Valproate products are FDA-approved drugs to treat seizures. Some valproate products are also approved to treat manic
Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect." Although mania is often conceived as a "mirror image" to depression, the heightened mood can be either euphoric or irritable; indeed, as the mania intensifies, irritability can be more pro…
Are there any unapproved uses of valproate?
They are also used off-label (for unapproved uses) for other conditions, particularly for other psychiatric conditions. Valproate products include: valproate sodium (Depacon), divalproex sodium (Depakote, Depakote CP, and Depakote ER), valproic acid (Depakene and Stavzor), and their generics.
When should valproate be discontinued?
Valproate should be discontinued and not be resumed if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established. Carbapenem antibiotics (for example, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem; this is not a complete list) may reduce serum Valproate concentrations to subtherapeutic levels, resulting in loss of seizure control.
Does valproate reduce the incidence of central venous insufficiency syndrome?
The second study assessed the capacity of valproate to reduce the incidence of CPS when administered as the sole AED. The study compared the incidence of CPS among patients randomized to either a high or low dose treatment arm.
How many mg of valproate are in a ML?
Each mL contains Valproate sodium equivalent to 100 mg valproic acid, edetate disodium 0.40 mg, and water for injection to volume. The pH is adjusted to 7.6 with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid. The solution is clear and colorless. Valproate sodium exists as the Valproate ion in the blood.

What is Depakote FDA approved for?
Depakote (divalproex sodium) is a valproate and is indicated for the treatment of the manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder. A manic episode is a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood.
When was valproate approved by the FDA?
2008Stavzor (valproic acid) Delayed Release Capsules Initial U.S Approval: 2008 WARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Noven Therapeutics, LLC at 1-800-455-8070 or FDA at 1-800- FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
What is valproic acid commonly prescribed to treat?
1. About valproic acid. Valproic acid is used to treat bipolar disorder. It's occasionally used to prevent migraine and can also be used to treat epilepsy. This medicine is only available on prescription.
Is Depakote FDA approved for bipolar maintenance?
Butler M, Urosevic S, Desai P, et al. Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review [Internet]....Table 1FDA-approved medications for bipolar disorder.Drug TypeAnticonvulsantsGeneric Name First Date ApprovedDivalproex sodium* or valproate 1995FDA –Listed Trade Name (Pharmaceutical Co.)Depakote (ABBVIE)ManicX13 more columns
What is valproate used for?
About sodium valproate Sodium valproate is used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder. It's occasionally used to prevent migraine headaches. This medicine is only available on prescription. It comes as capsules, tablets and a liquid that you swallow.
Is valproate FDA approved for migraine?
Valproate products are FDA-approved drugs to treat seizures. Some valproate products are also approved to treat manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar disorder (manic-depressive disorder), or for the prevention of migraine headaches.
Is valproate an antipsychotic?
Background. Many people with schizophrenia do not achieve a satisfactory treatment response with ordinary antipsychotic drug treatment. In these cases, various add‐on medications are used, and valproate is one of these.
Is valproic acid used for depression?
Conclusions: Valproate is effective for the reduction of depressive symptoms of acute bipolar depression, and was well tolerated.
How does sodium valproate treat epilepsy?
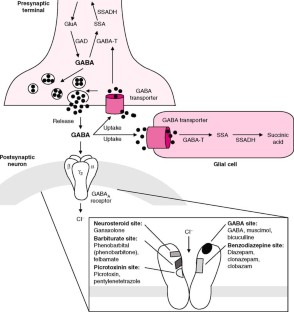
Sodium valproate prevents epileptic fits by stabilising excessive electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to achieve this in two ways: by increasing the activity of a natural 'nerve-calming' agent called GABA in the brain, and by preventing electrical signals from building up in nerve cells in the brain.
What is FDA approved for bipolar depression?
Results: Olanzapine-fluoxetine combination (OFC), quetiapine, and lurasidone are FDA-approved for the acute treatment of bipolar depression. Lurasidone is the most recently approved agent for bipolar depression.
What drugs are FDA approved for bipolar disorder?
Three drugs are FDA-approved for the treatment of bipolar depression: quetiapine (Seroquel) by itself, olanzapine (Zyprexa) when used with fluoxetine (Prozac) (which also comes as a combination pill called Symbyax), and lurasidone (Latuda) used alone or with lithium or valproate (Depakote).
What is lithium FDA approved for?
