
What are the types of statistical techniques?
Traditional clinical trials aim to find an optimal treatment ignoring patient variability, which means the optimal treatment is the same for all patients of a specific disease. However, due to inter-patient heterogeneity, a treatment can be very successful for some patients but not for others. ... Statistical methods for clinical trial designs ...
What are the types of statistical procedures?
treatment - placebo controlled superiority trial • New drug is not worse (in terms of efficacy), by a pre-specified and clinically relevant amount, than the current therapy - active controlled non-inferiority trial – Note that there are no placebo controlled non-inferiority trials!
What are examples of statistical tests?
This article presents an overview of fundamental statistical principles of clinical trials of pain treatments. Statistical considerations relevant to phase 2 proof of concept and phase 3 confirmatory randomized trials investigating efficacy and safety are discussed, including (1) research design; (2) endpoints and analyses; (3) sample size determination and statistical …
What are the types of statistical tools?
The proliferation of statistical research in the area of clinical trials coupled with the critical role of clinical research in the drug approval process and health care in general necessitate a ...
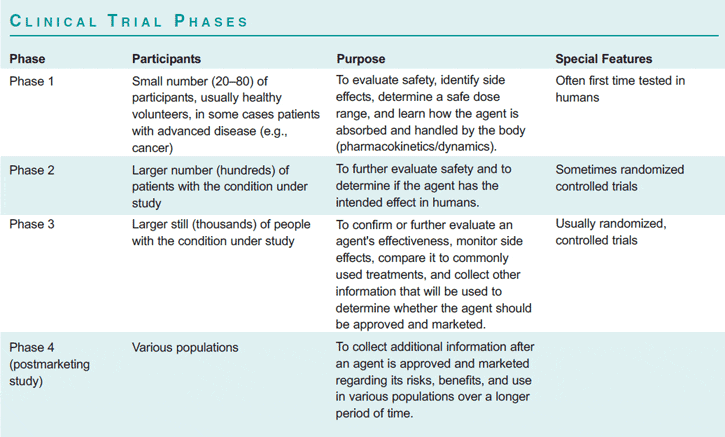
What statistical methods are used in clinical trials?
The two major approaches to statistical inference in clinical research are frequentist and Bayesian. The frequentist approach involves estimating confidence intervals, testing hypotheses, and drawing conclusions based on observed data.
How do you perform a statistical treatment?
Step 1: Write your hypotheses and plan your research design. ... Step 2: Collect data from a sample. ... Step 3: Summarize your data with descriptive statistics. ... Step 4: Test hypotheses or make estimates with inferential statistics. ... Step 5: Interpret your results.
How do I know which statistical test to use?
For a statistical test to be valid, your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied. To determine which statistical test to use, you need to know: whether your data meets certain assumptions. the types of variables that you're dealing with.Jan 28, 2020
What are the five statistical treatment a researcher can apply?
For this analysis, there are five to choose from: mean, standard deviation, regression, hypothesis testing, and sample size determination.Mar 6, 2020
What are the 5 basic methods of statistical analysis?
For this statistical analysis methods, there are 5 to choose from:Mean.Standard Deviation.Regression.Hypothesis Testing.Sample Size Determination.
What statistical treatment is used for correlation?
Correlation analysis in research is a statistical method used to measure the strength of the linear relationship between two variables and compute their association. Simply put - correlation analysis calculates the level of change in one variable due to the change in the other.
What is the statistical treatment used for data analysis?
Statistical Treatment in Data Analysis Treatments are divided into two groups: descriptive statistics, which summarize your data as a graph or summary statistic and inferential statistics, which make predictions and test hypotheses about your data.Oct 20, 2016
What is the 2 types of statistics?
The two major areas of statistics are known as descriptive statistics, which describes the properties of sample and population data, and inferential statistics, which uses those properties to test hypotheses and draw conclusions. Some common statistical tools and procedures include the following: Descriptive.
What statistical test is used for nominal data?
Nonparametric statistical tests are used with nominal data. While parametric tests assume certain characteristics about a data set, like a normal distribution of scores, these do not apply to nominal data because the data cannot be ordered in any meaningful way.Aug 7, 2020
What is statistical technique?
Statistical methods are mathematical formulas, models, and techniques that are used in statistical analysis of raw research data. The application of statistical methods extracts information from research data and provides different ways to assess the robustness of research outputs.
What are frequentist probabilities?
