Flame treatment refers to the process of oxidizing plastic surface with a strong oxidizing flame. It is mainly used to improve the painting characteristics and adhesive characteristics of polyolefin plastics. The technique is to increase surface activity and increase the primer adhesion to workpiece surface.
Full Answer
What is flame treatment for polyolefins?
Concluding remarks Flame treatment is a powerful technique for enhancing the surface attributes of plastic materials, especially those with a marked inherent hydrophobicity such as polyolefins.
What is flame treated polymer surface?
This treatment brings about a change to the polymer surface that increases its surface energy allowing fluids to effectively wet-out the surface and permits a strong adhesive molecular and mechanical bond. UHMW Sheets Flame Treated- Microscopic Surface Comparison Commercially Available Propane Torch
What type of flame is used in welding?
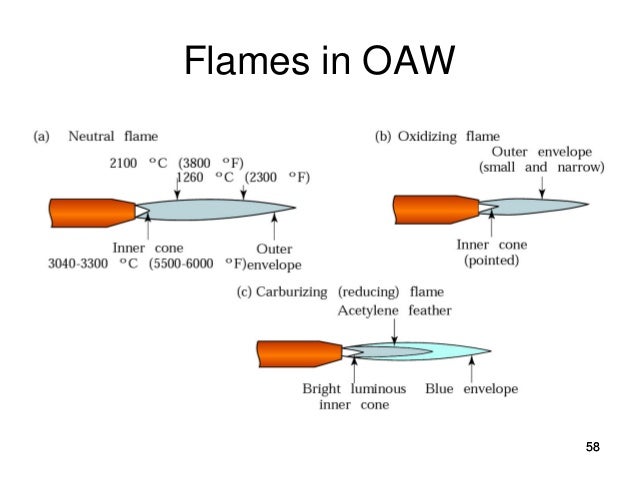
The neutral flame burns cleanly and is used for most welding applications. Carbonizing flames are cooler and often used when working with steel or iron. Oxidizing flames are the hottest and least used, due to the oxidation of the base material.
What is flame treatment?
Flame treatment is a commercial process to render polyolefins and polyethylene terephthalate adherable. The polymer article (e.g., film) is passed over an oxidizing flame formed by an oxygen-rich (relative to stoichiometry) mixture of hydrocarbon gas.

How does flame treatment work?
Flame treatment uses a carefully controlled blend of natural gas and air to create a hot, oxygen rich plasma. First, the heat removes contaminants. Then, after contaminant removal, the oxygen rich plasma activates the surface by partial oxidation.
What is flame treated plastic?
Flame Treating Plastic to Improve Adhesion Make two or three passes over the bonding area with the flame for a total of one second of exposure. When done correctly, the surface will not discolor or burn. This technique oxidizes the surface, improving adhesion without a visible change in the surface.
How long does flame treatment last?
A Flame Treating process consists of exposing the surface to a suitable oxidizing flame for a period in the range 0.2 to 3.0 seconds.
Why are bottles flame treated?
Flame Treating is the most commonly used means of rendering a molded bottle surface receptive to suitable inks, paints, etc. In this method, a hot oxidizing flame (2000 degrees to 5000 degrees) is applied directly to the intended label or decorated area.
How do you heat treat HDPE?
Here's how to do it.Step 1: clean the surface. Use an alcohol wipe to clean the surface that you're going to flame-treat.Step 2: flame-treat the surface. To flame-treat the plastic, hold a propane torch about 15cm above the surface so that the flame just touches the plastic. ... Step 3: apply the mixed epoxy.
How do you flame treat polypropylene?
1:403:38Flame Treatment Updated - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clip12 inches or 30 centimeters per three seconds. For this example the total time the material shouldMore12 inches or 30 centimeters per three seconds. For this example the total time the material should be exposed to the flame should be two to three seconds. About one half second per stroke.
What is plasma surface treatment?
Plasma surface treatment is a process that raises the surface energy of many materials so as to improve the bonding characteristics. One form of plasma treatment is also commonly known as a corona treatment, which was invented by Danish engineer Verner Eisby in the 1950s.
