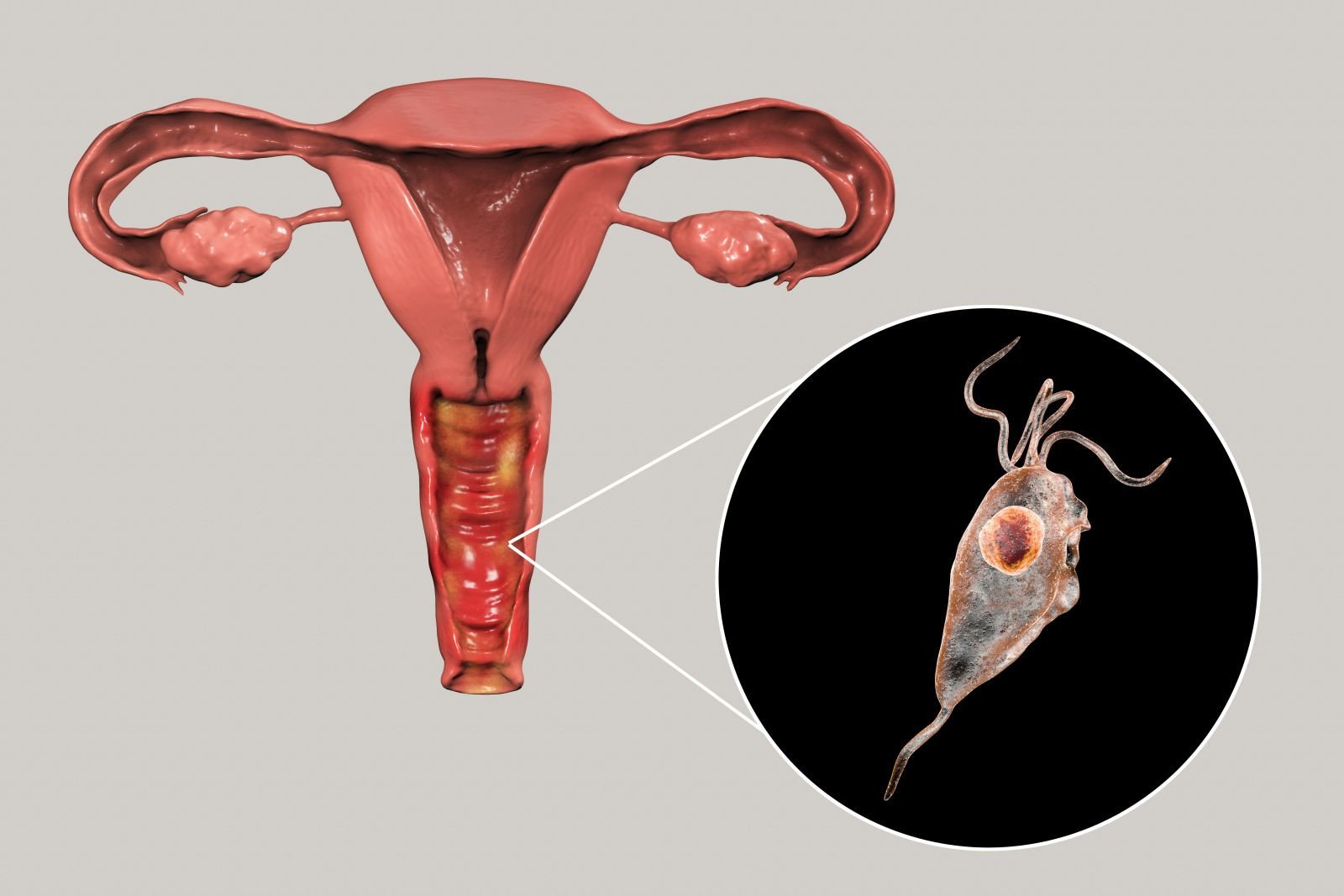
Can trichomoniasis go away on its own?
Metronidazole, given as a single dose, is likely to provide parasitological cure for trichomoniasis, but it is not known whether this treatment will have any effect on pregnancy outcomes. The cure rate could probably be higher if more partners used the treatment.
What antibiotic is used to treat trichomoniasis?
Treatment of T. vaginalis infection can relieve symptoms of vaginal discharge for pregnant women and reduce sexual transmission to partners. Although perinatal transmission of trichomoniasis is uncommon, treatment might also prevent respiratory or genital infection in the newborn (1136,1137). Clinicians should counsel symptomatic pregnant women with …
What medicine do you take for trichomoniasis?
How is trichomoniasis treated during pregnancy? The treatment for trichomoniasis is a large single dose of antibiotics, typically metronidazole or tinidazole. Common brand names for these are Flagyl or Tindamax. If both you and your partner test positive, it is suggested that both of you undergo the antibiotic treatment at the same time.
