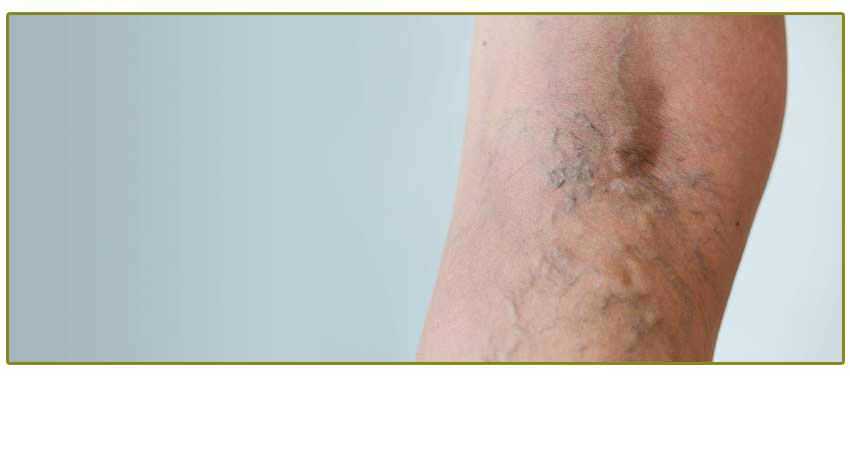
What is noninvasive treatment for varicose veins?
Noninvasive treatment for varicose veins is typically performed in a doctor’s office using local anesthetic. Be sure to tell your doctor if you’re pregnant, have any allergies, or are taking any medications, including any herbal supplements.
What are venous diseases?
What are venous diseases? Venous diseases include: Which can be found in the legs, arms, veins of the internal organs (kidney, spleen, intestines, liver, pelvic organs), in the brain ( cerebral vein thrombosis ), in the kidneys ( renal vein thrombosis ), or in the lungs ( pulmonary embolism ). Get more information about blood clotting disorders.
How many Americans suffer from varicose veins?
30 million Americans suffer from vein disease and even the more severe Chronic Venous Insufficiency Disease (CVI). Without treatment, varicose veins turn into CVI and progressively become worse. Only 1.9 million out of 30 seek treatment even though the screening process takes less than 15 minutes.
What is chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins?
Chronic venous insufficiency is characterized by pooling of blood, chronic leg swelling, increased pressure, increased pigmentation or discoloration of the skin, and leg ulcers known as venous stasis ulcer. Varicose and spider veins are abnormal, dilated blood vessels caused by a weakening in the blood vessel wall.
See more

How rare is wyburn Mason syndrome?
Wyburn-Mason Syndrome is a very rare disease with less than 100 cases reported.
What are 4 diseases related to blood vessels?
Examples of vascular diseasesPeripheral vascular disease. Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) refers to diseases of the blood vessels outside the heart and brain. ... Limb-threatening ischemia. ... Carotid artery disease. ... Abdominal aortic aneurysm. ... Chronic venous insufficiency. ... Varicose veins. ... Deep vein thrombosis. ... Pulmonary embolism.
Which diseases or disorders affect veins?
Venous diseases include:Blood clots. ... Deep vein thrombosis. ... Superficial venous thrombosis or phlebitis. ... Chronic venous insufficiency. ... Varicose and spider veins. ... Ulcers.
What is KTA syndrome 🥰?
Definition. Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS) is a rare congenital malformation involving blood and lymph vessels and abnormal growth of soft and bone tissue. Typical symptoms include hemangiomas (abnormal benign growths on the skin consisting of masses of blood vessels) and varicose veins.
What are names of vascular diseases?
Types of Vascular DiseaseAbdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Atherosclerosis.Carotid Artery Disease/Carotid Artery Stenosis.Chronic Venous Insufficiency.Intermittent Claudication.Deep Vein Thrombosis.
What are two examples of chronic diseases of the vascular system?
Vascular diseases affect the circulatory system. They include hypertension, stroke, aneurysms, and peripheral artery disease (PAD). Due to an aging population, an increase in obesity and chronic conditions like Type II diabetes, vascular diseases are a growing epidemic.
What is the most serious type of venous disorder?
Deep-vein thrombophlebitis (affecting the larger veins farther below the skin's surface) is more serious.
Is vein disease serious?
Vein disease is highly manageable if diagnosed and treated in its early stages. However, if the condition is left untreated, chronic venous insufficiency and other vein diseases can cause some very serious complications.
What is throm?
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block your blood vessels. There are 2 main types of thrombosis: Venous thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks a vein. Veins carry blood from the body back into the heart. Arterial thrombosis is when the blood clot blocks an artery.
Is Klippel-Trenaunay life threatening?
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS) is a rare congenital syndrome of vascular malformations and soft tissue and bone hypertrophy. Vascular malformations can affect multiple organ systems. Involvement of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is uncommon in KTS, but it can be a source of life-threatening bleeding.
What causes Klippel-Trenaunay Weber syndrome?
