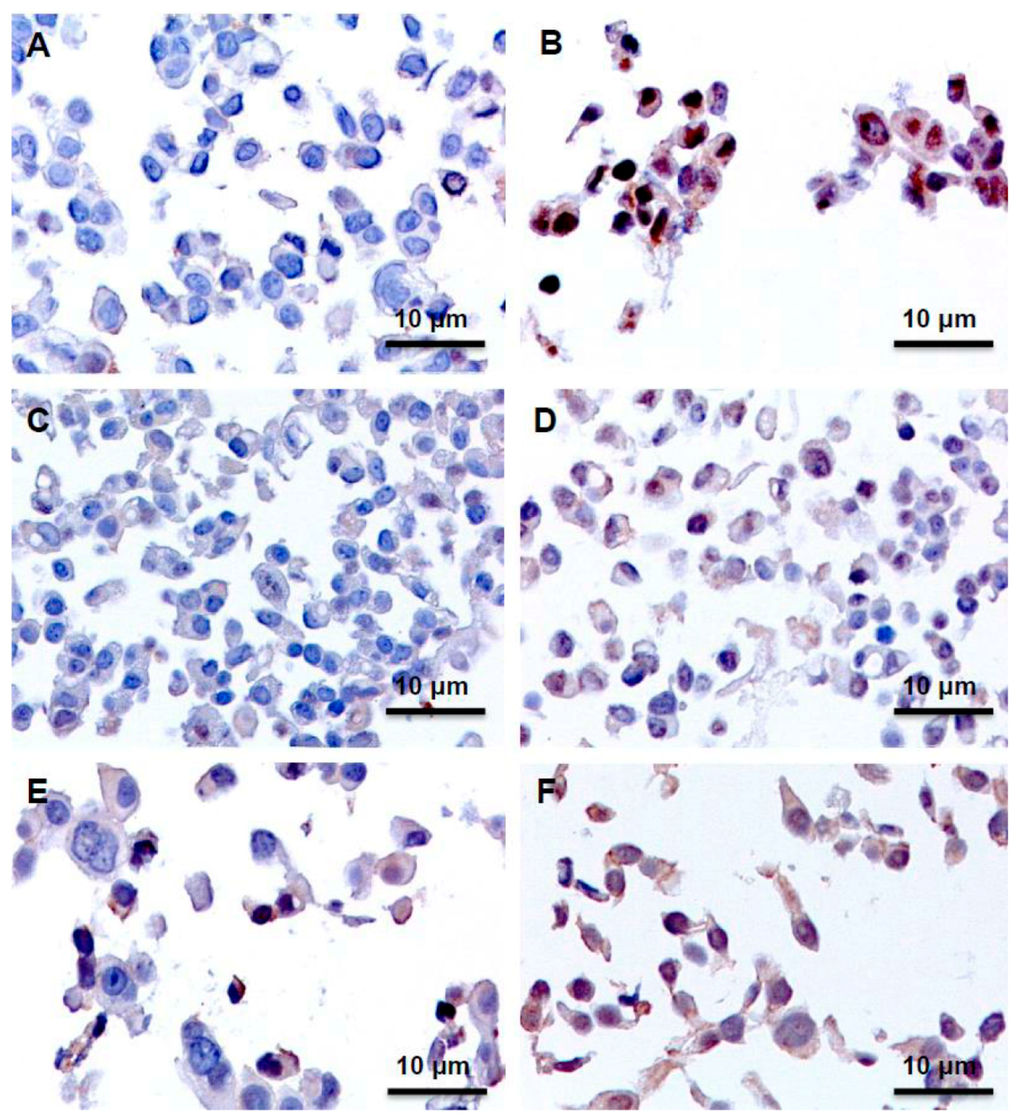
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator and is mainly indicated for the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and postsurgery neoadjuvant therapy in ER-positive breast cancers. Interestingly, 5-10% of the ER-negative breast cancers have also shown sensitivity to tamoxifen treatment.
Does tamoxifen really work?
When it comes to preventive uses, tamoxifen has a good track record of substantially reducing new or recurrent cancer in women with high levels of cancer risk. Another positive is its cost. As an older drug, tamoxifen is available in generic form, so it is likely to be less expensive than some newer medications.
What happens when you stop taking tamoxifen?
Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
- increased bone or tumor pain
- pain or reddening around the tumor site
- hot flashes
- nausea
- excessive tiredness
- dizziness
- depression
- headache
- thinning of hair
- weight loss
When to take tamoxifen?
When is tamoxifen given?
- Primary breast cancer. Tamoxifen may be prescribed if you have primary breast cancer. ...
- Breast cancer that has come back or spread
- To reduce the risk of breast cancer developing. Tamoxifen may be an option for some people who do not have breast cancer but higher risk of developing it because of ...
What is about not taking tamoxifen?
Supplements, vitamins & other exposures to be avoided on tamoxifen
- Licorice root supplements
- Maca root supplements
- Milk thistle supplements
- Quercetin supplements
- Red clover supplements
- Reishi mushroom (ok for IBC)
- Resveratrol supplements
- Rhein supplements
- Sage essential oil
- Sage & red sage root supplements

When is tamoxifen indicated?
