- Diuretics. Diuretics, sometimes called water pills, are medications that help your kidneys eliminate sodium and water from the body. ...
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ...
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ...
- Calcium channel blockers.
Explore
· There’s no cure for essential hypertension, but there are treatments. Lifestyle changes If you have elevated blood pressure or hypertension, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to lower...
What is the best treatment for essential hypertension?
· Researchers have also studied renal denervation is a form of interventional treatment where renal sympathetic supply is ablated, via specialized catheter equipment, as a potential treatment for resistant hypertension (where adequate blood pressure control is not achieved despite adequate compliance to two or three anti-hypertensive drugs and lifestyle …
What are the other names for essential hypertension?
Primary hypertension treatment typically includes lifestyle changes and medications. Lifestyle changes Maintaining a healthy lifestyle includes: Adding regular exercise to your routine. Avoiding alcohol and recreational drugs. Eating a heart-healthy diet, including low sodium consumption. Maintaining good sleep habits.
What is essential hypertension and what causes it?
· Essential hypertension treatment Hypertension can be managed through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Doctors may recommend a range of lifestyle adjustments that will commonly include: Adopting a healthy, nutritious diet, ideally vegetarian or vegan in nature Exercising Stress relief techniques Reducing alcohol and tobacco use
Which medications are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure)?
Lifestyle modifications for patients with prehypertension or hypertension include: 1. Diet and increase exercise to achieve a BMI greater than 25. 2. Drink 4 ounces of red wine at least once per week. 3. Adopt the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) diet. 4. Increase potassium intake.
What is the treatment for essential hypertension?
beta-blockers, such as metoprolol (Lopressor) calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine (Norvasc) diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide/HCTZ (Microzide) angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, such as captopril (Capoten)
What is the first line treatment for essential hypertension?
The strongest body of evidence indicates that for most patients with hypertension, thiazide diuretics are the best proven first-line treatment in reducing morbidity and mortality.
What are 3 treatments for hypertension?
The classes of blood pressure medications include: Diuretics. Beta-blockers. ACE inhibitors.
What is the most common treatment for hypertension?
Diuretics are often recommended as the first line of therapy for most people who have high blood pressure. However, your doctor may start a medicine other than a diuretic as the first line of therapy if you have certain medical problems. For example, ACE inhibitors are often a choice for people with diabetes.
What is the difference between hypertension and essential hypertension?
Primary Hypertension (Formerly Known as Essential Hypertension) Essential (primary) hypertension occurs when you have abnormally high blood pressure that's not the result of a medical condition. This form of high blood pressure is often due to obesity, family history and an unhealthy diet.
What are the 5 types of diuretics?
Let's take a closer look at the classes of diuretics and how they work, and what nurses need to know.Loop Diuretics. ... Thiazides and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. ... Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. ... Potassium-Sparing Diuretics. ... Osmotic Diuretics. ... Nursing Considerations.
Which drug is given during hypertension?
The first are called dihydropyridine CCBs and include amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), nifedipine (Procardia), and nicardipine (Cardene). The second, termed nondihydropyridine CCBs include two drugs, diltiazem (Dilacor, Cardizem, Cartia, and Tiazac), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan).
What is the latest treatment for high blood pressure?
This drug, nicknamed the “triple pill” by the investigators, combines low doses of three existing drugs for blood pressure. Namely, these are: telmisartan (20 milligrams), amlodipine (2.5 milligrams), and chlorthalidone (12.5 milligrams).
What are the factors that contribute to the development of essential hypertension?
One of the described factors for the development of essential hypertension is the patient genetic ability to salt response. [2][3]About 50 to 60% of the patients are salt sensitive and therefore tend to develop hypertension. [4] Epidemiology.
What is the definition of hypertension?
