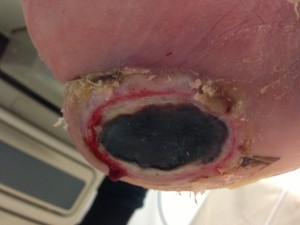
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury –Depth Unknown 2018 Pressure Ulcers •Friction & Shear management * Use lift/turn sheets * Maintaining Head of Bead at <30 degrees
Full Answer
What is a suspected deep tissue injury?
Treatment. To top. Obtain a physician order: Use Standard Precautions. Cleanse area gently. Pat dry: do not rub. Apply a thin Hydrocolloid Dressing such as Duo Derm Extra Thin or Tegaderm Clear to area. Change once a week and/or PRN. Apply skin prep for intact heels.
What is deep tissue injury (DTI)?
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury By: Cynthia A Fleck, MBA, BSN, RN, FACCWS President, American Academy of Wound Management (AAWM) History and Definition While believed to be a contemporary issue, deep tissue injury (DTI) has been noted in the literature since the late 1800s. DTI due to pressure exists as a form of pressure ulcer and is not well ...
What are the consequences of deep tissue injury?
: A deep tissue pressure injury (DTPI) is a serious type of pressure injury that begins in the muscle closest to the bone and may not be visible in its early stages. Its hallmark is rapid deterioration despite the use of appropriate preventive interventions. In 2007, the National Pressure Ulcer Advi …
Are nurses being educated on deep tissue injuries?
Jun 08, 2017 · Prompt identification and treatment of deep tissue injury is crucial, as these pressure injuries can rapidly evolve into ulcers involving all tissue layers. Hospitals and other healthcare organizations are being held accountable for these types of injuries, which can mean loss of revenue and extended hospital stays.

How do you treat a suspected deep tissue injury?
TreatmentUse Standard Precautions.Cleanse area gently.Pat dry: do not rub.Apply a thin Hydrocolloid Dressing such as Duo Derm Extra Thin or Tegaderm Clear to area.Change once a week and/or PRN.Apply skin prep for intact heels.More items...
What is a suspected deep tissue injury?
The new definition is: Suspected Deep Tissue Injury-Purple or maroon localized area of discolored intact skin or blood-filled blister due to damage of underlying soft tissue from pressure and/or shear.
Do you measure deep tissue injury?
Medical records should always capture the full extent of a pressure injury. Since your electronic health record system only allows one measurement, you should input the measurement of the entire deep tissue injury (DTI), rather than only the portion that is open.
How do you file a deep tissue injury?
Do describe what you see: type of wound, location, size, stage or depth, color, tissue type, exudate, erythema, condition of periwound. Don't guess at the type or the stage of a pressure ulcer or injury (hereafter, pressure injury [PI]) or the depth of the wound.Dec 17, 2020
How is a deep tissue injury diagnosed?
“Purple or maroon localized area of discolored intact skin or blood-filled blister due to damage of underlying soft tissue from pressure and/or shear. The area may be preceded by tissue that is painful, firm, mushy, boggy, warmer or cooler as compared to adjacent tissue.”
Can Deep Tissue Injury resolve?
By contrast, a deep-tissue injury may resolve without tissue loss. In addition, deep-tissue injuries often have a combined etiology involving both ischemia and pressure.Feb 3, 2020
How do you treat Epibole?
Treatment for epibole involves reinjuring the edges and opening up the closed tissue, which renews the healing process. Options include conservative or surgical sharp debridement, treatment with silver nitrate, and mechanical debridement by scrubbing the wound edges with monofilament fiber dressings or gauze.
What is the best medicine for injury?
Painkillers, such as paracetamol, can be used to help ease the pain. Ibuprofen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) tablets or creams can also be used to ease pain and reduce any swelling.
Where do deep tissue injuries occur?
A DTI can occur in a hospital, nursing home or any setting where a patient is left on a hard surface for an extended period. However, some of the group most prone to develop DTI's are patients receiving acute-care in a hospital or those undergoing lengthy surgery.
How long does it take for a deep tissue injury to heal?
This process begins in the weeks following tissue damage and can extend over 12 months or more depending on the size and type of the wound. This basic overview explains why tissue cannot simply heal overnight but takes weeks to months to fully restore.Dec 22, 2017
How long does deep tissue injury take to heal?
