Radiosurgery is indicated primarily for the therapy of tumors, vascular lesions and functional disorders. Significant clinical judgment must be used with this technique and considerations must include lesion type, pathology if available, size, location and age and general health of the patient.
What are the benefits of radiosurgery?
Radiosurgery for psychiatric disorders has been performed for more than 50 years. The use of deep brain stimulation has recently been expanded to the investigational treatment of specific psychiatric disorders. A literature review of past studies incorporating radiosurgical stereotactic lesions for psychiatric disorders was performed to provide historic context and possible …
What conditions can be treated with stereotactic radiosurgery?
Gamma Knife radiosurgery was administered in 82.85% of patients. Conclusion: Although microsurgery is the treatment of choice for acoustic neuroma, we consider radiosurgery as a valid alternative in selected patients (elderly, comorbidity, small tumour size and sensorineural hearing loss, among others). Keywords: Acoustic neuroma; Gamma Knife; LINAC; Microcirugía; …
What kind of brain tumors can be treated with radiosurgery?
Malignant (cancerous) brain tumors Arteriovenous malformations Functional disorders, such as trigeminal neuralgia Gamma Knife radiosurgery is effective for small to medium-sized brain tumors. Radiation delivered by the Gamma Knife damages the DNA of abnormal cells so they can no longer reproduce. As a result, the tumor gradually shrinks.
How many sessions of radiosurgery does it take to cure cancer?
radiosurgery is a choice of treatment in which disorder acoustic neuroma auditory receptor in the cochlea ortan of corti passages in inner ear assoc with maintaining equilibrium semicircular canals flap of the ear auricle small bones of middle ear ossicles channel b/t middle ear and nasopharynx eustachian tube

What is radiosurgery used for?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a very precise form of therapeutic radiation that can be used to treat abnormalities in the brain and spine, including cancer, epilepsy, trigeminal neuralgia and arteriovenous malformations.
Who is a candidate for stereotactic radiosurgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery has become an increasingly common approach for patients who have smaller brain tumors. Other candidates for stereotactic radiosurgery also include those patients whose disease is not surgically accessible or is too advanced for neurosurgery, as well as those who cannot tolerate anesthesia.
What are the different types of radiosurgery?
There are 3 types of radiosurgery. Each type uses different equipment and radiation sources....What are the types of radiosurgery?Head frame placement. ... Tumor location imaging. ... Radiation dose planning. ... Radiation treatment.
Why would you need stereotactic radiosurgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-surgical radiation therapy used to treat functional abnormalities and small tumors of the brain. It can deliver precisely-targeted radiation in fewer high-dose treatments than traditional therapy, which can help preserve healthy tissue.
What is the difference between radiotherapy and radiosurgery?
The difference between stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy has to do with the intensity and duration of the radiation treatments. Stereotactic radiosurgery delivers radiation at a very high intensity, all at once, to a small area.May 8, 2017
What is radiosurgery for a brain tumor?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a type of radiation therapy that uses narrow beams of radiation coming from different angles to very precisely deliver radiation to a brain tumor while sparing the surrounding normal tissue.
What is SRS treatment?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other problems in the brain, neck, lungs, liver, spine and other parts of the body. It is not surgery in the traditional sense because there's no incision.Apr 27, 2019
What is neuro radiosurgery?
Gamma Knife radiosurgery is a sophisticated radiation therapy technique that precisely delivers a single, finely focused, high dose of radiation to well-defined, small targets in the brain. It is especially effective for treating tumors, epilepsy, trigeminal neuralgia, and arteriovenous malformations.
What is SABR treatment?
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR), also known as stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), is a highly focused radiation treatment that gives an intense dose of radiation concentrated on a tumor, while limiting the dose to the surrounding organs.
What is conventional RT?
Radiation therapy is a common type of cancer treatment that uses high-energy particles, such as x-rays, gamma rays, electron beams or protons, to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells by damaging their DNA. As the DNA is damaged, the cancer cells stop dividing, slowing the growth of tumors.
What is radiosurgery for brain metastases?
Brain metastases are tumors that form when cancer from another part of the body spreads to the brain. SRS is a highly precise form of radiation therapy that treats each brain tumor with a single, targeted high-dose of radiation, delivered in an outpatient setting.Oct 26, 2020
Is Gamma Knife and SRS the same?
