
How to cure postpartum depression?
Feb 10, 2022 · There have not been conclusive studies published that looked specifically at folate or other B vitamins in the treatment of postpartum depression. Consider recommending to women who are postpartum to continue their prenatal vitamin or take a B-100 complex with about 1 mg (or 1,000 mcg) of folic acid, or folate.
What helps postpartum depression?
May 14, 2019 · Antidepressants can help relieve symptoms of depression and some can be taken while you're breastfeeding. Antidepressants may take several weeks to start working. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has also approved a medicine called brexanolone to treat postpartum depression in adult women. 6 Brexanolone is given by a doctor or nurse through an …
What triggers postpartum depression?
Postpartum depression is a serious mental health issue and can include symptoms such as feeling disconnected from your baby, feeling intense sadness or feeling incompetent as a mother. If these symptoms last for longer than two weeks or affect your ability to care for yourself or your family, you might have postpartum depression.
Who treats postpartum depression?
May 03, 2019 · Because postpartum depression is a mental health condition, it can be treated through psychotherapy. This includes talk therapy with a psychiatrist, psychologist or other mental health professional. For women who feel isolated, anxious and scared, talking about their feelings in a safe environment can be incredibly helpful.
How do you fix PPD?
Here are four ways to help cope:Make healthy lifestyle choices. Eat well, get adequate rest and include physical activity, such as a walk with your baby, in your daily routine. ... Set realistic expectations. You are recovering and having to mother at the same time. ... Make time for yourself. ... Meditate.Jun 10, 2020
How can I help someone with PPD?
How To Successfully Offer Practical HelpBe Specific. Don't leave an offer of help open-ended, be more specific. ... Sit With Her. ... Hang Out With Her Older Child. ... Give Her Alone Time. ... Emotional Support Is Just As Important.Encourage Her To Talk. ... Validate The Things She Does Well. ... Let Her Know She Is Not Alone.More items...
Can PPD go away without medication?
PPD can linger for months or even years if left untreated, but you don't have to deal with it in silence until it goes away.Jan 10, 2022
Can you get rid of PPD?
Outlook. PPD is treatable. Many women see their symptoms improve in six months. Call your doctor immediately if you feel disoriented or confused, have obsessive thoughts about your baby, feel paranoid, or experience hallucinations.
What do you mean by postpartum?
“Postpartum” means the time after childbirth. Most women get the “baby blues,” or feel sad or empty, within a few days of giving birth. For many women, the baby blues go away in 3 to 5 days. If your baby blues don't go away or you feel sad, hopeless, or empty for longer than 2 weeks, you may have postpartum depression.May 14, 2019
Is anxiety common after giving birth?
Lots of people are aware that you can become depressed after having a baby. But many people also experience anxiety during pregnancy and after giving birth. In fact, it is common to experience depression and anxiety together.
How long are you considered postpartum?
For this reason, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists considers postpartum care to extend up to 12 weeks after delivery [2]. Some investigators have considered women to be postpartum for as long as 12 months after delivery.Jan 3, 2022
How long can postpartum psychosis last?
The most severe symptoms tend to last 2 to 12 weeks, and it can take 6 to 12 months or more to recover completely from the condition. But with treatment and the right support, most people with postpartum psychosis do make a full recovery.
How long does it take to heal postpartum?
Your postpartum recovery won't be just a few days. Fully recovering from pregnancy and childbirth can take months. While many women feel mostly recovered by 6-8 weeks, it may take longer than this to feel like yourself again. During this time, you may feel as though your body has turned against you.Aug 28, 2020
What are the symptoms of postpartum psychosis?
Symptoms of postpartum psychosis can include:Delusions or strange beliefs.Hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren't there)Feeling very irritated.Hyperactivity.Decreased need for or inability to sleep.Paranoia and suspiciousness.Rapid mood swings.Difficulty communicating at times.
How common is postpartum depression?