How do you prevent trichomoniasis?
Conclusion: Although testing for and treatment of trichomoniasis during pregnancy is not routinely recommended, the high burden of infection among some pregnant women demonstrates a need to further understand patterns of T vaginalis testing and infection. Opportunities exist for improving timely treatment of trichomoniasis and test of reinfection.

What happens if you get trichomoniasis while pregnant?
Trich is a common sexually transmitted infection that's associated with a higher risk of preterm birth, prelabor rupture of the membranes, and having a low-birthweight baby. Symptoms (if any) might include vaginal discharge and irritation of the vagina and vulva.
Can metronidazole be used to treat trichomoniasis during pregnancy?
Metronidazole is effective against a trichomoniasis infection during pregnancy, but may increase the risk of preterm and low birthweight babies. Trichomoniasis is a very common sexually transmitted infection. Symptoms include vaginal itching and discharge.May 11, 2011
Can I take metronidazole 500mg while pregnant?
Conclusion: During pregnancy, treating bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis with metronidazole is effective and offers no teratogen risk. Benefit of metronidazole in the reduction of preterm birth was demonstrated for the combination of this medication with other antibiotics.
Can trichomoniasis cause miscarriage in early pregnancy?
A recent National Institutes of Health study found that treatment for another vaginal infection, trichomoniasis, with metronidazole might do more harm than good in pregnant women. Trichomoniasis, like bacterial vaginosis, has been shown to increase the risk of giving birth prematurely.Dec 5, 2002
Other Management Considerations
Providers should advise persons with T. vaginalis infections to abstain from sex until they and their sex partners are treated (i.e., when therapy has been completed and any symptoms have resolved). Testing for other STIs, including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia, should be performed for persons with T. vaginalis.
Follow-Up
Because of the high rate of reinfection among women treated for trichomoniasis, retesting for T. vaginalis is recommended for all sexually active women approximately 3 months after initial treatment regardless of whether they believe their sex partners were treated ( 137, 1115 ).
Management of Sex Partners
Concurrent treatment of all sex partners is vital for preventing reinfections. Current partners should be referred for presumptive therapy. Partners also should be advised to abstain from intercourse until they and their sex partners have been treated and any symptoms have resolved.
Recurrent Trichomoniasis
A recurrent infection can result from treatment failure (antimicrobial-resistant T. vaginalis or host-related problems), lack of adherence, or reinfection from an untreated sex partner. In the case of a recurrent infection, the origin of the repeat infection should be assessed because most recurrent infections likely result from reinfection.
Special Considerations
Metronidazole and tinidazole are both nitroimidazoles. Patients with an IgE-mediated-type hypersensitivity reaction to 5-nitroimidazole antimicrobials should be managed by metronidazole desensitization according to published regimens ( 1127, 1128) and in consultation with an allergy specialist. The optimal treatment for patients with T.
Treatment
Treatment reduces symptoms and signs of T. vaginalis infection, cures infection, and might reduce transmission. Likelihood of adverse outcomes among women with HIV infection is also reduced with T. vaginalis therapy.
What causes trichomoniasis in pregnant women?
It is caused by the microscopic parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. This STI is the most common curable one among young women who are sexually active, meaning that trichomoniasis during pregnancy can be common. It can affect a woman’s pregnancy by increasing her chances for a pre-term delivery or the baby having a low birth weight.
What is the best antibiotic for trichomoniasis?
The treatment for trichomoniasis is a large single dose of antibiotics, typically metronidazole or tinidazole. Common brand names for these are Flagyl or Tindamax. If both you and your partner test positive, it is suggested that both of you undergo the antibiotic treatment at the same time.
What is the STI in a woman?
Trichomoniasis [trik-uh-muh-naya-sis], or “trich,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) spread through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activities. The infection is treatable and can be cured with antibiotics. It is caused by the microscopic parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
What age group has the highest rate of trichomoniasis?
Young, sexually active women under 25 years old have the highest rates of trichomoniasis infections. If any of the above apply to you during your pregnancy, talk to your doctor to discuss screening and prevention techniques.
How do you know if you have trichomoniasis?
Though most women who have trichomoniasis do not show any signs, some possible symptoms include: Itching or burning sensation in the genitals. Soreness or redness of the genitals. Burning sensation during urination. The unpleasant feeling during sexual intercourse.
How does a syringe affect a woman's pregnancy?
It can affect a woman’s pregnancy by increasing her chances for a pre-term delivery or the baby having a low birth weight. Although rare, there is the chance that the infection could be passed to the baby during birth.
How long does it take for a vaginal discharge to show up?
Change in vaginal discharge with a foul odor (color can be white, gray, yellow, or greenish) Symptoms may come and go and can show up as early as 5 to 28 days after sexual contact. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. Call your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms during your pregnancy.