Lithium is indicated in the treatment of manic episodes of Bipolar Disorder. Bipolar Disorder, Manic (DSM-III) is equivalent to Manic Depressive illness, Manic, in the older DSM-II terminology. Lithium is also indicated as a maintenance treatment for individuals with a diagnosis of Bipolar Disorder.
Does ritonavir increase valproate?
Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases (such as ritonavir), may increase the clearance of Valproate. For example, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital (or primidone) can double the clearance of Valproate.
Can Valproate cause pancreatitis?
Cases of life-threatening pancreatitis have been reported in both children and adults receiving Valproate. Some of the cases have been described as hemorrhagic with a rapid progression from initial symptoms to death. Cases have been reported shortly after initial use as well as after several years of use.
Is Valproate sodium safe for bipolar?
Although Valproate Sodium Injection has not been evaluated for safety and efficacy in the treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, the following adverse reactions not listed above were reported by 1% or more of patients from two placebo-controlled clinical trials of divalproex sodium tablets.
Does Valproate cause thrombocytopenia?
Valproate is associated with dose-related thrombocytopenia. In a clinical trial of divalproex sodium as monotherapy in patients with epilepsy, 34/126 patients (27%) receiving approximately 50 mg/kg/day on average, had at least one value of platelets ≤ 75 x 109/L. Approximately half of these patients had treatment discontinued, with return of platelet counts to normal. In the remaining patients, platelet counts normalized with continued treatment. In this study, the probability of thrombocytopenia appeared to increase significantly at total Valproate concentrations of ≥ 110 mcg/mL (females) or ≥ 135 mcg/mL (males). The therapeutic benefit which may accompany the higher doses should therefore be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse effects. Valproate use has also been associated with decreases in other cell lines and myelodysplasia.
Does valproate affect IQ?
Valproate can cause decreased IQ scores following in utero exposure. Published epidemiological studies have indicated that children exposed to Valproate in utero have lower cognitive test scores than children exposed in utero to either another antiepileptic drug or to no antiepileptic drugs. The largest of these studies 1 is a prospective cohort study conducted in the United States and United Kingdom that found that children with prenatal exposure to Valproate (n = 62) had lower IQ scores at age 6 (97 [95% C.I. 94-101]) than children with prenatal exposure to the other antiepileptic drug monotherapy treatments evaluated: lamotrigine (108 [95% C.I. 105–110]), carbamazepine (105 [95% C.I. 102–108]), and phenytoin (108 [95% C.I. 104–112]). It is not known when during pregnancy cognitive effects in Valproate-exposed children occur. Because the women in this study were exposed to antiepileptic drugs throughout pregnancy, whether the risk for decreased IQ was related to a particular time period during pregnancy could not be assessed.
Can you take Valproate while pregnant?
Because of the risk to the fetus of decreased IQ, neurodevelopmental disorders, neural tube defects, and other major congenital malformations, which may occur very early in pregnancy, Valproate should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.2, 5.3, 5.4), USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS ( 8.1), and PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION ( 17) ].
Does Valproate stimulate HIV replication?
The clinical consequence, if any, is not known. Additionally, the relevance of these in vitro findings is uncertain for patients receiving maximally suppressive antiretroviral therapy. Nevertheless, these data should be borne in mind when interpreting the results from regular monitoring of the viral load in HIV infected patients receiving Valproate or when following CMV infected patients clinically.
What antiepileptics are used in the NEAD study?
The NEAD study included mothers with epilepsy who were taking one of four different antiepileptic drugs as monotherapy : lamotrigine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, or valproate products. 1,2 The study compared the results of IQ tests when children who had been exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero were 6 years old.
What does Category D mean for a drug?
Category D means there is positive evidence of risk to a baby based on data from studies or other experience in humans, but the potential benefits from the use of the drug in pregnant women may be acceptable despite its potential risks.
Can you take Valproate while pregnant?
Additional Information for Patients. Taking valproate during pregnancy can decrease your child’s IQ. There is also a higher risk of birth defects if you take valproate during pregnancy. If you are a woman of childbearing age and are taking a valproate product, you should use effective birth control.
Is valproate safe for pregnant women?
With regard to women of childbearing age who are not pregnant, valproate should not be taken for any condition unless the drug is essential to the management of the woman's medical condition.
Is Valproate approved for migraines?
Valproate products are approved for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy, the treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, and the prevention of migraine headaches. They are also used off-label (for uses not approved by FDA) for other conditions, particularly other psychiatric conditions.
Does the FDA update the label for Valproate?
