
Is rTMS effective in the acute treatment of depression?
This pooled analysis comprised data from 117 patients who participated in two RCTs comparing rTMS, tDCS, and VNF in the acute treatment of depression. We have found comparable efficacy of all three treatment modalities.
How many sessions of rTMS does it take to improve symptoms?
Early symptom improvement at 10 sessions as a predictor of rTMS treatment outcome in major depression. Brain Stimul. 2018;11(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2017.10.010. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
How many studies have been conducted on TMS in depression?
Since October 2008 (when TMS was first FDA cleared), over 360 studies investigating the application of TMS in depression have been published. Among those, there are more than 150 trials and 47 meta-analyses, with 29 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and 7 meta-analyses specifically addressing individuals with TRD.
How many times a week should I taper off of rTMS?
Although the intervention should ultimately be tailored to each patient’s clinical picture, it might consist of an rTMS taper of 4 times weekly for the first week, 3 times weekly in the following week, 2 times weekly for the subsequent 1 or 2 weeks, and then 1 session every 2 or 3 weeks over several months to years, depending on the case.
How much does Medicare pay for rTMs?
What is the difference between a muscle relaxant and a rTMS?
What is the treatment for depression?
What are some examples of people who shouldn't get rTMs?
Where is the coil for RTMS?
What is magnetic pulse therapy?
Is RTMS effective for depression?
See more
About this website

How many sessions of rTMS are required?
rTMS is usually offered in an outpatient setting, meaning patients are required to make 30 separate visits to the rTMS clinic to complete a treatment.
How long does rTMS therapy last?
rTMS therapy involves a series of treatment sessions. Treatment sessions vary in length depending on the TMS coil used and the number of pulses delivered but typically last around 30 – 40 minutes. Patients receive TMS 5 days a week. A typical course of rTMS is 4 to 6 weeks.
How often can you have TMS Therapy?
Repetitive TMS is usually done in a doctor's office or clinic. It requires a series of treatment sessions to be effective. Generally, sessions are carried out daily, five times a week for four to six weeks.
How long does TMS work for depression?
Most patients who complete TMS treatment experience relief from symptoms of depression for six months to a year. Your results could also last for more than a year.
Can you do TMS 3 times?
A 2012 randomized clinical trial demonstrated that a TMS schedule of three sessions/week was not inferior to the standard five/week regimen on final treatment outcomes, though the group assigned to daily sessions achieved symptom reduction in a shorter period of time.
Is rTMS treatment permanent?
It is important to acknowledge that these results, while encouraging, are not permanent. Like most other treatments for mood disorders, there is a high recurrence rate. However, most TMS patients feel better for many months after treatment stops, with the average length of response being a little more than a year.
Can you do TMS twice?
In MDE, a second course of TMS is likely to help those who remitted to a first course and then relapsed, as well as those who did not achieve remission with a first course.
Does TMS continue to work after treatment?
Patients that benefit from TMS treatment can experience full remission from their symptoms. Others may experience a significant decrease in symptoms. Most patients continue to see an improvement in their symptoms for a year or longer after treatment. Research on the longevity of TMS treatment is overall positive.
How long does rTMS take to work?
Some of our patients report feeling a slight improvement in their symptoms after two weeks of treatment, while others do not report noticeable changes until weeks four or five. If it takes longer to notice symptom relief using TMS compared to someone else, this does not mean that the treatment is ineffective.
Does TMS continue to work after treatment?
Patients that benefit from TMS treatment can experience full remission from their symptoms. Others may experience a significant decrease in symptoms. Most patients continue to see an improvement in their symptoms for a year or longer after treatment. Research on the longevity of TMS treatment is overall positive.
What is the success rate of TMS therapy?
Most TMS providers find that TMS has a success rate at between 70% or 80%, meaning that the vast majority of individuals find significant relief after treatment. About 50% of people experience complete remission, meaning that the symptoms of depression are absent after just one course of treatment.
Can you do TMS a second time?
In MDE, a second course of TMS is likely to help those who remitted to a first course and then relapsed, as well as those who did not achieve remission with a first course.
Does TMS have lasting effects?
TMS (neither rTMS nor dTMS) is also not associated with any long-term side effects. Short-term side effects that have been reported include scalp discomfort and headache that often go away within the first week of treatment.
How many TMS systems are there for TRD?
To date, there are seven TMS systems cleared for use in TRD: NeuroStar, BrainsWay (H1-coil), MagVenture, CloudTMS, Apollo, Nexstim, and Magstim. Since October 2008 (when TMS was first FDA cleared), over 360 studies investigating the application of TMS in depression have been published.
What is TRD in medical terms?
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD), or more specifically pharmacoresistant MDD, is defined as the lack of remission despite multiple (generally defined as >2) trials of a tolerable and evidence-based treatment, and is associated with significant disability.
What is TMS in medical terms?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of depression. TMS is typically used when other depression treatments haven't been effective.
How does transcranial magnetic stimulation work?
In transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), an electromagnetic coil placed against the scalp creates a magnetic field that stimulates certain areas of the brain. During an rTMS session, an electromagnetic coil is placed against your scalp near your forehead. The electromagnet painlessly delivers a magnetic pulse ...
