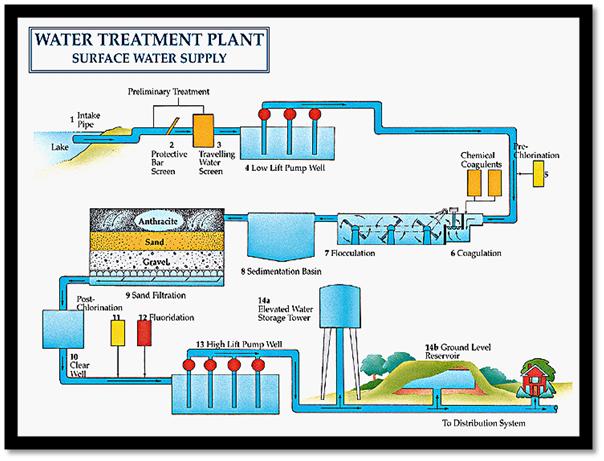
Nonetheless, the following steps demonstrate how a raw water treatment system will usually work:
- Intake. Raw water is drawn into a plant through gravity and/or pumps. ...
- Clarification. The water then continues for clarification, which is a multistep process used to remove suspended solids from a solution. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Lime softening. ...
- Ion exchange (IX). ...
- Distribution. ...
- Membrane filtration. ...
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
The first step of treatment is to remove the settleable and dissolved solids suspended in the water. In order to speed the settling and removal process …
How does a sewage treatment plant actually work?
Most of the water treatment plants make use of a sand filter. The sand filter is low-tech but is a very efficient way of carrying out water purification. Once the water reaches the filtration phase, it is made to pass through differing coarseness of sand. Particles keep on getting trapped as the coarseness of the sand filter decreases.
What are the steps of the water treatment process?
Nov 21, 2018 · For most everyone around the world, turning on your tap and getting fresh clean water is just a way of life. While this might seem to be a simple fact of mod...
What is the largest water treatment plant in the US?
Primary Treatment As sewage enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen, which removes large floating objects such as rags and sticks that might clog pipes or damage equipment. After sewage has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.

What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Learn More. ... Recommended Readings.
What are the steps of a water treatment plant?
They typically consist of several steps in the treatment process. These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution. Let's examine these steps in more detail.Dec 16, 2021
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.Nov 7, 2015
What are the 3 stages of water treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
How is water treatment done?
A common water treatment plant involves the following processes: (1) pretreatment to remove big objects that can be found in the pipelines that transport water from the supply to the treatment plant, (2) softening and/or coagulation for the removal of hardness and/or suspended particles, (3) filtering through sand beds ...
What is aeration in water treatment?
Aeration treatment consists of passing large amounts of air through water and then venting the air outside. The air causes the dissolved gases or volatile compounds to release from the water.Aug 23, 2019
How does coagulation work in water treatment?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.Apr 14, 2022
What are the resources used in water treatment?
The local water treatment plants usually rely on natural resources for procuring water, however; that is not always the case. The resources include river, dam, and well. The water that is obtained from these sources is treated thus making it safe for humans to consume at a mass level.
What are the three approaches to water treatment?
There are three approaches that can be employed; chlorination, ozone treatment, and ultraviolet treatment . These approaches can be used either individually or in combination. Once all of these steps are completed, water is pumped out to be used by the population. Check out the video below to learn more about water treatment.
What is the process of removing particles from water?
The process is not simple and begins with coagulation and flocculation. This particular process is responsible for removing all of the natural particles that accompany water from the actual water source. Coagulants, when added to the water, can make the debris stick together. An example of a typical coagulant is aluminum sulfites ...
What are some examples of coagulants?
An example of a typical coagulant is aluminum sulfites that possess a charge opposite to that of the suspended solids. As you all know, opposite charges attract; coagulant and suspended solids become attached to one another. These coagulants are introduced in the water when it enters the treatment plant.
Does filtration remove bacteria?