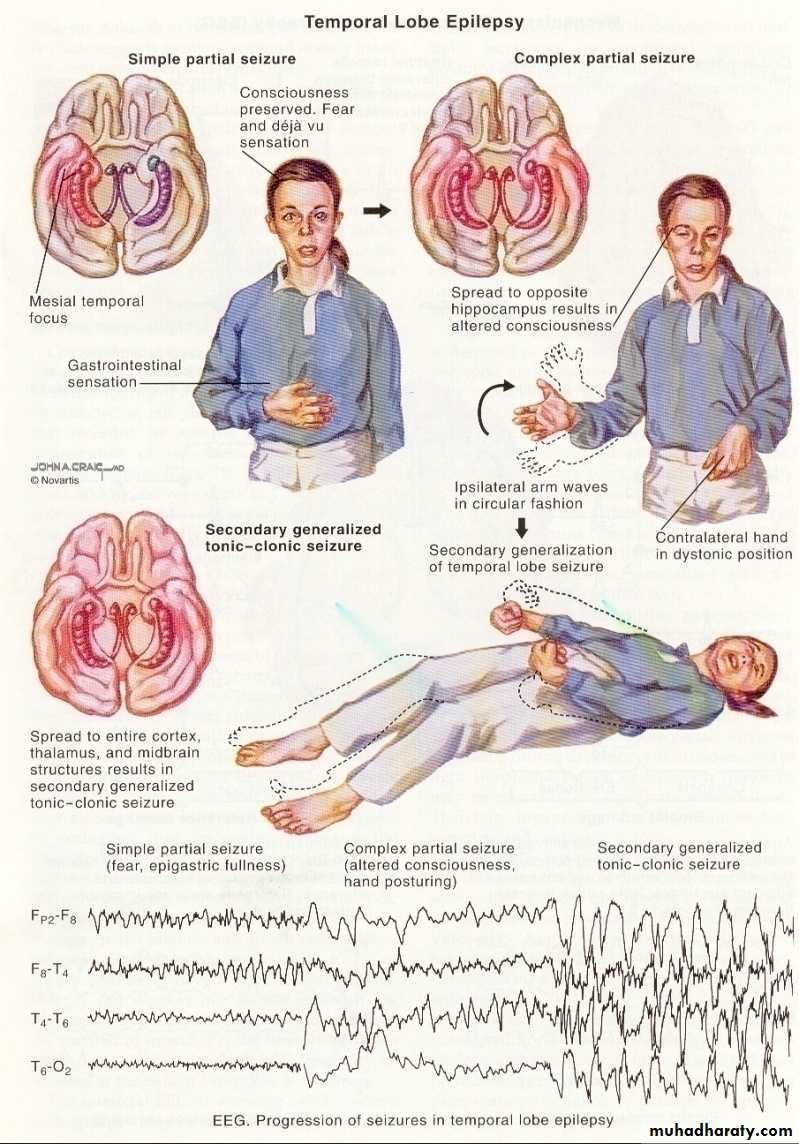
The current definition of hypertension (HTN) is systolic blood pressure (SBP) values of 130mmHg or more and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) more than 80 mmHg. Hypertension ranks among the most common chronic medical condition characterized by a persistent elevation in the arterial pressure. Hypertension has been among the most studied topics of the previous century and has been one of the most significant comorbidities contributing to the development of stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and renal failure. The definition and categories of hypertension have been evolving over the years, but there is a consensus that persistent BP readings of 140/90mmHg or more should undergo treatment with the usual therapeutic target of 130/80mmHg or less. This activity reviews the etiology, presentation, evaluation, and management of essential hypertension, and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating, diagnosing, and managing the condition.
Which blood pressure test is the most accurate?
Ambulatory blood pressure measurement is the most accurate method to diagnose hypertension and also aids in identifying individuals with masked hypertension as well as white coat effect.
What does the presence of lung rales and/or peripheral edema suggest?
Presence of lung rales and/or peripheral edema suggests cardiac dysfunction and gives a clue to the chronicity of hypertension.
What causes secondary hypertension?
Thyroid disorders (palpable/ painful or enlarged thyroid] which make up the common treatable causes for secondary hypertension
Is hypertension asymptomatic or asymptomatic?
Most cases of hypertension are asymptomatic and are diagnosed incidentally on blood pressures recording or measurement.
How many people have hypertension?
More than one billion adults worldwide have hypertension with up to 45% of the adult populace being affected with the disease[5]. The high prevalence of hypertension is consistent across all socio-economic and income strata, and the prevalence rises with age accounting for up to 60% of the population above 60 years of age. [5]
What is the best way to reduce blood pressure?
Diuretics . Diuretics , sometimes called water pills, help the kidneys get rid of excess water and salt (sodium). This reduces the volume of blood that needs to pass through the blood vessels. As a result, blood pressure goes down. There are three major types of diuretics defined by how they work.
What is the systolic pressure of a person with hypertension?
Hypertension (or high blood pressure) is present once the systolic pressure is 130 or higher, or the diastolic pressure is 80 or higher.
