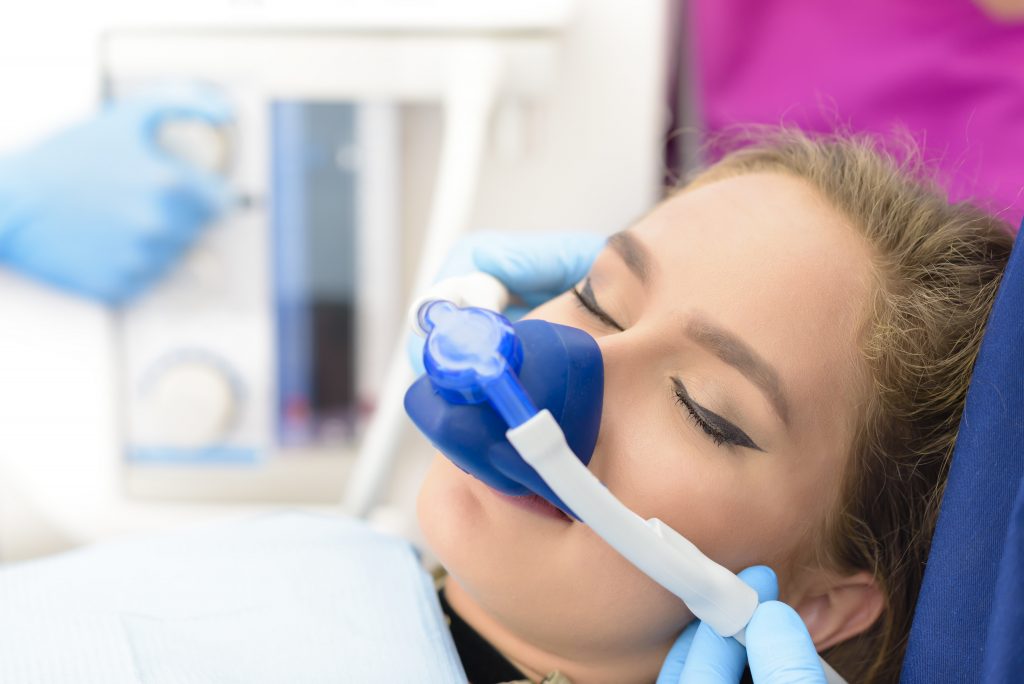
What is nitrous oxide used for in dentistry?
Nitrous oxide (with oxygen) is the most common inhaled anesthetic used in dentistry to control patient anxiety and pain. It is used by most (89%) dentists who provide care to pediatric patients and a majority (58%) of all dentists. 1-3 In certain states dental hygienists and dental assistants are also licensed to administer nitrous oxide. 4,5
What is nitrous oxide and how does it work?
The other important property of nitrous oxide is to produce an euphoric feeling which is very helpful for patients with anxiety, fears or dental phobia. This state of euphoria often makes people to want to laugh, which is why N2O is usually referred as ‘laughing gas’.
Is nitrous oxide and oxygen sedation safe?
The combination of inhaled nitrous oxide and oxygen is a safe and effective means of managing pain and anxiety in dentistry, when used appropriately. There is an inherent safety margin for the proper administration of nitrous oxide-oxygen sedation.
What is the history of nitrous oxide?
The first clinical application of nitrous oxide (N2O) was in 1844, by an American dentist named Horace Wells who used it to control pain during tooth extraction. Since then, N2O has shared a 170-year history with modern dental anesthesia.

Where is nitrous oxide excreted?
Nitrous oxide is administered by inhalation, absorbed by diffusion through the lungs, and eliminated via respiration. The elimination half life of nitrous oxide is approximately 5 minutes. It is excreted essentially unchanged (ie, nonmetabolized) via the lungs; less than 0.004% is actually metabolized in humans.
How long does nitrous oxide stay in your system?
The effects of laughing gas typically wear off within a few minutes. Children might be given 100% oxygen following the removal of the nitrous oxide mask. The oxygen helps them to fully recover within minutes.
Does nitrous oxide dissolve in blood?
The solubility of nitrous oxide in blood at 37.5” was found to be CY = 0.415 and X = 0.472. A brief summary is given of the nitrous oxide content of arterial blood during nitrous oxide anesthesia.