Gamma Knife radiosurgery is a type of radiation therapy used to treat tumors, vascular malformations and other abnormalities in the brain. Gamma Knife radiosurgery, like other forms of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), is not surgery in the traditional sense because there is no incision.May 13, 2021
What is radiosurgery used for?
Radiosurgery can be used to shrink the tumor and lessen the disruption of pituitary hormone regulation. Tremors. Stereotactic radiosurgery may be used to treat tremors associated with functional neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease and essential tremor. Other cancers.
How does stereotactic radiosurgery work?
Like other forms of radiation, stereotactic radiosurgery works by damaging the DNA of the targeted cells. The affected cells then lose the ability to reproduce, which causes tumors to shrink. Stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain and spine is typically completed in a single session. Body radiosurgery is used to treat lung, liver, ...
What is SRS in medical terms?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other problems in the brain, neck, lungs, liver, spine and other parts of the body. It is not surgery in the traditional sense because there's no incision. Instead, stereotactic radiosurgery uses 3D imaging to target high doses ...
What is a LINAC machine?
Linear accelerator (LINAC) machines use X-rays (photons) to treat cancerous and noncancerous abnormalities in the brain and other parts of the body. LINAC machines are also known by the brand name of the manufacturer, such as CyberKnife and TrueBeam.
How many sessions of SRS?
These machines can perform stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in a single session or over three to five sessions for larger tumors, which is called fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy. Gamma Knife machines use 192 or 201 small beams of gamma rays to target and treat cancerous and noncancerous brain abnormalities.
What is proton beam therapy?
Proton beam therapy (charged particle radiosurgery) is the newest type of stereotactic radiosurgery and is available in only a few research centers in the U.S, although the number of centers offering proton beam therapy has greatly increased in the last few years.
What is gamma knife used for?
Brain tumor. Stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife, is often used to treat noncancerous (benign) and cancerous (malignant) brain tumors , including meningioma, paraganglioma, hemangioblastoma and craniopharyngioma. SRS may also be used to treat cancers that have spread to the brain from other parts of the body (brain metastases).

Overview
Why It's Done
Risks
- Stereotactic radiosurgery doesn't involve surgical incisions, so it's generally less risky than traditional surgery. In traditional surgery, you may have risks of complications with anesthesia, bleeding and infection. Early complications or side effectsare usually temporary. They may include: 1. Fatigue.Tiredness and fatigue may occur for the first few weeks after stereotactic rad…
How You Prepare
- Preparation for stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy may vary depending on the condition and body area being treated but usually involves the following steps:
What You Can Expect
- Stereotactic radiosurgery is usually an outpatient procedure, but the entire process will take most of a day. You may be advised to have a family member or friend who can be with you during the day and who can take you home. You may have a tube that delivers fluids to your blood stream (intravenous, or IV, line) to keep you hydrated during the day if you are not allowed to eat or drin…
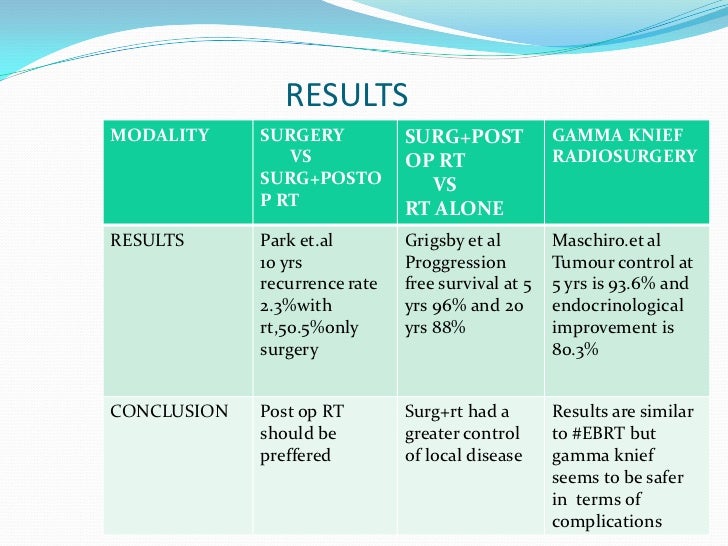
Results
- The treatment effect of stereotactic radiosurgery occurs gradually, depending on the condition being treated: 1. Benign tumors (including vestibular schwannoma).Following stereotactic radiosurgery, the tumor may shrink over a period of 18 months to two years, but the main goal of treatment for benign tumors is to prevent any future tumor growth. 2....
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.