What is the purpose of calcium channel blockers?
Calcium channel blockers limit calcium from entering the smooth muscle cells of the heart and blood vessels. This makes the heart beat less forcefully with each beat and helps blood vessels relax.
What is the purpose of beta blockers?
Beta-blockers help the heart to beat with less speed and force. The heart pumps less blood through the blood vessels with each beat, so blood pressure decreases. There are many drugs within this classification, including:
How many types of diuretics are there?
There are three major types of diuretics defined by how they work. They include:
Can lifestyle changes help with high blood pressure?
Some people find that lifestyle changes alone are enough to control their high blood pressure. But many also take medication to treat their condition. There are many different types of blood pressure medications with different modes of action.
What is considered high blood pressure?
The goal is to get your blood pressure below the high range. If normal is less than 120/80 mm Hg, what’s high? When the systolic blood pressure — the top number — is between 120 and 129, and the diastolic blood pressure — the bottom number — is less than 80, this is considered elevated blood pressure.
Overview
Primary (essential) hypertension is high blood pressure that is multi-factorial and doesn’t have one distinct cause. It’s also known as idiopathic or essential hypertension. Above-normal blood pressure is typically anything over 120/80 mmHg. This means that the pressure inside your arteries is higher than it should be.
Symptoms and Causes
Unhealthy habits and certain circumstances put you at risk for essential primary hypertension.
Diagnosis and Tests
A diagnosis of primary hypertension is made when you have high blood pressure, but none of the conditions that cause secondary hypertension. The best way to know if you have it is by seeing a healthcare provider who will:
Management and Treatment
Primary hypertension treatment typically includes lifestyle changes and medications.
Living With
Medications alone are not enough to lower your blood pressure. For the best results, you need to live a healthy lifestyle.
What is the best medication for hypertension?
Diuretics. There are three classes of diuretic drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Most commonly used are thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide or chlorthalidone. There is not usually an increased urine flow after the first one or two days of taking these medications. Nevertheless, it is best to take them in ...
What are the different types of diuretics?
Different Drugs: Thiazide diuretics include: hydrochlorothiazide (usual starting dose 12.5 to 25 mg daily) or chlorthalidone (similar dose range). Loop diuretics include: furosemide (Lasix), bumetanide (Bumex), and torsemide (Demadex), torsemide has a rather longer duration and is preferred in patients with heart failure. Ethacrinic acid (Edecrin) is used in the rare patients who are allergic to diuretics. Loop diuretics are not as effective as thiazides in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension. They are used especially to treat edema (swelling of the ankles) or heart failure. However, unlike thiazides, they effective in patients with poor kidney function in lowering blood pressure or treating edema.
What is angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor?
ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS (ACEIs) ACEIs are widely used to treat hypertension because they are effective, have relatively few side effects and in reduce the complications of hypertension such as heart attacks and strokes .
What diuretics can raise potassium levels?
Distal, potassium retaining diuretics include: amiloride (Midamor) and Triamterene (Dyrenium), together with spironolactone (Aldactone) and eplerenone (Inspra). All these agents can raise serum potassium. This is usually beneficial in patients receiving thiazide or loop diuretics who have increased loss of potassium in the urine. Thus these drugs are often prescribed together. However an increase in serum potassium predisposes to cardiac arrhythmias and can be especially dangerous in patients with a thickened heart (left ventricular hypertrophy) or coronary artery disease. Spironolactone causes problems with sexual performance and sometimes breast swelling in males, but is free of these kinds of effects in females. Eplerenone does not have these adverse effects, but is more expensive.
What is edecrin used for?
Ethacrinic acid (Edecrin) is used in the rare patients who are allergic to diuretics. Loop diuretics are not as effective as thiazides in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension. They are used especially to treat edema (swelling of the ankles) or heart failure.
Can a diuretic cause hypokalemia?
Adverse Effects: Diuretics increase the excretion of potassium and can lead to hypokalemia (low blood potass ium concentration) which predisposes to irregular heart beats, and muscular weakness. However, a combination of a thiazide or loop diuretic with a distal, potassium sparing agent (such as in the combined medications, Maxzide or Moduretic), prevents potassium loss and obviates this problem. Diuretics lead to some increase in uric acid and should not normally to be used in patients with gout. They cause a small increase in blood glucose, but it is unclear whether this predisposes to diabetes in the long term. Over treatment with diuretics can lead to low blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension (weakness, dizziness and possibly fainting on standing) and a feeling of tiredness and lethargy, all of which can be prevented or reversed by holding the diuretic for a day or two and resuming, if necessary, at a lower dosage.
