
Table 1
| Strategies | Cancer types | Stem cell applications | References |
| Stem cell modifications | |||
| Enzyme/prodrug therapy | Glioma | NSCs (retroviral transduction with CD) | [ 16, 26] |
| Enzyme/prodrug therapy | Glioma | NSCs (baculoviral transduction with HSV- ... | [ 29] |
| Enzyme/prodrug therapy | Glioma | MSCs (lentiviral and retroviral transduc ... | [ 27] |
What diseases can be treated with stem cell therapy?
- Multiple Sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease where inflammation is caused by the failure of the immune system, which damages cells of the brain or spinal cord.
- Cardiovascular Diseases. ...
- Diabetes and Diabetic Ulcer. ...
- Autism. ...
- Liver Diseases. ...
- Crohn’s Disease. ...
- Fibromyalgia. ...
- Parkinson’s Disease. ...
- Injuries and Musculoskeletal Pain. ...
- COVID-19. ...
How effective is stem cell therapy against cancer?
There are several problems:
- Type 1 diabetesis an autoimmune disease. The body is attacking the pancreatic islet cells. ...
- There are no known adult stem cells that reproducibly differentiate into pancreatic islet cells. ...
- Some research has looked into turning ESCs into islet cells. However, the patient would have to be on immunosuppressants fo
Are cancer stem cells the key to curing cancer?
The use of stem cells in cancer treatment is not for cure to replace cells after knocking out all cancer cells in blood and bone marrow with high does of chemotherapy and radiation. The stem cells travel to the knocked out bone marrow and replenish it and start producing normal cancer free blood cells in the patient.

What cancers can stem cell cure?
Stem cell or bone marrow transplants are treatments for some types of cancer including leukaemia, lymphoma and myeloma. You have them with high dose chemotherapy and sometimes radiotherapy. They are sometimes called stem cell rescue, or bone marrow rescue, or intensive treatment.
What type of cancers are most often treated with a stem cell transplant?
A bone marrow transplant is also called a stem cell transplant or, more specifically, a hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Transplantation can be used to treat certain types of cancer, such as leukemia, myeloma, and lymphoma, and other blood and immune system diseases that affect the bone marrow.
What are 3 disorders that might be treated using stem cells?
People who might benefit from stem cell therapies include those with spinal cord injuries, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, heart disease, stroke, burns, cancer and osteoarthritis.
Do all cancers have stem cells?
Cancer stem cells are a type of adult or progenitor cell found in most types of cancer. These cells generally represent just 1% to 3% of all cells in a tumor, but they are the only cells with the ability to regenerate malignant cells and fuel the growth of the cancer.
What cancers require bone marrow transplant?
The following diseases are the ones that most commonly benefit from bone marrow transplant:Leukemias.Severe aplastic anemia.Lymphomas.Multiple myeloma.Immune deficiency disorders.Some solid-tumor cancers (in rare circumstances)
What is the life expectancy after a stem cell transplant?
The relative mortality rate was high early after transplant as expected (standardized mortality ratio [SMR], 34.3 in the first 2-5 years) but persisted beyond 30 years (SMR, 5.4). Factors estimating mortality included age, high-risk disease, chronic GVHD, and use of PBSC grafts.
What is the success rate of stem cell treatment?
The popularity of stem cell treatments has significantly increased, thanks to its high effectiveness and recorded success rates of up to 80%. It is a modern type of regenerative medical treatment that uses a unique biological component called stem cells.
Can stem cells cure anything?
Today, doctors routinely use stem cells that come from bone marrow or blood in transplant procedures to treat patients with cancer and disorders of the blood and immune system.
Who needs stem cell transplant?
A stem cell transplant is used for treatment when: Your body cannot make the blood cells it needs because your bone marrow or stem cells have failed. Your bone marrow or blood cells have become diseased. In this case you need healthy stem cells to replace the diseased bone marrow/stem cells.