FDA is working with manufacturers to change the drug labels for valproate products with this updated risk information. FDA continues to evaluate information about the potential risks of valproate use during pregnancy and will update the public as more information becomes available.
Can you give Valproate to a woman?
Valproate products should not be administered to a woman of childbearing age unless the drug is essential to the management of her medical condition. This is especially important when valproate use is considered for a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death (e.g., migraine).
How long does it take for valproate to work?
It will probably take several weeks to see big enough changes in your symptoms to decide if valproate is the right medication for you. Mood stabilizer treatment is generally needed lifelong for persons with bipolar disorder.
How much Valproate should I take?
The dose usually ranges from 1000 mg to 3500 mg or more. Only your healthcare provider can determine the correct dose for you, as sometimes the dose required is based on your weight. Valproate tablets: Swallow whole. Do not crush, chew or split tablets.
What medications can lower the effect of Valproate?
Aspirin (high doses to treat fever or pain) The following medications may decrease the level and effect of valproate: Anticonvulsant medications such as phenytoin (Dilantin®), carbamazepine (Tegretol®/Carbatrol®/Equetro®), and phenobarbital.
Why do I bruise so easily?
Platelets help the blood to clot. Bruising easier than normal is a symptom of low platelets. Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and not feeling hungry.
What is the generic name for Valproate?
Generic names: Valproate (val PROE ate) Divalproex (dye val PRO ex) sodium. Valproic (val PROE ik) acid. Note: Throughout this fact sheet, the medication will be referred to as valproate. Even though valproate is available in different names, strengths, and formulations, all provide the same active medicine.
What are the symptoms of mania?
Sleep and eat more or less than usual (for most people it is less) Low energy, trouble concentrating, or thoughts of death (suicidal thinking) Psychomotor agitation (‘nervous energy’) Psychomotor retardation (feeling like you are moving in slow motion) Symptoms of mania include: Feeling irritable or “high”.
What are the symptoms of bipolar disorder?
Symptoms of depression include: Depressed mood — feeling sad, empty, or tearful. Feeling worthless, guilty, hopeless, or helpless. Loss of interest or pleasure in normal activities. Sleep and eat more or less than usual (for most people it is less)
How is valproate metabolized?
Valproate is metabolized almost entirely by the liver. In adult patients on monotherapy, 30-50% of an administered dose appears in urine as a glucuronide conjugate. Mitochondrial β-oxidation is the other major metabolic pathway, typically accounting for over 40% of the dose. Usually, less than 15-20% of the dose is eliminated by other oxidative mechanisms. Less than 3% of an administered dose is excreted unchanged in urine.
How much Valproate should I take daily?
Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50-100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. Concomitant antiepilepsy drug (AED) dosage can ordinarily be reduced by approximately 25% every 2 weeks. This reduction may be started at initiation of Depakene therapy, or delayed by 1 to 2 weeks if there is a concern that seizures are likely to occur with a reduction. The speed and duration of withdrawal of the concomitant AED can be highly variable, and patients should be monitored closely during this period for increased seizure frequency.
Why should valproate be reduced?
Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly , the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence. The ultimate therapeutic dose should be achieved on the basis of both tolerability and clinical response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13), Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Is Valproate toxic to animals?
The no-effect dose for these findings was less than the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Does amitriptyline decrease clearance?
Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline Administration of a single oral 50 mg dose of amitriptyline to 15 normal volunteers (10 males and 5 females) who received valproate (500 mg BID) resulted in a 21% decrease in plasma clearance of amitriptyline and a 34% decrease in the net clearance of nortriptyline. Rare postmarketing reports of concurrent use of valproate and amitriptyline resulting in an increased amitriptyline level have been received. Concurrent use of valproate and amitriptyline has rarely been associated with toxicity. Monitoring of amitriptyline levels should be considered for patients taking valproate concomitantly with amitriptyline. Consideration should be given to lowering the dose of amitriptyline/nortriptyline in the presence of valproate.
Does phenytoin increase valproate clearance?
Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases, may increase the clearance of valproate. For example, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital (or primidone) can double the clearance of valproate. Thus, patients on monotherapy will generally have longer half-lives and higher concentrations than patients receiving polytherapy with antiepilepsy drugs.
Is Depakene safe for bipolar?
Although Depakene has not been evaluated for safety and efficacy in the treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, the following adverse reactions not listed above were reported by 1% or more of patients from two placebo-controlled clinical trials of Depakote tablets.
When to use Valproate?
Weigh the benefits and risks of valproate when prescribing this drug to women of childbearing age, particularly when treating a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death. Alternative medications that have a lower risk of adverse birth outcomes should be considered.