Most soft tissue injuries heal without any problems in about six weeks. However, it may take a few months for your symptoms to settle – these can include pain or discomfort, stiffness, decreased strength, and swelling.
What does a deep tissue injury look like?
When there isn't an open wound but the tissues beneath the surface have been damaged, the sore is called a deep tissue injury (DTI). The area of skin may look purple or dark red, or there may be a blood-filled blister.
What is the importance of deep tissue injury?
Prompt identification and treatment of deep tissue injury is crucial, as these pressure injuries can rapidly evolve into ulcers involving all tissue layers. Hospitals and other healthcare organizations are being held accountable for these types of injuries, which can mean loss of revenue and extended hospital stays.
What is the problem with deep tissue injuries?
The problem with deep tissue injuries is that they are often misclassified and mismanaged. They often extend far deeper into the underlying tissue than may be initially suspected. They can evolve rapidly, exposing deeper tissue layers even when treatment is optimal.
Is deep tissue injury difficult to detect?
A deep tissue injury may be difficult to detect in people with darker skin tones.
What is a partial thickness loss of dermis?
Partial thickness loss of dermis presenting as a shallow open ulcer with a red pink wound bed, without slough. May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled or sero-sanginousfilled blister. Presents as a shiny or dry shallow ulcer without
What is nonblanchable skin?
Intact skin with non-blanchableredness of a localized area usually over a bony prominence. Darkly pigmented skin may not have visible blanching; its color may differ from the surrounding area. The area may be painful, firm, soft, warmer or cooler as compared to adjacent tissue. Category I may be difficult to detect in individuals with dark skin tones.
What is deep tissue injury?
What is a Deep Tissue Injury? A deep tissue injury is a unique form of pressure ulcer. The National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel defines a deep tissue injury as “A pressure-related injury to subcutaneous tissues under intact skin. Initially, these lesions have the appearance of a deep bruise.
What is the problem with deep tissue injuries?
The problem with deep tissue injuries is that they are not readily apparent. A patient who has fallen at home and lain on the floor for a day may be admitted to the hospital and have every inch of skin examined upon admission, and then develop the tell-tale area of purplish discoloration several days after admission. In many cases, hospitals and other care facilities are being blamed (and payment is being withheld) when patients end up with a gaping hole in their sacrum that takes several months (and several trips to the OR) to heal, if they don’t succumb to their injury.
Can dark skin ulcers be detected?
Also remember that these ulcers may be even more difficult to detect in dark-skinned individuals. The point is not to scare you, but to make you very aware of the danger that these types of ulcers present. It is important to be on your guard and watch for the development of these ulcers.
How to treat deep tissue pressure injury?
Treatment of deep tissue pressure injuries should include the measures used for any pressure injury, including frequent repositioning off the site of injury, good skin care, proper support surface selection, as well as correcting any systemic issues or nutritional deficiencies. Offloading and avoidance of shearing forces is crucial with these ulcers since ischemia and infarction of nutrient supply is thought to be a cause. Monitor the wound site carefully before beginning forceful removal of any tissue that appears to be necrotic. Skin beneath the covering blister should be left in place if the area is stable.
What is the term for a muscle injury that causes insufficient nutrient delivery?
Muscle injury associated insufficient nutrient delivery through the arterioles that feed the muscles (infarction) Injury or damage to the fascia (the layer of fibrous tissue that surrounds muscles, bones, blood vessels and nerves) Shearing injury or torsion of the perforating vessels.
What is a pressure injury?
Pressure injuries are localized areas of tissue necrosis that typically develop when soft tissue is compressed between a bony prominence and an external surface for a long period of time. Deep tissue pressure injuries (DTPI) are persistent non-blanchable deep red, purple or maroon areas of intact skin, non-intact skin or blood-filled blisters ...
How to prevent pressure bony prominences?
Provide adequate intake of protein and calories. Maintain current levels of activity, mobility and range of motion. Use positioning devices to prevent prolonged pressure bony prominences. Keep the head of the bed as low as possible to reduce risk of shearing. Keep sheets dry and wrinkle free.
Can deep tissue injuries be painful?
In addition to the localized discoloration (which may be more difficult to detect in patients with dark skin tones), deep tissue injuries can be preceded by tissue that is painful, differs in consistency (firm or boggy), or differs in temperature (warmer or cooler) as compared to adjacent tissue.