KTS is a genetic disorder. It involves genetic changes (mutations), most commonly in the PIK3CA gene. This gene is responsible for the growth of cells and the development of tissues in the body.
Can you get Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome?
Overview. Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS) is a rare congenital vascular disorder in which a limb may be affected by port wine stains (red-purple birthmarks involving blood vessels), varicose veins, and/or too much bone and soft tissue growth. The limb may be larger, longer, and/or warmer than normal.
How to treat varicose veins?
Doctors at Johns Hopkins recommend the following for treating varicose veins: Elevated feet. Raise the foot of your bed from two to four inches with blocks to aid circulation at night. Avoid scratching itchy skin above varicose veins, as this may cause ulceration or profuse bleeding.
What is the inflammation of the veins in the legs?
Thrombophlebitis is the inflammation of a vein (usually in an extremity, especially one of the legs) that occurs in response to a blood clot in the vessel. When it occurs in a vein near the surface of the skin, it is known as superficial thrombophlebitis, a minor disorder commonly identified by a red, tender vein.
What is the procedure for superficial varicose veins?
Sclerotherapy is an option for superficial varicose veins. In this outpatient procedure, the doctor injects small- and medium-sized varicose veins with a solution that scars those veins. The process closes the veins, forcing your blood to reroute to healthier blood vessels.
What are the symptoms of venous disease?
Symptoms of venous disease include: Varicose Veins: enlarged, swollen, knotted clusters of purple veins; edema (swelling in the legs); aching or a sensation of heaviness in the legs; itching skin above the affected veins; skin discoloration and ulcers on the inner aspect of the ankles (in advanced cases).
How many people in the US have varicose veins?
Approximately 15 percent of the United States population is affected by varicose veins, which generally do not pose great health risk. However, thrombophlebitis can be much more serious, even life-threatening, affecting millions of people each year.
What is the name of the thin-walled structures inside of which a set of valves keeps blood in the
Venous Disease Overview. Veins are thin-walled structures inside of which a set of valves keeps blood in the body flowing in one direction. The heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues through thicker-walled arteries; the veins return that blood to the heart. Veins located close to the surface of the skin are called superficial veins ...
Where do varicose veins appear?
Usually appearing in the legs, varicose veins may also occur in the anus, where they are known as hemorrhoids. While not a serious health risk, varicose veins can be eliminated for cosmetic reasons or if they cause discomfort.
What is a varicose vein?
Varicose veins are enlarged and bulging veins that typically appear on your legs and feet. It is this stage where most people become mildly concerned. For some, varicose veins do not accompany any swelling of the legs or pain but for others, there is a nagging pain that becomes frustrating and uncomfortable.
How to stop venous insufficiency?
By staying off your feet and raising your legs as much as possible, you can reduce the symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency disease, but you cannot stop them from happening.
What does it mean when your legs are purple?
Bulging dark purple veins. Veins that look twisted or tangled. Aches and a heaviness in the legs. Burning legs or itchy legs. Increased pain after standing for a prolonged period. Bleeding or leaking veins. Veins that change colors. Hardening of veins. Inflammation and swelling of legs around varicose veins.
How many people have varicose veins?
30 million Americans suffer from vein disease and even the more severe Chronic Venous Insufficiency Disease (CVI). Without treatment, varicose veins turn into CVI and progressively become worse. Only 1.9 million out of 30 seek treatment even though the screening process takes less than 15 minutes. Treatment starts with education.
What is the fourth stage of varicose vein disease?
The fourth stage of vein disease is a discoloration of the skin around the site of varicose veins. The skin may become brown and take on a rough leathery texture. The skin takes on this discoloration become the fatty tissue underneath the skin becomes inflamed.
What are the stages of vein disease?
Continue reading to learn more about the five stages of vein disease. 1. Reticular Veins (Spider Veins) The first stage of vein disease is reticular ve ins. Spider veins are bluish purple veins that do not protrude from the skin. These veins run in a spiderweb-like pattern, and they are small and sometimes hard to see.
Why do veins turn purple?
Age – As we age our veins lose their ability to expand and contract so , they become stretched out. As a result, the valves in the veins weaken, and blood flows backward. Blood then sits in the veins instead of flowing smoothly throughout causing that deep purple color of deoxygenated blood. Pregnancy.
What are the goals of venous disease treatment?
The goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Your health care provider will recommend the treatment option that is right for you.
How do veins work?
Veins return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Veins are flexible, hollow tubes with flaps inside called valves. When your muscles contract, the valves open and allow blood to move through the veins. When your muscles relax, the valves close, keeping blood flowing in one direction through the veins. Veins become larger and larger as they get ...
What is the term for swelling of the leg?
Chronic venous insufficiency is characterized by pooling of blood, chronic leg swelling, increased pressure, increased pigmentation or discoloration of the skin, and leg ulcers known as venous stasis ulcer.
Why do veins get bigger?
Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart. The superior vena cava is the large vein that brings blood from the head and arms to the heart, and the inferior vena cava brings blood from the abdomen and legs into the heart. If the valves inside your veins become damaged as a result of venous disease, ...