Which type of stem cells is most useful and why?
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they can give rise to every cell type in the fully formed body, but not the placenta and umbilical cord. These cells are incredibly valuable because they provide a renewable resource for studying normal development and disease, and for testing drugs and other therapies.
How much does a stem cell transplant cost?
Stem cell therapy cost can range anywhere between $5000 - $50,000. Patients must do their research and ask as many questions as they can before financially committing to treatment.
Can stem cells form tumors?
One hallmark of embryonic stem cells is that they cause a particular type of tumor called a teratoma. Stem cell researchers must learn how to prevent these tumors before any transplantation-based therapy can be successful.
When is stem cell transplant commonly used?
A stem cell transplant may be used to treat leukemia and lymphoma, cancers that affect the blood and lymphatic system. Additionally, transplants are used to treat hereditary blood disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, and autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis.
What are stem cell transplants used for?
Stem cell transplants are used to replace bone marrow cells that have been destroyed by cancer or destroyed by the chemo and/or radiation used to treat the cancer. There are different kinds of stem cell transplants. They all use very high doses of chemo (sometimes along with radiation) to kill cancer cells.
When is stem cell transplant recommended?
A stem cell transplant is used for treatment when: Your body cannot make the blood cells it needs because your bone marrow or stem cells have failed. Your bone marrow or blood cells have become diseased. In this case you need healthy stem cells to replace the diseased bone marrow/stem cells.
Is stem cell transplant a cure for leukemia?
When a person receives a stem cell transplant, the body can start making new blood cells. Alongside high dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment, this procedure can cure leukemia or cause a long-lasting remission.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Stem Cell Treatments for Cancer. Medically Reviewed by Kumar Shital, DO on July 17, 2020. If you have leukemia or lymphoma, you may need a stem cell transplant. These cells help replace cells damaged by the cancer. They also let your body recover faster from intense chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
What happens when you get stem cells from a donor?
When you get stem cells from a donor or cord blood, there’s a risk of something called graft-versus.-host disease. It’s when your body fights to get rid of the new cells, or the cells launch an attack against you. It could happen right after the transplant or not until a year later.
How do you get autologous stem cells?
In an autologous (AUTO) transplant, doctors take healthy stem cells from your bone marrow or blood. They’re frozen and carefully stored. Since they're outside your body, they aren’t harmed during the chemotherapy or radiation treatments you’ll need to get rid of your cancer cells.
Where do stem cells grow?
What Are Stem Cells? They grow inside your marrow, the soft tissue of your bones. They’re also in your blood, as well as blood from umbilical cords. As they mature, blood stem cells change into three types of cells your body needs: Platelets that help your blood clot.
Can you get stem cells from someone you don't know?
You can also get stem cells from someone you don’t know. Before an ALLO transplant, you’ll get chemotherapy, radiation, or both. This wipes out your own stem cells and gets your body ready for the new ones soon after your treatment is done. If your doctor can’t find a donor,they may use cells from donated umbilical cord blood.
Do stem cells keep cancer alive?
Now, there’s reason to believe that special, fast-growing cancer stem cells keep your disease alive by reproducing. If that’s true, in the next few years, the focus of treatments could shift from trying to shrink tumors to trying to kill this type of cell. Pagination.
Can you have high doses of chemotherapy?
If you’re being treated with your own stem cells, you may have high-dose chemotherapy first. This can cause side effects. What and how severe they are depend on the dose. You might have:
Why is stem cell treatment important?
The stem cell treatment will try to get the best out of the immune system for addressing the tumors. The antigens specific to cancer helped the development of antigen-specific immunotherapy. With dendritic cell vaccination, the body receives antigen and adjuvant to therapeutic T-cells. DCS has been recognized as the natural agent to deliver antigens. They’re fundamental for cancer treatment research, presenting the fantastic ability to control immunity and immune tolerance. It’s what makes DCS essential for boosting the protection against cancer.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Stem cells play an essential role in the cure of cancer, and dendritic cell immunotherapy is the most notable approach to date. It’s a very efficient autologous stem cell treatment for cancer that relies on the use of the dendritic, lymphokine-activated killer cells (LAK cells) and natural killer cells (NK cells).