Can you stop taking Valproate while pregnant?
Valproate should not be stopped without talking to a healthcare professional, even in pregnant women. Stopping valproate suddenly can cause serious problems. Not treating epilepsy or bipolar disorder (manic-depressive disorder) during pregnancy can be harmful to women and their developing babies.
Does Valproate lower IQ?
This conclusion is based on the results of epidemiologic studies that show that children born to mothers who took valproate sodium or related products throughout their pregnancy tend to score lower on cognitive tests (IQ and other tests) than children born to mothers who took other anti-seizure medications during pregnancy.
Is Valproate sodium safe for children?
Safety Announcement. [6-30-2011] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is informing the public that children born to mothers who take the anti-seizure medication valproate sodium or related products (valproic acid and divalproex sodium) during pregnancy have an increased risk of lower cognitive test scores than children exposed ...
Does Valproate lower cognitive test scores?
Data Summary. Several published epidemiological studies have indicated that children exposed to valpro ate in utero have lower cognitive test scores than children exposed to either another antiepileptic drug in utero or to no antiepileptic drugs in utero.
Can you use birth control while taking Valproate?
Women of childbearing age who decide to take valproate should use effective birth control (contraception) while taking the drug. Women should talk to their healthcare professionals about the best kind of birth control to use while taking valproate.
How is valproate metabolized?
Valproate is metabolized almost entirely by the liver. In adult patients on monotherapy, 30-50% of an administered dose appears in urine as a glucuronide conjugate. Mitochondrial β-oxidation is the other major metabolic pathway, typically accounting for over 40% of the dose. Usually, less than 15-20% of the dose is eliminated by other oxidative mechanisms. Less than 3% of an administered dose is excreted unchanged in urine.
How much Valproate should I take for epilepsy?
The therapeutic range in epilepsy is commonly considered to be 50 to 100 mcg/mL of total valproate, although some patients may be controlled with lower or higher plasma concentrations.
How long does depacon stay in a PVC bag?
Depacon was found to be physically compatible and chemically stable in the following parenteral solutions for at least 24 hours when stored in glass or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) bags at controlled room temperature 15-30°C (59-86°F).
How much Depacon should I take daily?
Depacon has not been systematically studied as initial therapy. Patients should initiate therapy at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage should be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made.
Why should valproate be reduced?
Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly , the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence. The ultimate therapeutic dose should be achieved on the basis of both tolerability and clinical response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13), Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Is Valproate toxic to animals?
The no-effect dose for these findings was less than the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Does ritonavir increase valproate?
Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases (such as ritonavir), may increase the clearance of valproate. For example, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital (or primidone) can double the clearance of valproate. Thus, patients on monotherapy will generally have longer half-lives and higher concentrations than patients receiving polytherapy with antiepilepsy drugs.
How is valproate metabolized?
Valproate is metabolized almost entirely by the liver. In adult patients on monotherapy, 30-50% of an administered dose appears in urine as a glucuronide conjugate. Mitochondrial β-oxidation is the other major metabolic pathway, typically accounting for over 40% of the dose. Usually, less than 15-20% of the dose is eliminated by other oxidative mechanisms. Less than 3% of an administered dose is excreted unchanged in urine.
How much Valproate should I take for epilepsy?
The therapeutic range in epilepsy is commonly considered to be 50 to 100 mcg/mL of total valproate, although some patients may be controlled with lower or higher plasma concentrations.
How much Depakote should I take daily?
The dose should be increased as rapidly as possible to achieve the lowest therapeutic dose which produces the desired clinical effect or the desired range of plasma concentrations. In placebo-controlled clinical trials of acute mania, patients were dosed to a clinical response with a trough plasma concentration between 50 and 125 mcg/mL. Maximum concentrations were generally achieved within 14 days. The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day.
What is the drug used for manic episodes?
Depakote (divalproex sodium) is a valproate and is indicated for the treatment of the manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder . A manic episode is a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood. Typical symptoms of mania include pressure of speech, motor hyperactivity, reduced need for sleep, flight of ideas, grandiosity, poor judgment, aggressiveness, and possible hostility.
Why should valproate be reduced?
Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly , the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence. The ultimate therapeutic dose should be achieved on the basis of both tolerability and clinical response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Does carbapenem reduce valproate?