[1] Specifically, it is indicated for the treatment of breast cancer in a variety of settings. It should be noted that evidence suggests that patients with estrogen receptor-positive tumors are more likely to benefit from tamoxifen. [2] Tamoxifen also has many off-labeled uses and may require additional data.
Is tamoxifen the first line treatment for breast cancer?
Since the late 1970s, tamoxifen has been the accepted gold-standard first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women, as studies showed that it was as effective as other therapies used at that time but was associated with fewer side effects.
Do all breast cancer patients take tamoxifen?
A study has found that more than 18% of premenopausal women diagnosed with early-stage, hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer were not taking hormonal therapy as prescribed, including more than 13% who were not taking the medicine at all.
Who is a candidate for tamoxifen?
Women with Stage III or Stage IV breast cancer (tamoxifen is usually prescribed in conjunction with chemotherapy or other treatment) Women with early stage breast cancer after breast surgery (lumpectomy or mastectomy) Women who have been identified to be at high risk of developing breast cancer.
Do you need radiation for Stage 1 breast cancer?
External beam radiation therapy is offered after breast-conserving surgery for stage 1 breast cancer. All of the breast and the lymph nodes under the arm and near the collarbone are treated. An extra dose, or boost, of radiation may be given to the area where the tumour was removed.
Should I switch to tamoxifen?
Tamoxifen has been and remains a good option for many women. However, if your risk of recurrence is high, you should certainly consider switching to one of the aromatase inhibitors.
Should I take tamoxifen to prevent breast cancer?
Tamoxifen and raloxifene have been shown to reduce the risk of breast cancer in women with a higher-than-average risk, but these drugs can have their own risks and side effects.
How often does atypical ductal hyperplasia turn into cancer?
At 25 years after diagnosis, about 30% of women with atypical hyperplasia may develop breast cancer.
What is the success rate of tamoxifen?
The absolute increased risk of death from endometrial cancer in women who took tamoxifen for 10 years versus 5 years was 0.2 percent....Ten Years of Tamoxifen Reduces Breast Cancer Recurrences, Improves Survival.5 Years10 YearsRisk of Death from Breast Cancer15.0 percent12.2 percent1 more row•Mar 20, 2013
When is tamoxifen not recommended?
Most experts agree that tamoxifen and raloxifene should not be used to reduce breast cancer risk in women who: Have a higher risk of serious blood clots* Are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Are breastfeeding.
Is weight gain a side effect of tamoxifen?
Some even call it the "backbone" of breast cancer treatment. Even with all that fanfare, tamoxifen has been loosely associated with weight gain. Studies have tracked weight gain and other side effects of the drug for years. Some resources even list weight gain as a possible side effect.
What are the worst side effects of tamoxifen?
The most serious health risks of tamoxifen, such as endometrial cancer (cancer of the lining of the uterus) and blood clots in the lungs, are rare [102].
What is tamoxifen used for?
1. What is tamoxifen? Tamoxifen is a hormone (endocrine) therapy drug. Tamoxifen is used to treat breast cancer in both premenopaus al women (women who have not yet gone through the menopause) and postmenopausal women. It can also be taken by men who have breast cancer.
How long does tamoxifen last?
People being treated for primary breast cancer will usually take tamoxifen for between five and ten years.
Why do people with breast cancer have a higher risk of blood clots?
People with breast cancer have a higher risk of blood clots. Their risk is higher because of the cancer itself and some treatments for breast cancer. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (secondary breast cancer), this also increases the risk.
What are the symptoms of a central line inserted to give chemotherapy?
Pain, redness/discolouration, heat and swelling of the calf or thigh. Swelling, redness or tenderness where a central line is inserted to give chemotherapy, for example in the arm, chest area or up into the neck. Shortness of breath. Pain or tightness in the chest. Unexplained cough or coughing up blood.
Can you take tamoxifen with ovarian suppression?
For younger women who are premenopausal, tamoxifen may be given alone or sometimes alongside ovarian suppression. If you’re taking tamoxifen for locally advanced breast cancer or for secondary breast cancer, you’ll usually continue to take it for as long as it is keeping the cancer under control.
Can tamoxifen be used for breast cancer?
Tamoxifen may be prescribed if you have primary breast cancer, recurrence or secondary breast cancer. It may also be used to reduce the risk of breast cancer developing in women who have a significant family history of breast cancer.
Can you take tamoxifen after breast surgery?
Tamoxifen may be prescribed if you have primary breast cancer. It’s usually given after surgery to reduce the risk of breast cancer returning in the same breast or spreading somewhere else in the body. This is known as adjuvant (additional) therapy. Occasionally, tamoxifen may be used as the first treatment for breast cancer.
What are the risks of tamoxifen?
In women with estrogen receptor-positive DCIS who have lumpectomy plus radiation therapy, tamoxifen may lower the risk of: 1 DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) 2 Invasive breast cancer
Is ductal carcinoma in situ invasive?
Introduction: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive breast cancer. Without treatment, DCIS can progress to invasive breast cancer over time. So, almost all cases of DCIS are treated. In women with estrogen receptor-positive DCIS who have lumpectomy plus radiation therapy, tamoxifen may lower the risk of: ...