
When charging a duty of care following refusal of care, the doctor must treat the patient, giving that patient their best interest, even if its limits are at risk. A decision must be made voluntarily if a decision needs to be made. When Can You Accept A Patient’S Refusal Of Care?
Full Answer
When is it appropriate to investigate why a patient is refusing care?
It is clearly appropriate to investigate the reasons why a patient is refusing a nursing care procedure, 24 and to provide information where it is believed that a deficit may be contributing to the patient’s reluctance to accept the care. There is clearly a line, however, between pressure to accept care that is acceptable and pressure which is not.
When is care refused not the most appropriate course of action?
In each of these incidents, the care refused by the patient was considered, on reflection, not to be the most appropriate course of action. In the first incident, a patient was admitted following an attempted overdose. She refused intervention, but it was considered she would recover without assistance.
What is an example of a goal in a treatment plan?
Examples of goals include: 1 The patient will learn to cope with negative feelings without using substances. 2 The patient will learn how to build positive communication skills. 3 The patient will learn how to express anger towards their spouse in a healthy way.
When are health care professionals prepared to override a patient’s refusal?
This failure to respect a patient’s refusal was also identified by Holm who found that health care professionals were prepared to override the refusal of a patient if harm from withholding the intervention could be expected. 30
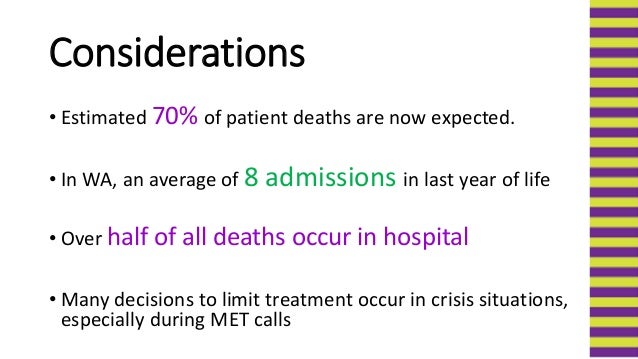
What would you do if a patient refuses care?
Understand their story Try to understand the patient/family's story before you try to change their mind. This means suspending your attitude toward their decision and as openly and non-judgmentally as possible, understanding the reasons for their decision.
What should a nurse do if a patient refuses treatment?
If your patient refuses treatment or medication, your first responsibility is to make sure that he's been informed about the possible consequences of his decision in terms he can understand. If he doesn't speak or understand English well, arrange for a translator.
What are your methods for handling patients who refuse to follow certain steps of their treatment program?
When Patients Refuse TreatmentPatient Education, Understanding, and Informed Consent. ... Explore Reasons Behind Refusal. ... Involve Family Members and Caregivers. ... Document Your Actions. ... Keep the Door Open.
What are some examples of treatment goals?
Treatment Plan Goals and Objectives Examples of goals include: The patient will learn to cope with negative feelings without using substances. The patient will learn how to build positive communication skills. The patient will learn how to express anger towards their spouse in a healthy way.
What are the nurse's legal and ethical responsibilities toward a patient who refuses to be seen for evaluation and treatment?
It is the nurse's responsibility to explain why a particular drug or treatment is important. However, if the patient still refuses, the nurse should obtain a release from liability because the treatment is not done or the drug is not taken. True, except in emergencies when the patient is unable to give consent.
What do you do when the family of a patient refuses to acknowledge the client's condition and treatment plan?
When patients, families disagree on treatment: 6 ways forwardGet to know the patient's family. ... Minimize confusion. ... Help everyone identify their values. ... Encourage the patient to be open. ... Preserve confidentiality. ... Don't hesitate to call in help.
How should the nurse respond to a client who is refusing medication?
If a client is refusing and saying they don't want to take their medication, you should:Try to find out the reason why e.g. unpleasant side effects? ... Explain calmly the consequences of not taking their prescribed medication.If no reason given, wait a while and ask again.More items...
What first action should be taken when dealing with a noncompliant patient?
Here are some key verbal intervention tips for managing the noncompliant person:Maintain your rationality. ... Place responsibility where it belongs. ... Explain the directive. ... Set reasonable limits. ... Be prepared to enforce your limits. ... Don't stress the negative. ... Summary.