Is thiazide a first line drug?
For this reason, the Joint National Commission on Hypertension Detection Evaluation and Treatment (JNCVII) recommended thiazide diuretics as first line therapy for patients with hypertension, unless there were special reasons to select another type of drug.
What is essential hypertension?
Essential hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that has no clearly identifiable cause, but is thought to be linked to genetics, poor diet, lack of exercise and obesity. It is by far the most common form of high blood pressure, affecting the majority of those who experience hypertension. It is also known as primary hypertension.
How to lower blood pressure with essential hypertension?
People diagnosed with essential hypertension generally stand a good chance of lowering their blood pressure through lifestyle changes, medication or a combination of the two. Lifestyle changes will normally need to be maintained for the rest of one’s life to ensure high blood pressure does not reoccur. Depending on the person, medications may need to be taken indefinitely. In some cases, the use of medication can be stopped after blood pressure has fallen, with these lower levels then maintained through lifestyle alterations.
Can hypertension be diagnosed with stress?
Stress, anger, physical exercise and other factors can temporarily raise a person’s blood pressure, meaning a diagnosis of essential hypertension can only be made when results are consistently high. Multiple readings, including readings taken outside of the hospital or doctor’s office, should be taken.
Is lack of physical activity a sign of hypertension?
A lack of physical activity is associated with hypertension. Exercise is one of the key methods of managing high blood pressure.
Does salt cause hypertension?
Excessive salt (sodium) consumption, defined by the American Heart Association as eating over 2300 mg per day, can play a role in the onset of essential hypertension. Salt increases retention of water in the body, which in turn increases the volume of blood and, consequently, blood pressure.
How many genes are linked to high blood pressure?
Those with a family history of essential hypertension are more likely to be at risk of developing the condition themselves. Fifty genes have been identified as linked to high blood pressure.
Is secondary hypertension the same as essential hypertension?
Secondary hypertension. Whereas essential hypertension is characterized by its lack of identifiable causes, secondary hypertension, another form of hypertension, is directly linked to a variety of vascular, endocrine (related to hormones), heart and kidney conditions. It is far less common than essential hypertension.
What is a chronic disease where patients may be taking drugs for a long time?
Hypertension is a chronic disease where patients may be taking drugs for a long time.
Do antihypertensive drugs come in generic form?
Few antihypertensive drugs come in generic formulations.
What does the number 2 mean in blood pressure?
blood pressure measurements include 2 numbers. This is the higher number. It represents pressure of blood against the artery wall when the heart contracts.
What causes arterial walls to thicken?
hardening of the arterial walls . HBP causes walls to thicken and harden.
Does HBP cause heart failure?
HBP will make the heart work much harder to pump blood to the lungs and body. Over time the heart muscle will thicken and stretch and this can lead to an enlarged heart and heart failure.
Can you take appetite control with hypertension?
patients with hypertension should not take drugs such as appetite control, asthma, colds, and hay fever without asking a prescriber.
What is the first choice for treating hypertension?
Treating essential hypertension. The first choice is usually a thiazide diuretic. We concluded in 2004 that the first-choice treatment for hypertension in adults was single-agent therapy with the thiazide diuretic chlortalidone or, when this drug is not available, the thiazide diuretic hydrochlorothiazide.
Is ACE inhibitor more effective than thiazide?
Several systematic reviews concluded that neither calcium-channel blockers, ACE inhibitors nor beta-blockers are more effective than thiazide diuretics in reducing mortality or the incidence of stroke. The efficacy of the thiazide diuretic chlortalidone is supported by the highest-level evidence, from three comparative clinical trials versus ...
Is chlortalidone an ACE inhibitor?
In one of these trials, chlortalidone was superior to the ACE inhibitor lisinoprilin preventing stroke.

Treatment
- There are three classes of diuretic drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Most commonly used are thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide or chlorthalidone. There is not usually an increased urine flow after the first one or two days of taking these medications. Nevertheless, it is best to take them in the morning to prevent annoying uri...
Interactions
- Diuretics increase the effectiveness or all other classes of antihypertensive agents. Therefore, almost any subject, except those with a contraindication, should receive a diuretic if their blood pressure requires more than one drug for its management.