Why do people get chemo?
The main reason the method works is insulin, which will make the cancer cell open and receive chemotherapy. With traditional chemo, patients have to obtain a large amount of chemo to work against cancer. Unfortunately, the cancer elements aren’t the only ones affected by the chemo, as healthy cells will be damaged and killed. The immune system will suffer, and patients will undergo severe adverse effects, such as graft versus host disease.
What is IPT treatment?
IPT treatment will result in many types of aggressive cancers, such as colon and lung cancer and other types of cancers. Bone marrow transplantation, also called stem cell transplant, may lead to surprising results for some sorts of cancer. Leukemia or specific types of lymphoma give results with stem cell transplant.
Which method of stem cell therapy is better for stage 4 patients?
The dendritic stem cell method gives impressive results to stage 4 patients. Immunotherapy will fight against cancer, no matter the stage of metastasis. We should also highlight that the dendritic cell method gives better results with therapies such as hyperthermia.
What does "low dose" mean in chemo?
When we mean a small dose of chemo, we mean one-tenth of the typical amount of chemotherapy. It’s why IPT has also named the low dose of chemotherapy. The method is useful because it aims only for the cancer cell, and the healthy elements aren’t affected by the small amount of chemotherapy.
Which cells are the most potent antigen presenting elements?
Dendritic cells are the most potent antigen-presenting elements. The DCS (dendritic cells) with tumor antigen can make the cytotoxic T lymphocytes (specific to tumors) in the lymphatic tissues. DC vaccination is a productive type of cancer immunotherapy, with specific mechanisms.
How do stem cells work for cancer?
In a typical stem cell transplant for cancer, very high doses of chemo are used, sometimes along with radiation therapy, to try to kill all the cancer cells. This treatment also kills the stem cells in the bone marrow. This is called myeloablation or myeloablative therapy. Soon after treatment, stem cells are given (transplanted) to replace those that were destroyed. The replacement stem cells are given into a vein, much like a blood transfusion. The goal is that over time, the transplanted cells settle in the bone marrow, begin to grow and make healthy blood cells. This process is called engraftment.
How to get rid of cancer cells after transplant?
Another treatment to help kill cancer cells that might be in the returned stem cells involves giving anti-cancer drugs after the transplant. The stem cells are not treated. After transplant, the patient gets anti-cancer drugs to get rid of any cancer cells that may be in the body. This is called in vivo purging.
What are the benefits of allogeneic stem cell transplant?
Benefits of allogeneic stem cell transplant: The donor stem cells make their own immune cells, which could help kill any cancer cells that remain after high-dose treatment. This is called the graft-versus-cancer or graft-versus-tumor effect. Other advantages are that the donor can often be asked to donate more stem cells or even white blood cells if needed, and stem cells from healthy donors are free of cancer cells.
Why is a mini transplant important?
And because the stem cells aren’t all killed, blood cell counts don’t drop as low while waiting for the new stem cells to start making normal blood cells. This makes it especially useful for older patients and those with other health problems. Rarely, it may be used in patients who have already had a transplant.
What is the first step in autologous stem cell transplant?
Autologous stem cell transplants. In this type of transplant, the first step is to remove or harvest your own stem cells. Your stem cells are removed from either your bone marrow or your blood, and then frozen.
What is the procedure called when you get a bone marrow transplant?
Depending on where the stem cells come from, the transplant procedure may be called: They can all be called hematopoietic stem cell transplants.
Why are white people better at stem cell transplants?
This is because ethnic groups have differing HLA types, and in the past there was less diversity in donor registries, or fewer non-White donors.