What is the right to refuse treatment?
Every competent adult has the right to refuse unwanted medical treatment. This is part of the right of every individual to choose what will be done to their own body, and it applies even when refusing treatment means that the person may die.
How do you write a goal and objective for a treatment plan?
2. Set SMART GoalsSpecific: Objectives need to be clear and specific, not general or vague. ... Measurable: Objectives need specific times, amounts or dates for completion so you and your patients can measure their progress.Attainable: Encourage patients to set goals and objectives they can meet.More items...•
What are treatment plan goals?
Treatment goals: Goals are the building blocks of the treatment plan. They are designed to be specific, realistic, and tailored to the needs of the person in therapy. The language should also meet the person on their level.
What should a treatment plan include?
A treatment plan will include the patient or client's personal information, the diagnosis (or diagnoses, as is often the case with mental illness), a general outline of the treatment prescribed, and space to measure outcomes as the client progresses through treatment.
Can a nurse refuse to take care of a patient?
The American Nurses Association (ANA) upholds that registered nurses – based on their professional and ethical responsibilities – have the professional right to accept, reject or object in writing to any patient assignment that puts patients or themselves at serious risk for harm.
Do patients have the right to refuse treatment?
To the extent permitted by law, participation shall include the right to refuse treatment." Under federal law, the Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) guarantees the right to refuse life sustaining treatment at the end of life.
What are the 7 ethical principles in nursing?
The ethical principles that nurses must adhere to are the principles of justice, beneficence, nonmaleficence, accountability, fidelity, autonomy, and veracity. Justice is fairness.
How do you document patient refusal?
DOCUMENTING INFORMED REFUSALdescribe the intervention offered;identify the reasons the intervention was offered;identify the potential benefits and risks of the intervention;note that the patient has been told of the risks — including possible jeopardy to life or health — in not accepting the intervention;More items...
What is treatment planning?
Treatment planning is a team effort between the patient and health specialist. Both parties work together to create a shared vision and set attainable goals and objectives.
What is the role of model and technique in a treatment plan?
Treatment plans provide structure patients need to change. Model and technique factors account for 15 percent of a change in therapy. Research shows that focus and structure are critical parts of positive therapy outcomes. Goal-setting as part of a treatment plan is beneficial in itself. Setting goals helps patients:
What information do counselors fill out?
Patient information: At the top of the treatment plan, the counselor will fill in information such as the patient’s name, social security number, insurance details, and the date of the plan. Diagnostic summary: Next, the counselor will fill out a summary of the patient’s diagnosis and the duration of the diagnosis.
What is a goal in a patient's life?
Both parties work together to create a shared vision and set attainable goals and objectives. A goal is a general statement of what the patient wishes to accomplish. Examples of goals include: The patient will learn to cope with negative feelings without using substances.
What are some examples of objectives?
Examples of objectives include: An alcoholic with the goal to stay sober might have the objective to go to meetings. A depressed patient might have the objective to take the antidepressant medication with the goal to relieve depression symptoms.
What is objective in a patient?
An objective, on the other hand, is a specific skill a patient must learn to reach a goal. Objectives are measurable and give the patient clear directions on how to act.
What is the third section of a treatment plan?
Problems and goals: The third section of the treatment plan will include issues, goals, and a few measurable objectives. Each issue area will also include a time frame for reaching goals and completing objectives. Counselors should strive to have at least three goals.
What is a goal in counseling?
Goals are the broadest category of achievement that clients in mental health counseling work towards. For instance, a common goal for those struggling with substance abuse may be to quit using their drug of choice or alcohol, while a patient struggling with depression may set a goal to reduce their suicidal thoughts.
Why do we need treatment plans?
Treatment plans can reduce the risk of fraud, waste, abuse, and the potential to cause unintentional harm to clients. Treatment plans facilitate easy and effective billing since all services rendered are documented.
What is the treatment contract?
Treatment Contract – the contract between the therapist and client that summarizes the goals of treatment. Responsibility – a section on who is responsible for which components of treatment (client will be responsible for many, the therapist for others)
What is the part of effective mental health?