What is the system of blood vessels that carry blood to every part of the body?
Overview. As the heart beats, it pumps blood through a system of blood vessels, called the circulatory system. The vessels are flexible, hollow tubes that carry blood to every part of the body. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart. Veins return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
Where are blood clots found?
Which can be found in the legs, arms, veins of the internal organs (kidney, spleen, intestines, liver, pelvic organs), in the brain ( cerebral vein thrombosis ), in the kidneys ( renal vein thrombosis ), or in the lungs ( pulmonary embolism ). Get more information about blood clotting disorders.
Is DVT a life threatening condition?
Even though deep vein thrombosis itself is not life-threatening, the blood clot has the potential to break free and travel through the bloodstream, where it can become lodged in the blood vessels of the lung ...
What is Vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome?
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is an inherited connective tissue disorder that is caused by defects in a protein called collagen. It is generally considered the most severe form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Common symptoms include thin, translucent skin; easy bruising; characteristic facial appearance; and fragile arteries, muscles and internal organs. [1] [2] Vascular EDS is usually caused by a change ( mutation) in the COL3A1 gene. Rarely, it may be caused by a mutation in the COL1A1 gene. [3] Inheritance is autosomal dominant. [2] Treatment and management is focused on preventing serious complications and relieving signs and symptoms. [2] [4]
What causes a vascular edema?
[1] [2] Vascular EDS is usually caused by a change ( mutation) in the COL3A1 gene. Rarely, it may be caused by a mutation in the COL1A1 gene. [3] .
Where is the vein of Galen located?
The vein of Galen is located under the cerebral hemispheres and drains the forward (anterior) and central regions of the brain into the proper sinuses. The malformations occur when the vein of Galen is not supported within the head by surrounding tissue and lacks the normal fibrous wall.
Why are veins and arteries connected?
Arteries and veins may be connected directly instead of being connected through fine capillaries for which reason they are often referred to as “shunt lesions” since the capillaries are by-passed. These abnormal “feeding” arteries progressively enlarge and as a result the “draining” veins dilate as well.
What are the different types of vascular malformations?
These types of VMB are: (1) arteriovenous malformations (AVM), abnormal arteries and veins; (2) cavernous malformations (CM), enlarged blood-filled spaces; (3) venous angiomas (VA), abnormal veins; (4) telangiectasias (TA), enlarged capillary-sized vessels; (5) vein of Galen malformations (VGM); and (6) mixed malformations (MM).
What is cavernous hemangioma?
A cavernous hemangioma acts like a “blood sponge” soaking up blood that has found its way between capillaries, in the spaces between tissues (sinusoids) and “larger cavernous spaces.”. These are “slow-flow lesions.”. There is not usually any brain tissue in these spaces in contrast with symptoms of AVMs.
What imaging can be used to see if a brain vessel is malformed?
Imaging apparatus, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, venograms and/or digital intravenous or common angiography can take pictures of the brain's blood vessels to see if vascular malformations are present.
Is VMB a genetic trait?
Three types or forms of VMB have a genetic component. The evidence for a genetic cause is strong in the case of cavernous hemangiomas and telangiectasias. The case is much weaker for arteriovenous malformation of the brain (AVM). In each of these cases, the condition is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait.
Can vascular malformations cause strokes?
Vascular malformations of the brain may cause headaches, seizures, strokes, or bleeding in the brain (cerebral hemorrhage). Some researchers believe that the type of malformation determines the symptoms and progression of the disease. Other researchers believe that only the severity rather than the type of malformation is important.
What is the rarest autoimmune disease?
Here are 10 in the category of rare autoimmune diseases: 1. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) Formerly known as Churg Strauss syndrome, this autoimmune disease is characterized by elevated levels of white blood cells called eosinophils, which often leads to inflammation in blood vessels. That, in turn, can lead ...
How many people are affected by a rare disease?
According to the National Institutes of Health, a rare disease is one that affects fewer than 200,000 people at any particular time in the United States.
What is the name of the disease that causes hard patches of skin?
Scleroderma is a disease of the connective tissues. People with this disease experience an abnormal thickening of the skin, according to the National Organization for Rare Disorders. In addition to hard leathery patches of skin, joint pain, fatigue and Raynaud’s syndrome are common. 10. Thyroid eye disease.
What is the most common genetic disease you have never heard of?
“Patients know their bodies much much better than anybody else,” she says. Next, the most common rare genetic disease you’ve never heard of: SMA.
How does a rare disease affect your life?
Find the support you need. Having a rare disease can turn your life upside down. Not only can be it challenging to explain to other people, it can affect every aspect of your life in ways that other people can’t quite grasp. That’s why it’s so crucial to reach out for support if you are diagnosed with one.
Can thyroid disease cause double vision?
It usually starts with an active phase, which might also involve pain, grittiness in the eyes, bulging eyes, watery eyes, double vision and other symptoms. If left untreated, it can lead to some vision loss.