What is the best treatment for T. vaginalisin?
For over three decades, single-dose (2 grams) metronidazole (MTZ) has been the recommended treatment for T. vaginalisin women and men in the U.S.(18) Single-dose (2 grams) tinidazole (TDZ) is an additional recommended treatment regimen which has better absorption and fewer gastrointestinal effects than MTZ.
What is the most common non-viral STI?
T. vaginalisis estimated to be the most common non-viral sexually transmitted infection (STI) worldwide among women.(1). Globally, the estimated prevalence of T. vaginalisin women aged 15-49 is 5.3% (higher than estimates of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) and 0.6% in men (higher than estimates of syphilis).
Is trigomonas vaginalisis a STI?
Trichomonas vaginalisis estimated to be the most common treatable sexually transmitted infection (STI) In the world and is associated with poor birth outcomes, cervical cancer, sperm motility and morphology issues, and HIV acquisition and transmission. Recent findings: The efficacy of the recommended 2 gram oral single-dose metronidazole (MTZ) ...
Do symptomatic women need more studies?
Most treatment studies have been conducted among symptomatic women. More studies are needed to determine the benefit of treating asymptomatic persons. The effectiveness of newer drugs such as SEC, and different configurations of existing drugs, such as pulse dosing, are needed.
Can T. vaginaliscan be re-infected?
Persistent infection with T. vaginaliscan occur in several circumstances, the most common of which is re-infection from an untreated sexual partner(s). A detailed sexual history should be taken to assess the likelihood of re-infection.
Is MTZ desensitization effective against T. vaginalis?
MTZ desensitization per a validated protocol with the assistance of an allergy specialist is recommended in these situations.(18, 41-43) While 5-nitroimidazoles are the only antimicrobial class known to be effective against T. vaginalis, there is anecdotal evidence for alternative regimens.
How early can you get pregnant with trichomoniasis?
Pregnant people are also at higher risk of delivering their babies prematurely, or before 37 weeks.
What are the risks of trichomoniasis?
Pregnant people with trichomoniasis are at greater risk of: 1 premature labor and delivery 2 having a baby with a low birth weight 3 transmitting trichomoniasis to a female baby during delivery (extremely rare)
How long after taking metronidazole can you drink alcohol?
You and your partner will both need treatment. Also, you both must avoid sexual intercourse until the trichomoniasis infection clears up. You should not consume alcohol for 24 hours after taking metronidazole or 72 hours after taking tinidazole. It can lead to severe nausea and vomiting.
How long does it take for a trigomonasis to spread?
It passes from person to person during sexual intercourse. The incubation period between exposure and infection is about 5 to 28 days.
How long does trichomoniasis last?
If left untreated, however, trichomoniasis can last for several months or years. Its symptoms can make sex unpleasant. But for pregnant people, it can also cause serious childbirth complications.
What causes a fishy smell in the penis?
In women, trichomoniasis can cause: a fishy genital odor. large amounts of white, gray, or green vaginal discharge. genital itching. pain while urinating or having sex. Symptoms in men are rare, but they may experience: irritation inside the penis. a burning sensation while urinating or after ejaculating.
What test can be used to test for trichomoniasis?
These include a culture test, nucleic acid amplification test, or rapid antigen test. Pregnant people displaying any symptoms of a trichomoniasis infection should see their doctors right away.
Signs Of Trichomoniasis During Pregnancy
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 70% of infected individuals remain asymptomatic. When present, the symptoms vary from mild to severe and are mostly non-persistent ( 2 ). The symptoms of trichomoniasis in pregnancy are similar to those that occur in a non-pregnant state and include the following ( 3) ( 4 ).
Risk Factors For Trichomoniasis In Pregnancy
Research suggests that the infection is more prevalent in the first trimester. The following factors may increase the risk of trichomoniasis in pregnant women ( 1) ( 3 ).
Diagnosis Of Trichomoniasis In Pregnancy
Diagnostic steps are usually conducted only if the pregnant woman has symptoms of the infection. Below are the common methods used for screening for trichomoniasis ( 4) ( 5 ).
Complications Of Trichomoniasis In Pregnancy
Trichomonas may cause significant risks to pregnant women when left untreated. Research suggests that a pregnant woman with trichomonas infection is more likely to contract other sexually transmitted infections and HIV ( 4 ).
Treatment For Trichomoniasis In Pregnancy
Trichomoniasis is treated with the antibiotic metronidazole, which is administered as a single-dose oral pill. The treatment may be considered only in symptomatic women, although this could vary based on your OB-GYN’s recommendation ( 6 ).
Prevention Of Trichomoniasis In Pregnancy
The following preventive measures may help you avoid trichomoniasis in pregnancy ( 8 ).