
Full Answer
What is the stimulant use disorder treatment guide?
This guide supports health care providers, systems, and communities seeking to treat stimulant use disorders. It describes relevant research findings, examines emerging and best practices, identifies knowledge gaps and implementation challenges, and offers useful resources.
Are psychostimulants effective for treating stimulant use disorder?
It is hypothesized that psychostimulant treatment for stimulant use disorder may be effective by substituting a slow acting drug with a similar mechanism of action, thereby reducing withdrawal symptoms and cravings [ 36 ].
What is the best stimulant addiction treatment?
While psychotherapy remains the most profound method of stimulant addiction treatment available at this time, new options are evolving to help master the art of providing comprehensive treatment and care for those in need. According to the Semel Institute, behavioral therapies are commonly used to treat prescription stimulant addictions.
Are contingency management programs effective in the treatment of stimulant use disorder?
There was sufficient evidence to support the efficacy of contingency management programs for treatment of stimulant use disorder. Psychostimulants, n-acetylcysteine, opioid agonist therapy, disulfiram and antidepressant pharmacological interventions were found to have insufficient evidence to support or discount their use.
What is the most effective treatment for substance use disorders?
Talk therapy (counseling) is the most commonly used treatment for substance misuse. Therapy is a treatment that helps people with emotional, physical, and mental health problems function better.
Is psychotherapy effective for substance abuse?
Psychotherapy for substance abuse is a hallmark of the most effective substance abuse treatment programs.
Can substance abuse cause bipolar disorder?
Drug abuse and addiction can cause changes in the brain that lead to bipolar disorder. Even people who were mentally healthy before their addiction can develop bipolar disorder.
What is a treatment plan for substance abuse?
A substance abuse treatment plan is an individualized, written document that details a client's goals and objectives, the steps need to achieve those, and a timeline for treatment. These plans are mutually agreed upon with the client and the clinician.
What are some treatments for the psychological piece of addiction?
Some of the most strongly supported include:Cognitive-behavioral therapy. CBT can help addicted patients overcome substance abuse by teaching them to recognize and avoid destructive thoughts and behaviors. ... Motivational interviewing. ... Contingency management.
What is the most effective treatment for bipolar disorder?
The most effective treatment for bipolar disorder is a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Most people take more than one drug, like a mood-stabilizing drug and an antipsychotic or antidepressant.
Can stimulants cause bipolar?
Using stimulants like Adderall during a depressive episode may increase the risk of a manic episode. A 2008 study found that 40 percent of participants using stimulants for bipolar disorder experienced stimulant-associated mania.
Does drug induced bipolar go away?
Although substance-induced disorders (depression and bipolar) subside after the biological effects of the drug fade, vulnerable individuals can develop a full-blown major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder, without proper management, psychiatric and medical complications can be fatal.
Decision Letter 0
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Decision Letter 1
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Acceptance letter
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
What is the best treatment for a stimulant addiction?
Inpatient rehab centers typically provide the highest chances of successfully overcoming a stimulant addiction. Inpatient rehab provides many benefits, including: Education about the disease of addiction. Healthy coping skills for relapse prevention, trauma, anxiety, depression, and other struggles. Stress management techniques.
How do I overcome stimulant addiction?
Once you’ve made that decision, there are several options for inpatient or outpatient rehab and counseling that can help you overcome your addiction. If you’re ready to take your life back, ...
What is the best medication for reducing cravings?
Prescribed for mood disorders like depression and obsessive compulsive disorder, Prozac has shown some limited potential in reducing cravings. Naltrexone. Naltrexone is commonly used for the treatment of opioid and alcohol dependencies, but has also showed potential in treating prescription stimulant dependence.
How long does a detox last?
During detox, doctors manage the physical part of the addiction by getting the stimulants out of the person’s system. Detox typically lasts up to a week, but could last longer depending on the severity of the addiction.
How long does inpatient rehab last?
Both psychiatric and physical care are provided. Patients typically remain in inpatient rehab for between 30 to 90 days.
What is outpatient therapy?
Outpatient therapy is often also used as an aftercare or step-down program upon completion of inpatient treatment to assist the client transition back into their daily life while maintaining their recovery.
Do stimulants still exist after withdrawal?
Even after withdrawal symptoms and the physical need for stimulants are reduced or over, the compulsive desire to use stimulants is still there. This makes ongoing treatment a must for those in recovery.
What to do if you suspect someone is using a stimulant?
If you suspect that a loved one is abusing a stimulant substance, you should proceed with caution. Approaching the situation without adequately preparing yourself may harm, rather than help, the situation (and your relationship). Rather than reacting too hastily, consider a thought-out plan and make sure you understand how someone suffering from a stimulant addiction may react to your attempts to reach out.
What is a stimulant?
