinic main campus for three to five days. Mild headaches and scratchiness of eye may persist for about two weeks.
How long does it take for a swollen eye to heal after a radioactive scleral
Although the eye may remain red and somewhat scratchy for about two weeks, you can expect to return to most of your normal activities within a week after your hospital discharge.
Can you get radioactive plaque off your glasses?
No. Once the plaque is removed, there will be no residual radioactivity in your body, on your clothing, your glasses or any other personal belongings.
Can you leave a room while a radioactive plaque is in place?
You are not permitted to leave your room and walk the halls while the radioactive plaque is in place.
Why do doctors watch small choroidal melanomas?
Many eye cancer specialists watch small choroidal melanomas for evidence of tumor-growth prior to treatment. This is because current belief is that “small choroidal melanomas” carry a low risk (6-10%) for metastases and that all current treatments risk severe vision loss. [9-11] Current observation of small choroidal melanomas is justified by the concept that “tumor-growth demonstrates malignancy.” In practice, documented tumor growth both reassures the doctor that the tumor is malignant and reassures the patient that treatment is indicated. Specifically, the risk of treatment-related loss of vision is more than offset by a reduction in the probability of metastasis and tumor-induced vision loss.
What is the potential to diagnose small choroidal melanoma?
Current research offers the potential to aid in the diagnosis of small choroidal melanoma. Onken, Harbour et al are exploring the use of molecular and genetic markers to assess a tumors metastatic potential.14 Genetic studies suggest that monosomy 3, together with other genetic markers may define a tumor’s metastatic potential. Similarly, physiologic-radiographic imaging (such as PET/CT) may offer the potential to assess a tumors metabolic activity and metastatic potential.15-18
Can eye cancer be classified as choroidal?
Current practice dictates that eye cancer specialists continue to perform clinical assessments, classify small choroidal tumors and discuss the potential risks and benefits of observation, biopsy and treatment with each patient. Keep in mind that your doctors recommendation will be influenced by his or her experience with treatment-related risk for vision loss versus that due to metastatic melanoma. Further, physicians will determine the patient’s ability to understand what has been presented and recommend an approach to do the “least” harm.
Can choroidal nevus grow?
Very few eye cancer specialists would recommend continued observation once definitive tumor-growth has been documented. Choroidal nevi grow, but typically exhibit small changes over years of observation. Relatively rapid (e.g. months) and measurable tumor growth is consistent with malignancy. Therefore as currently practiced widely, documented rapid tumor enlargement indicates that a “suspicious choroidal nevus” is actually a malignant choroidal melanoma, and will (by continued enlargement and/or secondary retinal detachment) cause loss of vision. Once a small melanoma has grown, treatment offers the best chance for preservation of both life and vision in the affected eye.
Is choroidal melanoma malignant?
Once an eye cancer specialist is convinced that a tumor is a malignant (albeit small) choroidal melanoma, treatment becomes the most reasonable choice. In support of this approach, one can cite Packard’s and the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study’s (COMS) findings that increased tumor size (specifically largest tumor diameter – LTD) was associated with an increased risk of metastatic death. [10,11] Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that waiting for documentation of malignant melanoma growth increases (albeit marginally) a patient’s risk for metastases.
Can you observe choroidal melanomas?
This is particularly true for patients with small choroidal melanomas close to the fovea, monocular or systemically ill patients. In these cases, serial observation may allow for years of useful vision prior to treatment. For all patients, the case for observation of small melanoma growth has been governed by the potential benefit of vision preservation (in the affected eye).
Can choroidal melanoma be enucleated?
In the past, eyes were enucleated with the diagnosis of choroidal melanoma only to find simulating or benign lesions on histopathology. [4] The advent and evolution of modern diagnostic techniques such as indirect ophthalmoscopy, ultrasonography, photography, angiography and subspecialty centers have improved our diagnostic ability to detect small changes in tumor size and patterns of leakage.
What is slaser therapy?
sLaser therapy is sometimes used to treat eye melanoma, especially when surgery or radiation are not possible.
Does TTT kill melanomas?
It uses infrared light to heat and kill the tumor. TTT alone is mainly used to treat very small eye melanomas because of side effects like bleeding, retinal detachment and blockage of blood vessels in the eye, as well as a high risk of recurrence (cancer coming back).
Can laser therapy cause vision loss?
As with radiation therapy, the main concern with laser therapy is damage to parts of the eye that could result in loss of vision. The risk depends on the size and location of the tumor.