Why are stem cells important?
Some day, stem cells will be enlisted to help repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. They will rescue us from diseases for which drugs can only treat the symptoms. But they may have another role in our lives, one that is not so beneficial. They may in fact be the source of some, and possibly most cancers.
What do embryonic stem cells do?
Embryonic stem cells produce the progenitors and patterns that determine how our organs, muscles, sinews, and skeletons are formed and how they are arranged in the body. After their work is done, they leave behind a guardian population of stem cells that repair each tissue as the need arises.
What happens when a stem cell divides into two?
When the stem cell divides into two, it creates one progenitor and renews itself. The progenitor continues its path of differentiation into mature, specialized cells, while the new stem cell waits for the next round when it is called upon to replenish tissue. Stem cells survive much longer than ordinary cells, increasing the chance ...
What is the name of the cell that initiates melanomas?
A recent study completed by Markus Frank, Assistant Professor at Harvard Medical School, and Associate Faculty member of HSCI, identified a class of stem cells that initiate melanomas (skin cancer) in an animal model, and identified an antibody that slowed tumor growth by specifically targeting these stem cells.
What is the rationale for a new treatment strategy?
A rationale for a new treatment strategy is emerging that specifically targets the cancer stem cells, which may only be a very small percentage of the total tumor mass. In combination with current treatments, however, these new treatments may lead to a more complete and durable response.
Who discovered that tumors are linked to embryonal tissue growth?
Throughout the mid-19th century, theories and observations accumulated that tumors were linked to embryonal tissue growth, culminating in a comprehensive “embryonal rest” theory put forward by Julius Cohnheim in 1875.
Who discovered stem cells in breast cancer?
In 2003, Michael Clarke of the University of Michigan and now at Stanford, found cancer stem cells in breast tumors and demonstrated that most other cells in the tumor were incapable of seeding growth on their own. Others followed with similar discoveries in brain cancer, colon cancer, bone cancer and melanoma.
What are stem cells used for?
Stem cells can function as in situdrug factories, secreting antitumor agents for an extended period of time, and overcoming various cancer therapy limitations, such as high systematic toxicity and short drug half-life. TNF-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is one of the most widely used, secreted therapeutic agents, and induces tumor cell apoptosis [30]. However, its short half-life reduces its therapeutic effectiveness in vivo[31]. This could be mitigated by encapsulating TRAIL-expressing stem cells in a synthetic extracellular matrix (sECM) that is introduced into the GBM resection cavity after surgical debulking [32]. The encapsulated cells could continually release therapeutic molecules at resection margins. This approach delays malignant and invasive brain tumor regrowth and increases survival in mice.
What are the properties of stem cells?
Stem cells have unique properties, such as migration toward cancer cells, secretion of bioactive factors, and immunosuppression, which promote tumor targeting and circumvent obstacles currently impeding gene therapy strategies. Preclinical stem cell-based strategies show great promise for use in targeted anti-cancer therapy applications. Nevertheless, there remain scientific concerns regarding the use of stem cell therapies, and further studies are needed to validate preclinical findings. This review summarizes recent anti-cancer stem cell therapy studies, and identifies advantages, opportunities, and potential challenges.
Can iPSCs be used for immunotherapy?
Patient-specific iPSCs could also potentially benefit immunotherapy approaches [52, 53]. The pre-rearranged TCR gene is retained in T lymphocyte-derived human iPSCs, which can be further induced to differentiate into functionally active T cells [54–56]. Functional, tumor antigen-specific T lymphocytes can be produced in vitroby reprogramming selected T cells into iPSCs which then differentiate back into T lymphocytes for infusion into patients. However, the safety of T cell-derived human iPSCs must be further validated.
Can ESCs differentiate into all cells?