What is a flame treater?
For 3D objects, the plant typically consists of ( Fig. 5 a ):#N#(1)#N#a conveyor belt, which allows a continuous loop of material, i.e., the polyolefin objects, which are normally mounted on heat-resistant holders;#N#(2)#N#a cleaning device, such as a stream of compressed air or a brush-like system. This is normally placed a few centimetres in front of the burners to assure the removal of all small particles (e.g., dust) that might negatively affect successful flame treatment; and#N#(3)#N#a burner, i.e., the basic part of the equipment that produces the oxidising flame.
What is a laminar flame?
A laminar flame (which is ordinarily employed by flame treaters) is defined as a mixture of a fuel and an oxidiser, thoroughly premixed before combustion. The term ‘premixed laminar flame’ is interchangeable with the term ‘deflagration’ to indicate the propagation of the combustion process accompanied by a decrease in both density and pressure together with an increase in velocity (contrary to the propagation known as ‘detonation’). Within a laminar flame profile, three main zones can be observed ( Fig. 2 ), which correspond to specific reactions. As a consequence, different thermal gradients and reactive species can be encountered. These zones are briefly described here.
What is the gap between a flame and a web surface?
It is widely recognised that the gap between the flame and web surface (i.e., the distance between the tips of the luminous flame cones and polyolefin surface) is a key factor in determining the extent of activation accomplished by the treatment. As a general trend, it has been observed that when the film passes through the flame, a rapid depletion in the wettability of the treated surface occurs. As the distance between the cone of the flame and film surface increases, surface activation decreases, although a beneficial effect arising from the treatment is still appreciable up to approximately 20 mm.
What is the formula for polyolefins?
The term polyolefin encompasses all those polymers produced by an olefin as a starting monomer, whose general formula is C n H 2n. Most common polyolefins in the packaging field are polyethylene (PE) and PP. Although they have different specific properties, it is recognised that both polymers are inherently hydrophobic, which is in turn responsible for their typical poor wettability, especially to waterborne systems. For this reason, polyolefins generally need to be surface-activated before the deposition of inks, paints, adhesives, metals, and coatings. Flame treatment is a valuable technique to improve the surface energy of polyolefins, although it has been exploited to a minor extent with respect to corona treatment so far. However, because of improvements in safety conditions as well as in some technical aspects, it is receiving renewed attention, especially by those sectors (e.g., packaging) that historically lagged behind in the exploitation of the technique.
What is the coldest region of a flame?
This region, also called the ‘dark zone’, has a typical dark bluish colour. It is the coldest region of a flame because even though some of the hydrogen formed is oxidised to water the combustion process has not yet reached the explosion condition, and thereby the amount of net energy released is negligible. In this region, the only abundant free radical is the hydrogen atom, which reacts quickly with hydrocarbons and oxygen, thereby impeding the formation of the radical pool. For this reason, this zone is also known as the ‘reducing zone’. This is an ineffective and unimportant region for surface activation purposes, since it in no way contributes to the oxidation of the plastic substrate.
Can a flame propagate spontaneously?
This means that if the air/hydrocarbon mix is within its flammability limits (i.e., it has a suitable composition) and within its explosive conditions (i.e., within adequate pressure/temperature boundaries for the same composition), the flame is generated and can spontaneously propagate.
Do polyolefins need to be activated?
For this reason, polyolefins generally need to be surface-activated before the deposition of inks, paints, adhesives, metals, and coatings. Flame treatment is a valuable technique to improve the surface energy of polyolefins, although it has been exploited to a minor extent with respect to corona treatment so far.
How to flame treat plastic?
To flame treat a plastic surface, hold a propane torch so the flame just touches the surface and move it across the surface at a rate of 12 to 16 inches per second. Keep the torch moving and overlap the previous pass slightly.
How to test if flame treatment is effective?
The best way to test if the flame treatment was effective is with a water break test. Oxidizing the plastic surface with a flame changes the surface from a low-energy surface to a high-energy surface. An excellent example of a low-energy surface is a waxed hood of a car. Water beads up and rolls off.