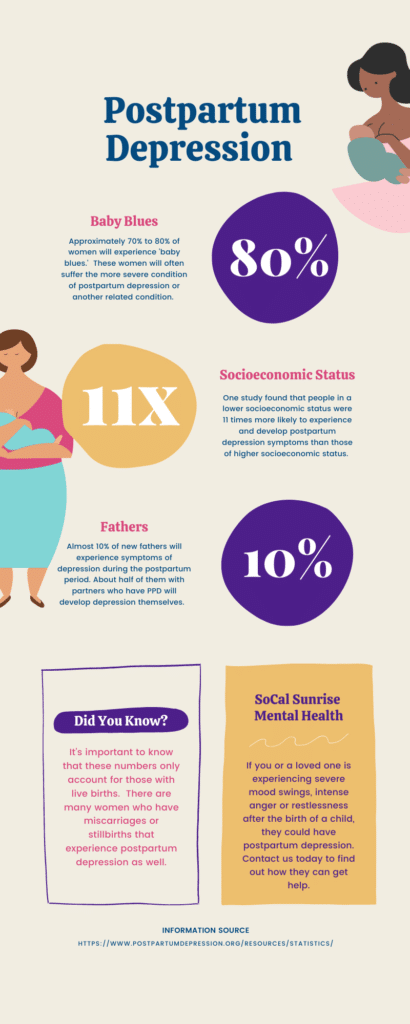
Postpartum depression is a major international public health problem that affects at least 1 in 8 mothers and their children in the year after childbirth worldwide. PPD may be more common and may be associated with more morbidity for both mothers and children in resource-poor countries. PPD has been associated with significant negative effects not only on depressed women themselves, but on the physical, cognitive and emotional development of their children. Early detection and intervention are important in mitigating these risks. There are validated and easily administered screening tools for PPD available in many languages, such as the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale; most experts recommend screening women for PPD 4–6 weeks after delivery.
What are the symptoms of a postpartum depression episode?
However, studies suggest that depressive episodes are significantly more common in women in the first three months after delivery, 32 and an increased vulnerability to psychiatric illness may persist for a year or more. 33 It is important to differentiate PPD from other psychiatric and nonpsychiatric diagnoses. The “postpartum blues” or “baby blues” is a transient mood disturbance that affects up to 75% of new mothers in the 10 days following delivery, and consists of crying, irritability, fatigue, anxiety, and emotional lability. Symptoms are generally mild and self-limited, and do not involve total loss of pleasure or interest, persistent low mood, or suicidal ideation. 34 On the other extreme, postpartum psychosis is a psychiatric emergency that requires immediate intervention, and is characterized by the rapid onset of severe mood swings, a waxing and waning sensorium, delusions, hallucinations or disorganized behaviors, and a relatively high incidence of suicidal ideation or homicidal ideation toward the infant. 35 Women presenting with a depressive episode, mood elevation, or psychotic symptoms should be screened for any prior history of mania or hypomania to rule out previously undiagnosed bipolar disorder. 36 Anxiety disorders are common in perinatal women, and women may have depression comorbid with obsessive-compulsive symptoms, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder. 37 Substance use and medical causes of psychiatric symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, should also be considered.
What is psychosocial intervention?
As compared with IPT or CBT, psychosocial interventions are unstructured and nonmanualized, and include nondirective counseling and peer support. Nondirective counseling (also known as “person-centered”) is based on the use of empathic and nonjudgmental listening and support. In the first notable study evaluating this intervention, Holden randomized 50 women with PPD to 8 weekly nondirective counseling sessions with a health visitor or routine primary care. 108 A health visitor in the UK is a public health nurse who conducts home visits with pregnant and postpartum women. This study found that the rate of recovery from PPD for counseling (69%) was significantly greater than that of the control group (38%). In a similar study conducted in Sweden, Wickberg and Hwang randomized 31 women with PPD to receive six nondirective counseling sessions by child health clinic nurses or routine primary care. 109 As in the Holden study, a significantly greater percentage of women in the treatment group (80%) had remission of depression than in the control group (25%). Study limitations include the removal of four study participants, two in each group, for more intensive mental health services due to illness severity.
What are the benefits of Omega 3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids have received specific attention in the treatment of perinatal depression, because of the known health benefits of these compounds for pregnant and postpartum women as well as some data showing positive effects on mood in the general population. 128 Omega-3 fatty acids such as the eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosa-hexaenoic acid (DHA) found in fish oils, are the key building blocks for the development of a baby’s central nervous system while in utero, 129 and depletion of maternal omega-3 fatty acids occurs during pregnancy to facilitate this process. 130 One often-cited cross-national study 131 evaluating major depression in the general population demonstrated that per capita fish consumption was inversely related to the risk of developing major depression. Further epidemiologic data support an association between low omega-3 intake from seafood and increased risk of high levels of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. 132
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
As with treatment-refractory major depression in the general population, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is an option for depressed postpartum women who do not respond to antidepressant medication or who have severe or psychotic symptoms. Data specific to this population are very limited.
What is interpersonal therapy?