Carbapenem antibiotics (for example, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem; this is not a complete list) may reduce serum valproate concentrations to subtherapeutic levels, resulting in loss of seizure control. Serum valproate concentrations should be monitored frequently after initiating carbapenem therapy. Alternative antibacterial or anticonvulsant therapy should be considered if serum valproate concentrations drop significantly or seizure control deteriorates [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Does Valproate cause hyperammonemia?
Hyperammonemia has been reported in association with valproate therapy and may be present despite normal liver function tests. In patients who develop unexplained lethargy and vomiting or changes in mental status, hyperammonemic encephalopathy should be considered and an ammonia level should be measured. Hyperammonemia should also be considered in patients who present with hypothermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. If ammonia is increased, valproate therapy should be discontinued. Appropriate interventions for treatment of hyperammonemia should be initiated, and such patients should undergo investigation for underlying urea cycle disorders [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions

Indications and Usage For Valproate
- Epilepsy
Valproate Sodium Injection, USP is indicated as an intravenous alternative in patients for whom oral administration of Valproate products is temporarily not feasible in the following conditions: Valproate Sodium Injection, USP is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treat… - Important Limitations
Because of the risk to the fetus of decreased IQ, neurodevelopmental disorders, neural tube defects, and other major congenital malformations, which may occur very early in pregnancy, Valproate should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant …
Valproate Dosage and Administration
- Epilepsy
Valproate Sodium Injection is for intravenous use only. Use of Valproate Sodium Injection for periods of more than 14 days has not been studied. Patients should be switched to oral Valproate products as soon as it is clinically feasible. Valproate Sodium Injection should be administered a… - General Dosing Advice
Dosing in Elderly Patients Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of Valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly, the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutri…
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Valproate Sodium Injection, equivalent to 100 mg of valproic acid per mL, is a clear, colorless solution in 5 mL single dose vials, available in trays of 10 vials. Recommended storage: Store vials at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. No preservatives have been added. Unused portion of container should be discarded.
Contraindications
- Valproate Sodium Injection should not be administered to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- Valproate Sodium Injection is contraindicated in patients known to have mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (POLG; e.g., Alpers-Huttenlocher Syndrome) and...
- Valproate Sodium Injection should not be administered to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
- Valproate Sodium Injection is contraindicated in patients known to have mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (POLG; e.g., Alpers-Huttenlocher Syndrome) and...
- Valproate Sodium Injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.11)].
- Valproate Sodium Injection is contraindicated in patients with known urea cycle disorders [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)].
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity
General Information on Hepatotoxicity Hepatic failure resulting in fatalities has occurred in patients receiving Valproate. These incidents usually have occurred during the first six months of treatment. Serious or fatal hepatotoxicity may be preceded by non-specific symptoms such as … - Structural Birth Defects
Valproate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Pregnancy registry data show that maternal Valproate use can cause neural tube defects and other structural abnormalities (e.g., craniofacial defects, cardiovascular malformations, hypospadias, limb malfo…
Adverse Reactions
- The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling: 1. Hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] 2. Birth defects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] 3. Decreased IQ following in utero exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] 4. Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] 5. Hyperammonemic encephalopath…
Drug Interactions
- Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate Clearance
Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases (such as ritonavir), may increase the clearance of Valproate. For example, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital (or primidone) can double the clearance … - Effects of Valproate on Other Drugs
Valproate has been found to be a weak inhibitor of some P450 isozymes, epoxide hydrase, and glucuronosyltransferases. The following list provides information about the potential for an influence of Valproate co‑administration on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of sev…
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy
Pregnancy Registry There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including Valproate Sodium Injection, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking Valproate Sodium Injection during pregnancy to e… - Lactation
Risk Summary Valproate is excreted in human milk. Data in the published literature describe the presence of Valproate in human milk (range: 0.4 mcg/mL to 3.9 mcg/mL), corresponding to 1% to 10% of maternal serum levels. Valproate serum concentrations collected from breastfed infants …
Overdosage
- Overdosage with Valproate may result in somnolence, heart block, deep coma and hypernatremia. Fatalities have been reported; however patients have recovered from Valproate serum concentrations as high as 2120 mcg/mL. In overdose situations, the fraction of drug not bound to protein is high and hemodialysis or tandem hemodialysis plus hemoperfusion may result in signi…
Valproate Description
- Valproate sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid designated as sodium 2-propylpentanoate. Valproate sodium has the following structure: Valproate sodium has a molecular weight of 166.2. It occurs as an essentially white and odorless, crystalline, deliquescent powder. Valproate Sodium Injection, USP is available in 5 mL single dose vials for intravenous injection. Each mL contains …