Part of effective mental health treatment is the development of a treatment plan. A good mental health professional will work collaboratively with the client to construct a treatment plan that has achievable goals that provide the best chances of treatment success. Read on to learn more about mental health treatment plans, how they are constructed, ...
What is a mental health treatment plan?
At the most basic level, a mental health treatment plan is simply a set of written instructions and records relating to the treatment of an ailment or illness. A treatment plan will include the patient or client’s personal information, the diagnosis (or diagnoses, as is often the case with mental illness), a general outline ...
What is intervention in therapy?
Interventions – the techniques, exercises, interventions, etc., that will be applied in order to work toward each goal. Progress/Outcomes – a good treatment plan must include space for tracking progress towards objectives and goals (Hansen, 1996)
What is blended care in therapy?
Blended care involves the provision of psychological services using telecommunication technologies.
How Do You Handle A Patient Refusing Care?
The importance of patient education, understanding, and informed consent….
How Should The Nurse Respond To A Client Who Is Refusing Medication?
See why certain side effects are unpleasant: e.g. nausea and headaches…
What Steps Should Be Taken By The Nurse When A Client Refuses Therapy?
empathize with a patient’s wants and needs at the beginning of every therapy refusal.
What Should You Do If Your Patient Refuses Care?
When charging a duty of care following refusal of care, the doctor must treat the patient, giving that patient their best interest, even if its limits are at risk. A decision must be made voluntarily if a decision needs to be made.
What Is The Best Course Of Action If A Patient Refuses Treatment?
The fact that your medical recommendation cannot be followed without getting written consent from the patient is considered in accordance with your duty to explain the reasons for the recommendation to him and show potential benefits if you don’t follow it.
What Should You Do If A Patient Refuses Treatment?
You want to make sure to inform your patient what could happen if he refuses treatment or medication so that he knows as much as possible about the possible consequences of his decision. Your staff may also want to arrange a translator if they do not speak or understand English very well.
Does The Patient Have The Right To Refuse Treatment?
It is important to you that your consent is informed. Participation includes the right to refuse medical treatment if the law allows for it. Federal law guarantees that life-support treatment will not be offered to people dying from their illnesses.
What happens when someone you love refuses to get treatment?
When someone you love refuses to get professional treatment for their mental health disorder—such as depression, bipolar disorder, or substance abuse —this can put you, as a family member, in a very uncomfortable and difficult position. You care for the person and can see that he or she needs help, but feel powerless and unable to just stand by.
Why does my loved one refuse to move forward?
If your loved one refuses to move forward, it’s useful to try to understand what is behind his reasons for refusing treatment and then address those issues. A person may refuse to accept mental health treatment for many reasons, including: He may believe it indicates he is a failure.
What does it mean to distancing yourself from a sick family member?
That, a lot of times, means distancing yourself from the sick family member who refused treatment. Everyone has limits, and when said mentally sick family member has a long history of repeated abusive behavior I say family members have a right to protect themselves from harm.
What are the areas of concern?
Common areas of concern are: alterations in overall appearance. decreased level of energy. fatigue. lack of interest in previously enjoyed people or activities. changes in sleep, appetite, or weight.
Can elderly people not participate in treatment?
Other's won't participate, and, if they aren' t a danger to themselves or others, have a right to not participate in treatment. The author mentioned elderly people. Elderly people (probably over the age of 75 or so) didn't grow up with treatment options, and thus, many won' t participate in them.
Is it hard to keep up with meds?
It's really hard to keep up your motivation and keep on trying when so many things don' t go your way, when meds don't work or you have side effects to them. I know, I've been there too. It feels like you have nothing left to do, but actually there's always something else to try. This I know for sure.
What does it mean to refuse life sustaining treatment?
Treatment has to be reasonable, this means that it has to be effective and that the benefits need to be in proportion to the burden for the patient of undergoing the treatment. There are two aspects of the refusal of life-sustaining treatment. The goals of medicine establish the purposes of treatment.
What are the goals of medicine?