Interpersonal therapy (IPT) is a time-limited treatment for major depression based on addressing the connection between interpersonal problems and mood, 98 which frames depression as a medical illness occurring in a social context. 99 In IPT, the patient and clinician select one of four interpersonal problem areas (role transition, role dispute, grief, or interpersonal deficits) as a treatment focus. Over the course of the therapy (typically 12–20 weeks), strategies are pursued to assist patients in modifying problematic approaches to relationships and in building better social supports. IPT has been adapted to address problem areas relevant to postpartum depression such as the relationship between mother and infant, mother and partner, and transition back to work. 100 The fact that IPT is both time-limited and problem-focused fits well with the demands of the postpartum mother.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), a well-studied and effective treatment for major depression, 105 is based on the premise that both perceptions and behaviors are intimately linked to mood. CBT focuses on helping depressed patients to modify distorted patterns of negative thinking and to make behavioral changes that enhance coping and reduce distress. 106 There have been several trials assessing CBT alone or with other interventions for the treatment of PPD. In a randomized controlled psychotherapy-pharmacotherapy study, Appleby et al assigned 87 women with PPD to one of four conditions in a factorial design, varying based on treatment with either one or six sessions of CBT-based counseling, and treatment with fluoxetine or placebo. 52 All four treatment groups had significant improvement in depressive symptoms. Women who received six CBT sessions versus one had greater decrease in depressive symptoms. Six sessions of CBT plus placebo pill was as effective as treatment with fluoxetine plus one session of CBT, but there was no added benefit in the group receiving 6 counseling sessions in combination with fluoxetine. It should be noted that the counseling sessions were delivered by briefly trained nonspecialists, and six sessions of CBT may not be a sufficient representation of a standard course of treatment. In another combination medication-CBT study, Misri et al randomized 35 women with PPD and comorbid anxiety either to paroxetine monotherapy or paroxetine and 12 weekly manualized CBT sessions with a psychologist. 53 While both groups had significant decreases in depressive symptoms, there were no significant differences between the two groups in response rates, time to remission or dose of medication required, suggesting no measurable added benefit to the CBT treatment in combination with an SSRI over the 12 week study period, as consistent with Appleby’s findings. In a randomized controlled trial looking at the effectiveness of CBT versus a control condition, Prendergast and Austin assigned 37 women with PPD either to six weekly one-hour home-based CBT sessions delivered by early childhood nurses (ECNs) or to “ideal standard care”, which consisted of six weekly visits to ECNs in a clinic setting. 107 Both groups with PPD had significant mood improvement, though there was a nonsignificant trend towards CBT being more effective at six-month follow-up. Among study limitations, ECNs administering CBT were not experienced therapists, though they received CBT training prior to the study and supervision throughout. Additionally, the control group more closely resembled a supportive psychotherapy rather than no-treament. These studies support CBT interventions as helpful in the treatment of PPD, though they do not support an additional benefit to CBT in combination with pharmacotherapy and do not clarify a specific benefit of CBT for this population in comparison with other treatments. Two of these studies also suggest a role for the training of nonmental-health professionals in this modality.
What is the treatment for postpartum depression?
Postpartum depression. Postpartum depression is often treated with psychotherapy (also called talk therapy or mental health counseling), medication or both. Psychotherapy. It may help to talk through your concerns with a psychiatrist, psychologist or other mental health professional.
How to treat postpartum psychosis?
Treatment may include: Medication. Treatment may require a combination of medications — such as antipsychotic medications, mood stabilizers and benzodiazepines — to control your signs and symptoms.
What is ECT therapy?
ECT is a procedure in which small electrical currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry ...
What to do if your thyroid is underactive?
Order blood tests to determine whether an underactive thyroid is contributing to your signs and symptoms. Order other tests, if warranted, to rule out other causes for your symptoms.
How to make a house for a baby?
Do what you can and leave the rest. Make time for yourself. Take some time for yourself and get out of the house. That may mean asking a partner to take care of the baby or arranging for a sitter.
What to do after first mental health appointment?
After your first appointment, your doctor may refer you to a mental health professional who can create the right treatment plan for you . You may want to find a trusted family member or friend to join you for your appointment to help you remember all of the information discussed.
How to speed up recovery from a syphilis?
Lifestyle and home remedies. In addition to professional treatment, you can do some things for yourself that build on your treatment plan and help speed recovery. Make healthy lifestyle choices. Include physical activity, such as a walk with your baby, and other forms of exercise in your daily routine.
How common is postpartum depression?
Depression is a common problem after pregnancy. One in 9 new mothers has postpartum depression. 1
How do I know if I have postpartum depression?
Some normal changes after pregnancy can cause symptoms similar to those of depression. Many mothers feel overwhelmed when a new baby comes home. But if you have any of the following symptoms of depression for more than 2 weeks, call your doctor, nurse, or midwife:
What causes postpartum depression?
Hormonal changes may trigger symptoms of postpartum depression. When you are pregnant, levels of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone are the highest they’ll ever be. In the first 24 hours after childbirth, hormone levels quickly drop back to normal, pre-pregnancy levels.
What is postpartum psychosis?
Postpartum psychosis is rare. It happens in up to 4 new mothers out of every 1,000 births. It usually begins in the first 2 weeks after childbirth. It is a medical emergency. Women who have bipolar disorder or another mental health condition called schizoaffective disorder have a higher risk of postpartum psychosis. Symptoms may include:
What should I do if I have symptoms of postpartum depression?