Adverse effects
- Adverse Effects: Diuretics increase the excretion of potassium and can lead to hypokalemia (low blood potassium concentration) which predisposes to irregular heart beats, and muscular weakness. However, a combination of a thiazide or loop diuretic with a distal, potassium sparing agent (such as in the combined medications, Maxzide or Moduretic), prevents potassium loss a…
Types
- Different Drugs: Thiazide diuretics include: hydrochlorothiazide (usual starting dose 12.5 to 25 mg daily) or chlorthalidone (similar dose range). Loop diuretics include: furosemide (Lasix), bumetanide (Bumex), and torsemide (Demadex), torsemide has a rather longer duration and is preferred in patients with heart failure. Ethacrinic acid (Edecrin) is used in the rare patients who …
Medical uses
- ACEIs are widely used to treat hypertension because they are effective, have relatively few side effects and in reduce the complications of hypertension such as heart attacks and strokes. They have a special use in patients with diabetes mellitus who have protein the urine (diabetic nephropathy) and in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in whom they appeared to have …
Examples
- Individual Drugs: The following are examples of ACEIs in clinical practice: benazepril (Mylan), captopril (Capoten), enalapril (Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), Lisinopril (Prinivil), moexipril (Univasc), quinapril (Accupril), ramipril (Altace) and trandolapril (Mavik). There are some small differences in how long these drugs act in the circulation, they are relatively small and, with the e…
Side effects
- Biochemical changes with ACEIs are usually insignificant in patients with normal kidney function. However, in those with impaired kidneys, they can raise the serum potassium concentration to levels that are dangerous and require either a change in therapy, or increasing thiazide or loop diuretic dosage to promote potassium loss. Such patients should discuss with their physician o…
Contraindications
- Special Indications: As these include patients with chronic kidney disease (but see the adverse effects above), early diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, or left ventricular hypertrophy. These drugs will not be discussed in detail since they are used infrequently.
Mechanism of action
- This group of drugs was introduced next after diuretics, to be used for hypertension. They act on a part of the nervous system that controls blood pressure, known as the sympathetic nervous system. Blockade of the sympathetic nervous system reduces blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels, and decreasing the rate and force of contraction of the heart. Therefore, beta blockers a…
Pharmacology
- The actions of these agents are enhanced in patients taking diuretic drugs and therefore are a good second or third line selection in those patients who are not controlled with a diuretic and an ACEI or ARB. Unfortunately, alpha blockers have been shown to be less affective than other groups of blood pressure lowering agents in preventing the complications of heart failure and he…
Categories
- Individual drugs: They fall into two categories. The first are called dihydropyridine CCBs and include amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), nifedipine (Procardia), and nicardipine (Cardene). The second, termed nondihydropyridine CCBs include two drugs, diltiazem (Dilacor, Cardizem, Cartia, and Tiazac), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan). Both groups are e…
Effects
- Non-dihydropyridine CCBs cause cardiac slowing. This typically reduces the heart rate by about 10%. It can be beneficial in some patients with a fast heart rate or who have irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation), but in those with a slow initial heart rate, it can cause symptoms of decreased cardiac output (tiredness, lethargy, and dizziness on exertion). This group of drugs also can cau…
Research
- This is a rapidly developing field with extensive research, both by Centre scientists in the laboratory and clinical investigators in patients with hypertension. The following outlines some of the areas of research conducted at the Centre at Georgetown. Research at the Hypertension, Kidney and Vascular Research Centre at Georgetown has focused on a different path, namely dr…
Pathophysiology
- Oxidative stress occurs in cells and tissues of the body when oxygen reacts to form toxic molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS). These can inactivate the normal signaling pathways between cells, damage cell membranes and proteins, and alter the DNA that forms the basis of our genes. Therefore, oxidative stress has widespread effects in the body. Increasing ev…
Cause
- Amongst those factors that are under our control which influence the probability of developing hypertension, an excessive dietary salt intake is probably the most important. Research in animal models at Georgetown at the Center for Hypertension, Kidney, and Vascular Research has linked dietary salt intake with oxidative stress that may underlie the hypertension and adverse consequ…
Resources
- For further information about how to support the research in Georgetown Universitys Center for Hypertension, Kidney, and Vascular Research, please see Georgetown Universitys Office of Advancement.