Can you drive home after TMS?
Repetitive TMS isn't invasive, doesn't require anesthesia and can be performed on an outpatient basis. You don't need to arrange for someone to drive you home after treatment — unless, for the first treatment, you prefer a driver until you get a sense of how you'll feel afterward.
Can you have a metal implant with a rtms?
In some cases, people with metal implants or devices can have rTMS. However, due to the strong magnetic field produced during rTMS, the procedure is not recommended for some people who have the following devices: Aneurysm clips or coils. Stents. Implanted stimulators. Implanted vagus nerve or deep brain stimulators.
Does repetitive TMS require surgery?
Risks. Repetitive TMS is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation used for depression. Unlike vagus nerve stimulation or deep brain stimulation, rTMS does not require surgery or implantation of electrodes. And, unlike electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), rTMS doesn't cause seizures or require sedation with anesthesia.
What is a rTMS?
What to Know About Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on June 29, 2021. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) uses painless, magnetic pulses to help lessen the symptoms of depression. You do not have to be hospitalized for rTMS, and you don’t need sedation or anesthesia.
How long does a rtms stay in the hospital?
Typically, you go five times a week to a clinic or doctor’s office for the treatments. A course of rTMS usually lasts four to six weeks.
How long does it take for rtms to go away?
Like most treatments for depression, the effects of rTMS are not permanent. On average, symptoms return after about a year. Some people choose to have another set of rTMS treatments when their depression returns. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print.
What is the first treatment for depression?
If you have depression, antidepressants and talk therapy are the first treatments your doctor will try. Antidepressants are medications that help your brain control your mood. In talk therapy, you work with a counselor to learn new ways of thinking and behaving that can help relieve the symptoms of depression. .
Is it safe to get dizzy after a rtms?
The dizziness typically goes away quickly after the session and is less noticeable with each treatment. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is considered a safe and effective treatment , with little risk of serious side effects.
Does rTMS cause tingling?
Less commonly, people feel a tingling or twitching in the muscles of their face during their first rTMS treatment. Others say they feel pain on their scalp under the electromagnetic coil. The doctor can adjust the position of the coil and the strength of the magnetic pulses right away to make the treatment less painful.
Does rtms cause headaches?
During rTMS treatment, some people do experience mild and temporary side effects, such as: Headaches. About 50% of people have headaches during or after their first rTMS sessions. These headaches are generally mild ...
What is rTMS in psychology?
rTMS ( repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation) has been shown to produce changes in neuronal activity in regions of the brain implicated in mood regulation, such as the prefrontal cortex. As each magnetic pulse passes through the skull and into the brain, this induces brief activity of brain cells underlying the treatment coil.
How long does a TMS last?
Treatment sessions vary in length depending on the TMS coil used and the number of pulses delivered but typically last around 30 – 40 minutes. Patients receive TMS 5 days a week. A typical course of rTMS is 4 to 6 weeks. However, this can vary depending on an individual’s response to treatment.
Does RTMS require anesthesia?
Unlike ECT, rTMS does not require any sedation or general anesthesia, so patients are fully awake and aware during the treatment. There is no “recovery time”, so patients can drive home afterwards and return to their usual activities.
Is rtms a side effect?
rTMS is well-tolerated and associated with few side-effects and only a small percentage of patients discontinue treatment because of these. The most common side-effect, which is reported in about half of patients treated with rTMS, is headaches. These are mild and generally diminish over the course of the treatment.
Is rtms safe?
At Johns Hopkins, we follow up-to-date safety guidelines that are designed to minimize the risk of seizures. While rTMS is a safe procedure, it is important to point out that because it is a new treatment , there may be unforeseeable risks that are not currently recognized.
Who administers TMS?
The treatment itself is administered by an experienced TMS technician under the supervision of the TMS physician or by the TMS physician. The TMS technician or physician will always be present to monitor the patient during the treatment. The patient can stop a treatment at any time by asking the staff member present.
Can earplugs cause rtms?
No evidence suggests these effects are permanent if earplugs are worn during the treatment. rTMS has not been associated with many of the side-effects caused by antidepressant medications, such as gastrointestinal upset, dry mouth, sexual dysfunction, weight gain, or sedation. The most serious risk of rTMS is seizures.
How much does Medicare pay for rTMs?
per treatment session. Medicare typically reimburses rTMS at an average of $206 per session. Trusted Source. . A person may have anywhere from 20 to 30 or more treatment sessions per year. Another study suggests that a person may pay between $6,000 and $12,000 annually for rTMS treatments.
What is the difference between a muscle relaxant and a rTMS?
Doctors also give you a muscle relaxant, which keeps you from shaking during the stimulation portion of the treatment. This differs from rTMS because people receiving rTMS don’t have to receive sedation medications, which can reduce the risks for potential side effects.
What is the treatment for depression?
Doctors can offer several brain stimulation therapies that may help treat depression. While rTMS is one, another is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). ECT involves placing electrodes on strategic areas of the brain and generating an electric current that essentially causes a seizure to occur in the brain.
What are some examples of people who shouldn't get rTMs?