As pluripotent cells, ESCs can differentiate into all cell types except those in the placenta [4], and are therefore used as gold standards in the evaluation of all pluripotent cells cultured in vitro. However, due to ethical considerations, applications for ESCs in scientific studies and human clinical trials are restricted. To this end, ESCs can be replaced by induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) reprogrammed from adult somatic cells (e.g. skin fibroblasts) through enforced expression of pluripotency factors, because iPSC establishment does not require embryo destruction [5]. iPSCs are similar to ESCs, but lack immunogenic or ethical limitations, and so may be more clinically applicable than ESCs.
Can stem cells suppress tumor growth?
Stem cells can also be modified to selectively deliver growth inhibitory proteins (e.g. IFN-β), rendering the microenvironment inhospitable to tumor growth. Ling, et al.studied the migration of IFN-β-expressing MSCs and their engraftment into primary breast tumor sites, and found that tumor cell growth was suppressed, and hepatic and pulmonary metastases were alleviated [33]. MSCs secreted IFN-β at high levels in the tumor microenvironment but not in the circulation. This study also suggested that in situIFN-β expression in MSCs suppressed or abrogated cancer cell growth by inactivating signal transducer activator transcription factor 3 (Stat3).
Can stem cells be used for chemo?
Given their self-renewal and differentiation capabilities, stem cells can be used to repair human tissues after chemotherapy. Transplanting HSCs has been widely clinically employed to facilitate lifelong hematological recovery after treatment of malignancies with high-dose radiotherapy or chemotherapy. This treatment aims to reconstitute bone marrow under marrow failure conditions (e.g. aplastic anemia) and to treat blood cell genetic diseases, and works by supplying stem cells that differentiate into a desired type of blood cell. Transplantation and successful engraftment of only one HSC can reconstitute hematopoiesis in recipients [43, 44].
Do stem cells have migratory properties?
In addition to their self-renewal and differentiation capabilities, stem cells have immunosuppressive, antitumor, and migratory properties. Because stem cells express growth factors and cytokines that regulate host innate and cellular immune pathways [13, 14], they can be manipulated to both escape the host immune response and act as cellular delivery agents. Stem cells can also secret factors, such as CCL2/MCP-1, and physically interact with tumor cells, changing co-cultured tumor cell phenotypes and exerting intrinsic antitumor effects [15].
What is the treatment for cancer?
Radiation Therapy . Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Learn about the types of radiation, why side effects happen, which ones you might have, and more.
What is stem cell transplant?
Stem cell transplants are procedures that restore blood-forming stem cells in cancer patients who have had theirs destroyed by very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Learn about the types of transplants, side effects that may occur, and how stem cell transplants are used in cancer treatment.
How many types of cancer treatments are there?
There are many types of cancer treatment. The types of treatment that you receive will depend on the type of cancer you have and how advanced it is. Some people with cancer will have only one treatment. But most people have a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. Learn how targeted therapy works against cancer and about common side effects that may occur.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer. This page covers the types of immunotherapy, how it is used against cancer, and what you can expect during treatment.
What is the procedure that removes cancer from the body?
Surgery. When used to treat cancer, surgery is a procedure in which a surgeon removes cancer from your body. Learn the different ways that surgery is used against cancer and what you can expect before, during, and after surgery.
What is precision medicine?
Precision Medicine. Precision medicine helps doctors select treatments that are most likely to help patients based on a genetic understanding of their disease. Learn about the role precision medicine plays in cancer treatment, including how genetic changes in a person's cancer are identified and used to select treatments.