The stimulants are a broad class of substances that affect the nervous system in a way that leads to increased activity across a number of mental and physical processes—serving, in varying degrees, to boost energy and attention but also capable of impacting our cardiovascular and respiratory systems . The stimulant category encompasses drugs that ...
How many people use meth in 2014?
Per the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, in 2014 1: About 570,000 people admitted current methamphetamine use. Over 1 million people used prescription stimulants nonmedically. About 1.5 million people currently used cocaine. Of the 1.5 million, about 350,000 people were using crack.
What is a CRAFT intervention?
During an intervention, a group of people that care about the stimulant user compel him or her towards treatment through peer pressure and the threat of negative consequences.
How does drug abuse affect the brain?
Drug abuse can, in some cases, change the brain of the user in ways that may diminish self-control and judgment, which makes your task more complex 4.
Why do stimulants affect your life?
You may be unable or unwilling to see the negative impact that stimulants play in your life in the early stages of abuse or addiction, due to the perceived benefits like higher energy, improved concentration, or weight loss.
What to do when you are emotionally high?
Provide your love, support, understanding, and patience. If you speak when emotions are high, your message will be lost and your loved one will only absorb your anger or sadness. Ask many questions. People become defensive when told what to do.
What is stimulant detox?
Stimulant Detox. Treatment for Stimulant Use Disorders. References. Stimulants are a class of drugs whose pharmacologic actions increase alertness and energy, and in some cases are used therapeutically to improve focus and attention. 1 As these drugs stimulate certain brain processes, they also stimulate physical ones—heart rate, blood pressure, ...
How does therapeutic therapy help people?
Therapeutic techniques such as these help people to embrace their need for treatment, stay engaged with their ongoing treatment efforts, and make positive changes to their thoughts and behaviors to solidify the gains made during recovery work.
How do stimulants affect the brain?
When a stimulant drug is abused, it releases a large amount of dopamine into the brain and prevents the reabsorption of the neurotransmitter. This floods synapses, causing greater and faster communication between neurons. While very small, therapeutic doses of prescription stimulants like Adderall can help to manage the symptoms of ADHD, stimulant abuse commonly involves the use of these substances at higher-than-recommended doses. Such intentional misuse makes it more likely that a person will experience the rush of energy and rewarding euphoria than can reinforce continued use and lay the groundwork for addiction. Especially at nonmedical doses, stimulants can be highly addictive because of the intense pleasure associated with dopamine release.
Why are stimulants addictive?
Especially at nonmedical doses, stimulants can be highly addictive because of the intense pleasure associated with dopamine release. Pronounced psychological side effects may also be associated with nonmedical misuse of stimulant drugs.
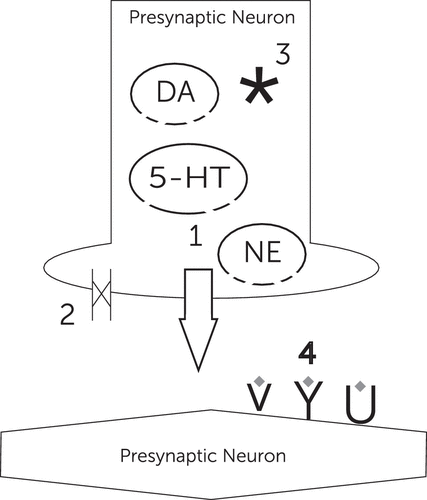
How do stimulants affect the nervous system?
Many types of stimulant drugs affect the central nervous system by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters called monoamines — a class of signaling molecules that includes dopamine. Some stimulants also affect the release and prevent the reabsorption of norepinephrine or serotonin.
What are the symptoms of a stimulant withdrawal?
Additionally, stimulant withdrawal may include symptoms such as insomnia, fatigue, and dysphoria. 1,7 To avoid the “comedown” commonly reported with drugs like cocaine and methamphetamine, people may begin to use the drugs more and more frequently. Such binge use may take place in an attempt to avoid feeling depressed or exhausted;
What is the meaning of "inability to stop the continued use of stimulant drugs"?
An inability to stop the continued, compulsive use of stimulant drugs. Spending increasing amounts of time and resources to obtain and use the drug. Choosing to take the drug over going to work, school, or social engagements.
Tapering the Dose
Most treatment professionals and doctors alike recommend that stimulant addiction be first treated using a method of tapering off the medication to prevent or minimize withdrawal symptoms. Tapering off a dose involves gradually lowering the dose of the medication to allow the body time to adjust without going into panic mode.
Behavioral Therapy
Stimulant addiction treatment involves behavioral therapy such as contingency management, cognitive-behavior therapy and similar approaches that look to help the user better cope with their thoughts and behaviors as they associate with their addiction.
When to Seek Stimulant Addiction Treatment
If you or someone you love is addicted to stimulants, there can be some challenges associated with determining when it’s time to seek help. Not all people will require treatment but for some, without professional help, there is little hope for full recovery.
What are the stimulants in psychotherapy?