Examples of people who shouldn’t get rTMS include those with: aneurysm clips or coils. bullet fragments or shrapnel near the head. cardiac pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD) facial tattoos that have magnetic ink or ink that’s sensitive to magnets. implanted stimulators.
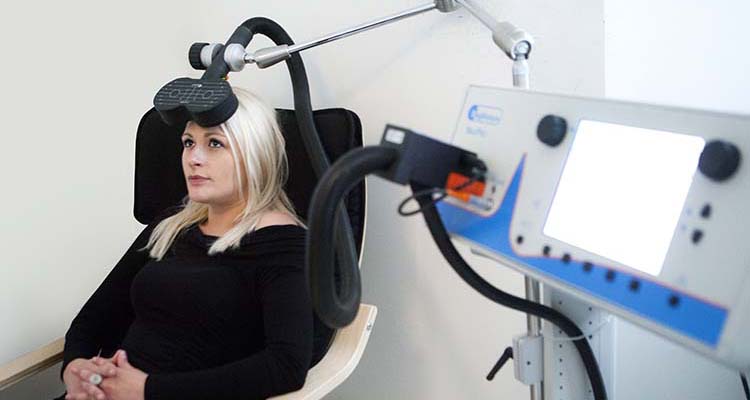
Where is the coil for RTMS?
Here’s what you can expect at a typical rTMS treatment session: You’ll sit or recline while a doctor places a special electromagnetic coil near your head , specifically a brain area that regulates mood. The coil generates magnetic pulses to your brain.
What is magnetic pulse therapy?
This therapy involves using magnetic pulses to target specific areas of the brain. People have been using it since 1985 to relieve the intense sadness and feelings of hopelessness that can come with depression.
Is RTMS effective for depression?
A 2019 literature review found rTMS is effective for treatment after one medication trial has worked well in treating major depressive disorder. Many studies now in progress have researchers examining the long-term effects of rTMS and finding out what types of symptoms best respond to the treatment.
Treatment
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved rTMS as a treatment for major depression when other treatments havent been effective. Sometimes doctors use rTMS in addition to traditional treatments. Several therapies exist that involve stimulating the brain in different ways. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is one such treatment. ECT involves placing electrodes on strategic areas of the brain and creating an electric current that e…
Qualification
- The most qualified candidates for rTMS are people with depression who havent had success with other methods. People who arent in good enough health for a procedure such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) might be better candidates for rTMS. This is true for those who have a higher risk for seizures or may not tolerate anesthesia, which is needed for ECT.
Symptoms
- Pain isnt usually a side effect of rTMS. However, people may describe the sensation of the magnetic pulse as uncomfortable. Some people describe this as a knocking or tapping feeling with each pulse. The electromagnetic pulses can cause muscles in the face to tighten or tingle.
Mechanism
- One of the other key differences between the two is the ability to target certain areas of the brain. When the rTMS coil is held over a certain area of the brain, the impulses travel only to that part of the brain. Electroconvulsive therapy is unable to target specific areas.
Scope
- While doctors use both rTMS and ECT to treat depression, ECT is usually reserved for patients with severe and potentially life-threatening depression. Other conditions that ECT may be used to treat include:
Risks
- There are some people who cant get rTMS, even if they could benefit from it. The magnetic coil used in the treatment can be dangerous for anyone who has metal implanted somewhere in their head or neck.
Cost
- While the treatment costs can vary based on location, the average costs for treatment can range from $6,000 to $12,000 for a four- to six-week treatment course. Some hospitals, doctors offices, and healthcare facilities offer payment plans or discounted programs for those who are unable to pay the entire amount.
Research
- Researchers have written a number of research trials and clinical reviews on rTMS. Some of the results include: Many studies now in progress have researchers examining the long-term effects of rTMS and finding out what types of symptoms best respond to the treatment.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Depression is a treatable condition, but for some people, standard treatments aren't effective. Repetitive TMS is typically used when standard treatments such as medications and talk therapy (psychotherapy) don't work.
Risks
- Repetitive TMS is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation used for depression. Unlike vagus nerve stimulation or deep brain stimulation, rTMS does not require surgery or implantation of electrodes. And, unlike electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), rTMS doesn't cause seizures or require sedation with anesthesia. Generally, rTMS is considered safe and well-tolerated. However, it can cause some side effects.
How You Prepare
- Before having rTMS, you may need a: 1. Physical examand possibly lab tests or other tests 2. Psychiatric evaluationto discuss your depression These evaluations help make sure that rTMS is safe and a good option for you. Tell your doctor or mental health provider if: 1. You're pregnantor thinking of becoming pregnant. 2. You have any metal or implanted medical devices in your body. In some cases, people with metal implants or devices can …
What You Can Expect
- Repetitive TMS is usually done in a doctor's office or clinic. It requires a series of treatment sessions to be effective. Generally, sessions are carried out daily, five times a week for four to six weeks.
Results
- If rTMS works for you, your depression symptoms may improve or go away completely. Symptom relief may take a few weeks of treatment. The effectiveness of rTMS may improve as researchers learn more about techniques, the number of stimulations required and the best sites on the brain to stimulate.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.