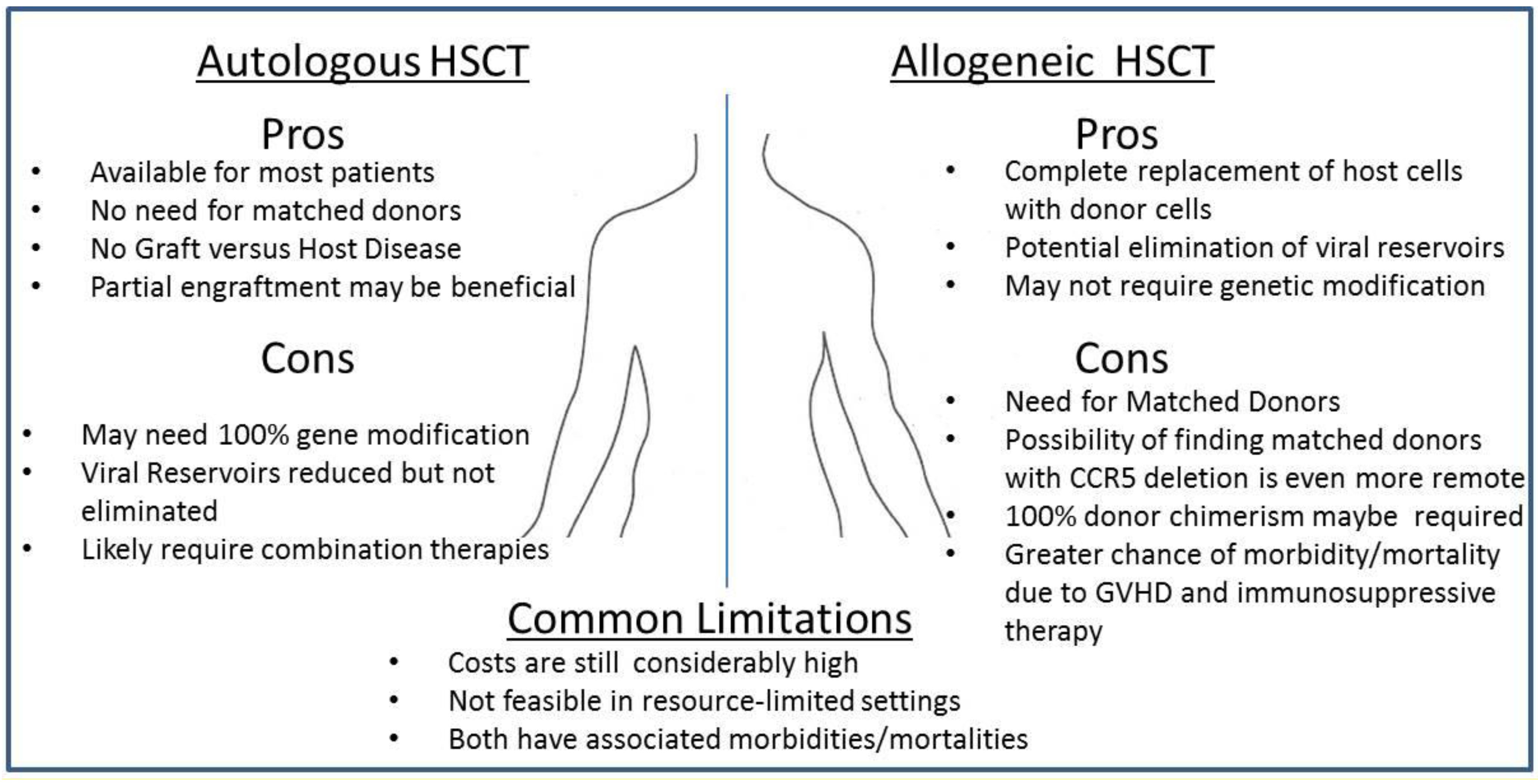
Autologous Stem Cell Transplants
Tandem (Double autologous) Transplants
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants
Mini-Transplants
Syngeneic Stem Cell Transplants
- This is a special kind of allogeneic transplant that can only be used when the patient has an identical sibling (twin or triplet) – someone who has the exact same tissue type. An advantage of syngeneic stem cell transplant is that graft-versus-host disease will not be a problem. Also, there are no cancer cells in the transplanted stem cells, as the...
Half-Matched Transplants
The Importance of Matching Patients and Donors