Can you use alcohol wipes on plastic?
With most plastics, you achieve a higher bond strength with just an alcohol wipe and flame treatment than you would with the typical solvent wipe and sanding method required for most substrates. For example, PVC allows for an acceptable bond with a suitable solvent wipe and sanding with 80-grit sandpaper, but adhesion can be improved ...
Can you peel epoxy off with your fingers?
And, for HDPE, flame treating is required, otherwise could peel the epoxy off with your fingers. The directions that come with G/flex list how to prepare the surface for different plastics and other hard-to-bond materials. If you are in doubt about what type of plastic you are working with, sand, alcohol wipe, and flame treat for surface prep.
Can you flame treat PVC?
When bonding a plastic fabric like Hypalon or PVC, we do not recommend flame treating the fabric surface. A simple solvent wipe and sanding with 80-grit will be the most effective on these fabric surfaces.
What type of adhesive do you use to bond polyolefin?
You use a special primer (such as Permabond POP) and cyanoacrylate adhesive. You use a special adhesive such as Permabond TA4610 which has been developed for bonding untreated polyolefin materials.
Why pretreat plastic?
Why pretreat? Certain plastic substrate materials have a low surface energy which give them a non-stick nature. Typical “offenders” are common plastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, PTFE (Teflon) plus also some rubbers such as EPDM and Santoprene.
Is polyethylene a non-stick material?
Polyethylene has a low surface energy so is a fairly non-stick surface. There are several options of surface preparation and industrial adhesive choice that could yield high bond strengths: Corona treatment of surface. Plasma treatment of surface. Flame treatment.
Can you use adhesive on polyethylene?
However, once the surface is treated, you can use a wide variety of different industrial adhesive products when bonding polyethylene. This type of equipment is worth considering if the bonded assemblies are going to be manufactured in large numbers.
Can you use Permabond with cyanoacrylate?
Permabond offers POP Primer for use with cyanoacrylate industrial adhesive – the POP is brushed on to the Polyethylene and the cyanoacrylate applied to the other part. When the joint is clamped shut the industrial adhesive will cure in seconds.
Is induction heating a good method of bonding polyethylene?
This makes solvent welding, ultrasonic or infrared welding or induction heating a good method of bonding polyethylene (to itself). However, if you need to bond it to a different type of plastic or substrate such as wood, metal, rubber or some kind of composite, it is necessary to look to some other joining method such as industrial adhesive bonding.
What are the three types of flames used in welding?
So what are the types of gas welding flame? The three basic flames used for gas welding include neutral, carburizing, and oxidizing.
What is the hottest flame for welding?
When adjusted properly, the inner cone can reach 6300 degrees Fahrenheit, making the oxidizing flame the hottest flame for gas welding. When adjusting the neutral flame to create an oxidizing flame, the flow of oxygen is increased until the inner cone is about one-tenth of its original size.
Why does an oxidizing flame burn faster?
An oxidizing flame has less acetylene and more oxygen. The excess oxygen allows the gas to burn quickly. As it doesn’t need to travel as far, the inner cone can reach hotter temperatures.
How to make a carburizing flame?
To create a carburizing flame, I first achieve a neutral flame. I then slowly open the acetylene valve to increase the ratio of acetylene to oxygen. As the ratio increases, a white stream extends from the inner cone.
How does gas welding work?
T he flame is used to heat metal or thermoplastics, fusing them as they cool. Most gas welding processes use oxyfuel welding.
What is the process of welding gas?
Most gas welding processes use oxyfuel welding. It’s one of the oldest welding processes, first developed in 1903. With oxyfuel welding, which is also called oxyacetylene welding, you need a liquid fuel or gas, such as acetylene. The gas is combined with oxygen to increase the temperature of the flame.
What is the neutral flame?
Neutral Flame for Gas Welding. The neutral flame is the starting point for other flames. It has a one-to-one ratio of oxygen and acetylene. Burning all the available gas produces a clean flame. The inner cone is often bluish-white with a tip that can reach temperatures of about 5850 degrees Fahrenheit.