The goals of medicine, which guide the goals of all health care professionals, are: to prevent, cure, slow down or arrest the development of an illness; to stabilize a satisfactory condition; or to relieve the distressing symptoms of illness.
What is autonomy in health care?
In health care, autonomy can be expressed in this way: the patient is the source of the health care professional’s right to treat her or him.
What is ethical analysis in health care?
The basic starting point for ethical analysis in health care, is the encounter between the patient and the health care professional. This relationship is shaped by the goals of that encounter, both the goals that health care professional has and the goals that the patient has.
Is it possible to meet all of your goals?
It is also important to recognize that it is not necessarily possible to meet all of these goals all of the time. The other person in the encounter is the patient, who also has her or his own goals, both health and broader goals in life, as well as values and preferences.
Is it a goal of medicine to prolong the dying process?
It is not a goal of medicine to prolong the dying process. The second aspect of any decision to forgo treatment is the patient’s right to choose whether or not to accept such treatment, even if the treatment has a reasonable chance of being effective.
What is the tension of refusing nursing care?
On the one side, nurses are aware that care cannot be carried out without the patient’s consent. There is evidence in the study that they will go to great lengths to achieve the agreement of the patient.
Why did nurses not respect the refusal of the patient?
The nurses in this incident did not respect the refusal of the patient. They proceeded with nursing care because they felt it to be essential . In another incident, a patient was in great pain and unable to sit in a chair because of the backache this caused.
What happens when a patient does not agree to the administration of a nursing care procedure?
When a patient did not eventually agree to the administration of a nursing care procedure, the tension between respect for patient choice and the perceived duty to care could not be resolved. In these instances, nurses did what they indicated they would do in earlier incidents.
What are the principles of informed consent?
The principles of informed consent are well discussed in the ethical literature. 1,2 Informed consent requires that a patient be informed and competent, and thereafter gives voluntary consent. 3 The role of informed consent within the context of nursing care is also well established. 3,4 The principle that a nursing care procedure cannot be undertaken without the consent of the patient is widely acknowledged. 5–11 Indeed, the United Kingdom Central Council for Nursing, Midwifery, and Health Visiting advises that all care procedures should be undertaken within a “framework of informed consent”. 12 It should be acknowledged, however, that there is little discussion of the application of the principles of informed consent prior to nursing care procedures in the nursing literature. Discussion is focused almost entirely on the nurse’s role in facilitating consent prior to medical and research procedures. 4,13
Why did a dying patient refuse a nasogastric tube?
In a third incident, a dying patient refused a nasogastric tube. This refusal was upheld because there was no clear benefit to be gained from continuing the feeding. In a fourth incident, a patient’s refusal of antibiotics for a severe chest infection was respected.
Is consent necessary in nursing?
In their view, consent can be described as desirable but ultimately not essential. Nurses demonstrated some knowledge of ethical principles and were concerned to incorporate these into their practice but seemed unaware how to do so when faced with a patient who refused nursing care.
Can nurses be absolved of their duty to care?
It is therefore argued that nurses are absolved from their duty to care if the patient (informed, voluntarily and competently) refuses that care. As a result, care, even life saving in nature, cannot be administered if the patient refuses.
What are therapeutic interventions for noncompliance nursing?
The following are the therapeutic nursing interventions for Noncompliance nursing diagnosis: Develop a therapeutic relationship between and among the patient and significant others. This allows the patient to gain trust from the nurse and will boost confidence in the completion of the treatment.
What is a noncompliance in nursing?
The nursing diagnosis Noncompliance is defined as behavior of person and/or caregiver that fails to coincide with a health-promoting or therapeutic plan agreed on by the person (and/or family and/or community) and health care professional. In the presence of an agreed-on health-promoting or therapeutic plan, a person’s or caregiver’s behavior is ...
What are the factors that contribute to noncompliance?
Factors associated with noncompliance include past history of noncompliance, stressful lifestyles and environment, socioeconomic status, contrary cultural or religious beliefs and values, ...
What is compliance in medical terms?
Compliance is defined as the extent to which a person’s behavior (in terms of taking medications, following specific regimens, or dealing with lifestyle modification) coincides with medical or health advice.