What happens to your body on laughing gas?
When you inhale the gas, it displaces the air in your lungs and prevents oxygen from getting to your brain and blood. This deprivation is what causes all the giggles. Some people even experience mild hallucinations. It takes about two minutes for the effects to wear off once you stop breathing in the nitrous oxide.
Does nitrous oxide show up in urine?
Inhaled nitrous oxide can be detected in blood or urine shortly after exposure20,21 using special techniques and precautions,14 but it is not detected on results of routine drug screening panels.
What are the negative side effects of nitrous oxide?
Negative side effects may include nausea or vomiting, headache, increased sleepiness, and/or excessive sweating or shivering. Headaches can result if a patient does not receive oxygen for at least five minutes after the nitrous oxide has been turned off.
Why do dentists not use nitrous oxide anymore?
Q: What are the primary dangers to both dental personnel and patients in nitrous oxide administration? A: Acute exposure to nitrous oxide may cause lightheadedness, eye and upper airway irritation, cough, shortness of breath, and decreases in mental performance and manual dexterity.
How safe is nitrous oxide for dental procedures?
The combination of inhaled nitrous oxide and oxygen is a safe and effective means of managing pain and anxiety in dentistry, when used appropriately. There is an inherent safety margin for the proper administration of nitrous oxide-oxygen sedation.
Why is nitrous oxide contraindicated in the presence of bowel obstruction?
Since the bowel is compliant, it will get larger as the air expands and make surgery more technically difficult – leading to unhappy surgeons. At some point, the bowel may rupture – leading to really unhappy surgeons. Thus, nitrous oxide is contraindicated in patients with an acute intestinal obstruction.
Does nitrous oxide damage lungs?
As the gas is also under constant pressure, it can cause ruptures in lung tissue when inhaled directly from these containers. Releasing the nitrous oxide into a balloon helps to warm the gas and normalise the pressure before inhaling. People can also harm themselves if they use faulty gas dispensers, which may explode.
Can nitrous oxide cause brain damage?
Further evidence is now mounting which implies nitrous oxide may also cause neurotoxicity. Often, neurological damage may not have overt symptoms and vulnerable patients, such as the elderly, may experience cognitive changes which may go unnoticed.
Does nitrous oxide lower blood pressure?
Nitrous oxide caused significant decreases in mean arterial pressure in a dose-related fashion; pressure fell 6 mm Hg at 10% nitrous oxide and 11 mm Hg at 60% nitrous oxide (6 and 13% decreases). These changes were not associated with significant alteration in pulmonary artery pressure or cardiac index.
Can nitrous oxide make you sick the next day?
However, some side effects can occur after inhaling nitrous oxide. The side effects result from inhaling the gas too fast or perhaps receiving too much gas. The most common side effects of laughing gas are shivering, nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating, fatigue, and dizziness.
Does nitrous oxide damage lungs?
As the gas is also under constant pressure, it can cause ruptures in lung tissue when inhaled directly from these containers. Releasing the nitrous oxide into a balloon helps to warm the gas and normalise the pressure before inhaling. People can also harm themselves if they use faulty gas dispensers, which may explode.
Does nitrous oxide affect your heart?
Sixty percent nitrous oxide for 15 minutes significantly increased PaCO2, heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, mean arterial blood pressure, and central venous pressure. Inhalation of 60% nitrogen also produced no significant change in any cardiovascular variable.
What is the responsibility of dentists and dental staff?
Dentists and dental staff share responsibility for adhering to recommended practices to minimize exposure to nitrous oxide and other anesthetic gases used during dental procedures.
What is the most common inhaled anesthetic used in dentistry?
Overview. Nitrous oxide (with oxygen) is the most common inhaled anesthetic used in dentistry to control patient anxiety and pain. It is used by most (89%) dentists who provide care to pediatric patients and a majority (58%) of all dentists. 1-3 In certain states dental hygienists and dental assistants are also licensed to administer nitrous oxide.
Does Nitrous Oxide increase exposure?
However, adherence to other recommended practices for administering nitrous oxide was lacking (see below), which may increase exposure risk. Successful management of nitrous oxide should include: Regular inspection for leaks of nitrous oxide delivery and scavenging equipment.