Sensitivity (the probability of a diagnostic test being positive when a person is truly diseased) and specificity (the probability of a diagnostic test being negative when a person is truly non-diseased) are examples of frequentist probabilities.
What is an ITT analysis?
An alternative to an ITT analyses is a “per protocol” (PP) analyses.
What is the function of p-value?
The p-value is a function of effect size, sample size, and variability. Larger effect sizes, larger sample sizes, and smaller variation all contribute to smaller p-values. Researchers often incorrectly interpret the p-value as providing direct information about the effect size.
What is a forest plot?
A forest plot is an effective method for reporting the results of subgroup analyses. The number of subgroup analyses conducted should be transparent so that results can be interpreted within the appropriate context. Subgroup analyses should generally be considered exploratory analyses rather than confirmatory.
Why is there missing data?
Missing data is usually caused by loss-to-follow-up or patient refusal to participate and provide data. Missing data can be the cause of biased treatment comparisons or estimates of treatment effects. This is because “missingness” is usually not random (e.g., could be related to treatment, or outcome, or both).
What is confirmatory efficacy study?
Confirmatory efficacy studies typically involve anumber of investigative centers and , accord-ingly, are known as multicenter trials. Multi-center trials have a number of benefits, whichare discussed later. A common analysis methodused in multicenter trials is to account for differ-ences from center to center by including them inthe analysis. Stratifying the randomization totreatment assignment by investigative centerensures that there are approximately equalnumbers of participants assigned to test orplacebo within each center. Analyses fromstudies with this design typically account forcenter as it is conceivably another source of vari-ation. This is accomplished by calculating asummary test statistic within each center andthen pooling or calculating weighted averages of the within-center statistics across all centers,thereby removing the effect of the centers fromthe overall test statistic.
What is the v2 test?
An alternative method to the Zapproximationfor the comparison of two proportions fromindependent groups is called the v2test, which isconsidered a goodness-of-fit test; this quantifiesthe extent to which count data (for example, thenumber of individuals with and without theresponse of interest) deviate from counts thatwould be expected under a particular mathemat-ical model. The mathematical model used inclinical studies for goodness-of-fit tests is that ofhomogeneity. That is, if a particular response ishomogeneous with respect to treatment, wewould expect all the responses of interest to beproportionally distributed among all treatmentgroups. The assumption of homogeneity willallow us to calculate the cell counts that wouldbe expected. These will then be compared withwhat was actually observed. The more theexpected counts under the particular model ofinterest (for example, homogeneity) deviatefrom what is observed, the greater the value ofthe test statistic, and therefore the more the datav2 do not represent goodness of fit. The test isuseful because it can be used to test homogeneityacross two or more treatment groups. We firstdescribe the case of two groups and the moregeneral case is described in Section 10.5.3.If there are two independent groups of interest(for example, treatment groups in a clinical trial)each representing an appropriate population,the proportions of participants with the charac-teristic or event of interest are represented by pˆ
What is statistical analysis?
The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. The results and inferences are precise only ...
What is descriptive statistics?
Descriptive statistics provide a summary of data in the form of mean, median and mode. Inferential statistics[4] use a random sample of data taken from a population to describe and make inferences about the whole population. It is valuable when it is not possible to examine each member of an entire population.
What is the branch of science that deals with the collection, organisation, analysis of data and drawing of inferences from
Statistics is a branch of science that deals with the collection, organisation, analysis of data and drawing of inferences from the samples to the whole population.[1] . This requires a proper design of the study, an appropriate selection of the study sample and choice of a suitable statistical test. An adequate knowledge of statistics is necessary ...
What is categorical data?
Categorical or nominal variables are unordered. The data are merely classified into categories and cannot be arranged in any particular order. If only two categories exist (as in gender male and female), it is called as a dichotomous (or binary) data.
What is an example of an interval scale?
A good example of an interval scale is the Fahrenheit degree scale used to measure temperature.
What is ratio scale?
Ratio scales are similar to interval scales, in that equal differences between scale values have equal quantitative meaning. However, ratio scales also have a true zero point, which gives them an additional property. For example, the system of centimetres is an example of a ratio scale.
What is the difference between median and mode?
Median[6] is defined as the middle of a distribution in a ranked data (with half of the variables in the sample above and half below the median value) while mode is the most frequently occurring variable in a distribution. Range defines the spread, or variability, of a sample.[7] .