Other stimulant drugs include cocaine, methylxanthines (theophylline and caffeine), nicotine, and vareniciline. It should be noted that nearly all psychotropic prescription medications produce better results for people in treatment if they are paired with a type of psychotherapy.
What are the different types of stimulants?
Types of Stimulants. Central nervous system stimulants can be divided into three groups: Convulsants and Respiratory Stimulants : Bicuculline, Picrotoxin, Pentylenetetrazol, and Doxapram are the drugs of this group. These drugs have no clinical application and are often used in poisons, in intensive care settings, and for research.
What are the stimulants in the brain?
They include: Other stimulant drugs include cocaine, methylxanthines (theophylline and caffeine), nicotine, and vareniciline.
How do drugs affect the brain?
Mechanism of Action. These drugs achieve their beneficial effects by increasing the levels of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain. Dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters, is related to concentration, attention, and feelings of reward and pleasure. Norepinephrine plays an important role in alertness.
What is a stimulant?
Stimulants are a type of drug that alters activity within the central and peripheral nervous systems. Most stimulants have an effect on blood pressure, heart rate, and alertness. Some drugs within this category have immense therapeutic value, while some have no clinical application.
What are the drugs that cause hallucinations?
Psychotomimetic Drugs/ Hallucinogens: These drugs produce hallucinations by altering the perception of the surrounding environment. Drugs in this group include lysergic acid, psilocybin, and mescaline. Psychomotor Stimulants: These psychotropic medications stimulate the central nervous system ...
Do stimulants increase glutamate levels?
Some stimulant drugs also increase the level of glutamate, a neurotransmitter associated with behavioral control and inhibition. People experiencing attention deficit hyperactivity (ADHD) often have low levels of glutamate. Methyxanthines inhibit the phosphodiesterase enzymes.
What is behavioral sensitization?
Another important source of information about systems involved in addiction arises from studies of behavioral sensitization, which refers to the progressive enhancement of species-specific behavioral responses to drugs of abuse that develops over the course of repeated drug exposure and persists after long periods of withdrawal. As mentioned above, sensitization occurs not only to the locomotor activating effects of psychostimulants but perhaps also to the incentive motivational effects of drugs of abuse, i.e., wanting ( Robinson and Berridge, 1993; Deroche et al., 1999 ). Previous exposure to cocaine or amphetamine, resulting in locomotor sensitization, promotes drug self-administration ( Horger et al., 1990; Mendrek et al., 1998; Lorrain et al., 2000) and enhances stimulus–reward learning and responding for conditioned reward ( Taylor and Horger, 1999; Taylor and Jentsch, 2001 ). The expression of sensitization is also associated with the reinstatement of self-administration after long-term extinction ( De Vries et al., 1998 ), whereas environmental stimuli and conditioning strongly modulate sensitization in rats, as well as drug craving in humans ( Robinson et al., 1998 ).
What happens after extinction of drug self administration?
After extinction of drug self-administration, exposure to drug-associated stimuli, experimenter-administered drug , or stress reinstates drug-seeking behavior, i.e., responding in extinction on a lever that previously resulted in drug infusions. This procedure was introduced, refined, and detailed by Stewart and colleagues ( de Wit and Stewart, 1981; Shaham et al., 1994) and has led to many investigations of psychological and neurobiological mechanisms of relapse. We focus here on cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking, because this not only models key aspects of relapse in human addicts, but also reveals the involvement of limbic cortical–ventral striatopallidal systems (Fig. 1) in cocaine addiction. A basic feature of this procedure is that established drug taking is first extinguished and then its reinstatement is subsequently studied. Although an effective and fruitful model of relapse, extinction of drug self-administration is not a means by which human addicts achieve abstinence, which is more likely to arise through an active decision to abstain or through forced abstinence. Moreover, because the extinguished response is so readily reinstated, it is unlikely that extinction training will provide an effective clinical approach to treatment. On the other hand, non-reinforced exposure to cocaine-associated stimuli, and thereby extinction of their motivational effects, might be a useful therapeutic strategy ( O'Brien et al., 1990, 1992; Robbins et al., 1992 ), although cue exposure in the clinic is unlikely to be sufficient because the cues may remain potent elicitors of craving in the original drug-associated environment.
Can D1 and D2 prevent cocaine seeking?
However, systemic psychopharmacological studies have shown that D2, but not D1, DA receptor agonists can precipitate reinstatement of cocaine seeking ( Self et al., 1996) and that both D1 and D2/D3 DA receptor antagonists can prevent conditioned reinstatement ( Weiss et al., 2001 ).
Is NAC DA responsive to drugs?
Although NAc DA may be especially responsive to many drugs of abuse initially ( Di Chiara and Imperato, 1988 ), the fact that DA transmission is increased in both the NAc and DS when drugs are self-administered over extended periods of time may contribute powerfully to aberrant learning involving both structures.