However, filtration helps remove the bacteria as well. Most of the water treatment plants make use of a sand filter. The sand filter is low-tech but is a very efficient way of carrying out water purification. Once the water reaches the filtration phase, it is made to pass through differing coarseness of sand.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment. Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment, also called biological stage, is based on natural processes. WWTPs use bacteria which consume the contaminants, in particular biodegradable organics, carbon and phosphorus. Dead bacteria and organic residues subsequently transform into sludge. 6.
What is industrial water treatment?
An industrial water treatment system treats water so it is more appropriate for a given use, whether for consumption, manufacturing, or even disposal. That said, each system will vary depending on the facility’s needs and many of the technologies that make up these systems can be similar.
What is raw water?
What they are. Raw water is any untreated water that occurs naturally in the environment, including sources such as rainwater, groundwater, wells, lakes, and rivers. In industrial settings, raw water may be used for cooling, rinsing, product formulations, or even human consumption if it is properly purified.
What is boiler feed water?
A boiler feed water treatment system will typically include some or all of the following steps: Makeup water intake. As boilers are used, they lose water to steam consumption, loss of condensate return, and leaks. This water must be replaced with what is known as makeup water.
What is a membrane filtration unit?
When used for pretreatment ahead of IX and other equipment, membrane filtration units can be a cost-effective means of preventing fouling and excess maintenance of downstream equipment. Softening. IX is often used for removing hardness from boiler feed water, including bicarbonates, sulfates, chlorides, and nitrates.
What is post treatment?
There are various types of post-treatment options that may be used depending upon plant conditions. If large quantities of water are required for cooling, or if water is scarce at the facility’s location, plants may opt to treat the blowdown water with RO or IX and reuse it.
What are the contaminants in wastewater?
While the contaminants present in a waste stream can vary greatly from one process to the next, wastewater treatment systems commonly treat for biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), nitrates, phosphates, pathogens, metals, TSS, TDS, and synth etic chemicals.
Can water be disinfected?
If biological contamination and/or water potability is a concern, the water may then be disinfected to remove any pathogens. Disinfection may be accomplished through the application of chemical disinfectants (e.g. chlorine), physical disinfectants (e.g. UV or heat), as well as some forms of membrane filtration. Lime softening.
What is the role of chlorine in water?
Chlorine acts as a barrier between germs and water. It also reacts to any organic agent available in the water. The reaction between chlorine-based compounds and organic agents can generate carcinogens and other harmful chemicals. Also, it protects water all through the distribution process.
What happens when you add chlorine to water?
Once chlorine is added to water, the remaining chlorine present in water is less concentrated. Chlorine acts as a barrier between germs and water. It also reacts to any organic agent available in the water.
What is UV in water?
What is UV? UV is Ultraviolet radiation, an energy band within the electromagnetic energy spectrum. It is a colorless, tasteless, odorless and chemical free way to ensure your water supply is safe and clear of germs and other microorganisms that can make you sick.
What are the advantages of UV disinfection?
UV has many advantages over other disinfection processes: 1 UV is effective and quick. No need for holding tanks and reaction times. No need for storing chemicals. 2 UV does not alter the taste of water, which makes it ideal for use in bottling plants and food processing applications. 3 UV is safe. NO need to add or handle hazardous chemicals or risk polluting the environment. 4 UV is compatible with all other water treatment processes. No need for de-chlorination if using RO systems. In fact, UV enhances the use of other water treatment by keeping them free from germs. 5 UV is economical. Almost always, the cost of UV disinfection units is much less than the cost of chemical treatment systems. The cost of service and maintenance of UV units is very low. The electrical running cost of an UV unit in a house is about that of a regular light bulb. 6 UV is more effective against viruses than chlorine. 7 Easy installation. UV units are very easy to install and require very little space.
What temperature should UV light be?
UV units are normally designed to operate best between two and forty degree Celsius. Freezing will cause damage to the UV unit and water temperature higher than forty degree C will cause a reduction in UV energy and therefore, a reduced germ kill ratio.
Is UV disinfection safe?
No need for storing chemicals. UV does not alter the taste of water, which makes it ideal for use in bottling plants and food processing applications. UV is safe.