Ask your partner or a loved one to call for you if necessary. Your doctor, nurse, or midwife can ask you questions to test for depression. They can also refer you to a mental health professional for help and treatment.
How is postpartum depression treated?
Therapy. During therapy, you talk to a therapist, psychologist, or social worker to learn strategies to change how depression makes you think, feel, and act.
What can happen if postpartum depression is not treated?
Untreated postpartum depression can affect your ability to parent. You may:
How to treat postpartum depression?
Postpartum Depression Therapy. Because postpartum depression is a mental health condition, it can be treated through psychotherapy. This includes talk therapy with a psychiatrist, psychologist or other mental health professional. For women who feel isolated, anxious and scared, talking about their feelings in a safe environment can be incredibly ...
How to help a wife recover from postpartum depression?
Depending on the situation, relationship therapy for spouses may be an important factor in recovering from postpartum depression. In general, therapy can help women develop a more positive way of acknowledging, addressing and recovering from their postpartum depression. Learn More About Therapy Options.
What is the best medication for postpartum depression?
Antidepressants are the most commonly prescribed type of medication for postpartum depression. Antidepressants work to elevate and stabilize the mood. This prevents postpartum depression symptoms such as mood swings, sadness and irritability.
What is the effect of SSRIs on mood?
SSRIs block the reabsorption of serotonin in the brain making it more readily available in the brain. This helps to elevate mood and reduce general symptoms of postpartum depression.
What are the factors that affect postpartum depression?
These factors include: The severity of the condition. Medical history and background of the mother. Other individual needs. Postpartum depression treatments generally include therapy with a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. Another common treatment method, used in conjunction with therapy, ...
What are the two types of mental health professionals?
There are generally two types of mental health professionals who can provide treatment for postpartum depression: psychologists and psychiatrists. Both professions work to treat mental conditions and improve emotional well-being. However, they have distinct differences in educational background, scope of practice and approach to therapy.
How does mental health help women?
Mental health professionals use therapy to help women find ways to understand and cope with their feelings. Therapy also helps mothers solve problems and set realistic goals as they work to manage their postpartum depression. There are two common types of psychotherapy that are referred to as talk therapy.
What are the risks of postpartum depression?
Having one or more of the following risk factors for postpartum depression can increase your likelihood of developing the condition: 1 Stressful life events, including a traumatic birth 2 Inadequate social support, including being a single mom or experiencing domestic abuse 3 Personal or family history of depression 4 Pregnancy or birth complications, including preterm birth or a baby’s hospitalization 5 Being a teen mom 6 Giving birth to twins or triplets 7 Having had difficulty getting pregnant
How long does postpartum depression last?
If these symptoms last for longer than two weeks or affect your ability to care for yourself or your family, you might have postpartum depression. Risk factors can include histories of depression, stressful life events or inadequate social support.
What to do if you can't care for your baby?
If you do not think you will hurt your baby but cannot care for him or her, call a trusted family member or friend . If you cannot reach anyone or don’t know who to call and it’s not an emergency, call the “warmline,” a help line operated by Postpartum Support International, at 800-944-4773 or text 503-894-9453.
What does it feel like to be numb to a baby?
Feeling numb or disconnected from your baby, not wanting to be around your baby or being worried you will hurt your baby. Feeling incapable of or incompetent at caring for your baby, including feeling guilty about not being “good enough”. Unexplained physical symptoms, such as headaches, nausea and stomachaches.
Who is at higher risk for postpartum psychosis?
Women with a history of psychosis, schizophrenia or bipolar disorder are at higher risk for postpartum psychosis. Tara Haelle is a health and science journalist, mother and co-author of “The Informed Parent: A Science-Based Resource for Your Child’s First Four Years.”. Advertisement.
Can you ask your family for help during postpartum?
You can and should ask your family and friends for help. Severe postpartum depression and postpartum psychosis are health emergencies and should be treated as such. I have a history of depression, so in the weeks following the births of both of my children, my husband and mother were on high alert for any signs of postpartum depression.
Can postpartum depression cause anxiety?
Postpartum anxiety can also occur alongside postpartum depression and might include symptoms such as panic attacks, insomnia, obsessive fears about your baby’s health and safety, an inability to sit still or physical pain or discomfort, such as frequent headaches or stomachaches.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
- Your doctor will usually talk with you about your feelings, thoughts and mental health to distinguish between a short-term case of postpartum baby blues and a more severe form of depression. Don't be embarrassed ― postpartum depression is common. Share your symptoms with your doctor so that a useful treatment plan can be created for you. As part of your evaluatio…
Preparing For Your Appointment