How does nitrous oxide work?
During dental procedures, the gas is mixed with oxygen. The gas is then inhaled through a mask that covers your nose. It works within minutes and gives an overall sense of calm and relaxation to patients. Here are some benefits to using nitrous oxide as opposed to other sedation dentistry options:
What is the purpose of Nitrous Oxide?
It can be used for patients with a mild anxiety about their dental cleaning to those with a paralyzing fear of lying back in the dental chair. Nitrous oxide is an oxide of nitrogen. It has a slight sweet odor and taste. During dental procedures, the gas is mixed with oxygen. The gas is then inhaled through a mask that covers your nose.
Why do dentists use laughing gas?
It can also be used to help patients take advantage of cosmetic dental services, helping them get the smile of their dreams in the most comfortable and relaxed way.
Can you breathe on your own after a nitrous oxide mask is removed?
You are able to breathe on your own, move your body, and be conscious enough to communicate with your dentist or hygienist. Quick and Easy Recovery: The effects of Nitrous Oxide wear off very quickly after the mask is removed. There are no severe side effects.
Is Nitrous Oxide safe for children?
Very Safe: Nitrous oxide is safe for both adults and children. Although recreational use of nitrous oxide can be dangerous, the drug is combined with oxygen during dental procedures – which is what ensures that nitrous oxide remains safe for the brain and prevents hypoxia. Nitrous oxide is non-addictive and non-allergic, ...
Can you drive home after a dental appointment?
Patients are able to drive home after their appointment and carry on their normal activities. Dosage Control: Unlike oral sedation (a pill), nitrous oxide is easily controlled and adjusted by your dentist at any time during your procedure. Laughing gas is the mildest form of sedation dentistry.
Is nitrous oxide safe for chronic pulmonary disease?
Nitrous oxide is non-addictive and non-allergic, but it is not recommended for people with certain medical conditions such as chronic pulmonary disease. Relaxed but Aware: Nitrous Oxide has the ability to put patients in a comfortable state of relaxation, yet remain aware of their surroundings.
What is nitrous oxide sedation?
Nitrous oxide sedation dentistry is also known as inhalation sedation, because the patient inhales nitrous oxide through a mask placed over the nose. Actually the patient breaths a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen, with the oxygen level always maintained over 30% to avoid hypoxia. The percentage of nitrous oxide is fully adjustable ranging from 30%-70% based on the necessary level of sedation and the patient’s tolerance to the gas. Special equipment is used for the safe administration of N 2 O.
When was Nitrous Oxide discovered?
Nitrous oxide was discovered in 1772 by Joseph Priestley who is also known for the discovery of oxygen. Its first use as an anesthetic for dentistry was made in 1844 by Horace Wells, a dentist in Hartford Connecticut, who got his tooth extracted under the analgesic effect of nitrous oxide.
What is laughing gas?
Nitrous oxide sedation dentistry , also known as inhalation sedation, is the most commonly used method for patient relaxation in dental offices. Dentists use nitrous oxide, also known as “laughing gas”, for over 160 years to provide more comfortable and painless dental treatments to their patients. It is estimated that over one third of U.S. dentists use laughing gas to help patients with dental anxiety and phobia.
Why is nitrous oxide so popular?
Additionally to its effectiveness in anxiety and pain control, the main advantages of N 2 O include its rapid onset without the need of any preparation, the ability to instantly regulate the depth of sedation, the fast recovery and its low cost.
Is inhalation sedation safe?
Although inhalation sedation dentistry is considered as the safest relaxation method, some risks still exist. They are mostly related with errors in the proper administration of the gas (with ‘hypoxia’ as the most dangerous one) or complications in patients who are not suitable candidates for using it.
Can you use nitrous oxide for dental sedation?
Dental sedation using nitrous oxide can be used by the vast majority of dental patients who need a light to moderate level of relaxation. However there are some contraindications that make N 2 O sedation dentistry not suitable for some patients groups with breathing or lung problems, drug abusers, women in the first trimester of pregnancy, or patients after a recent eye or ear surgery.
Does nitrous oxide cause nausea?
Another reason for the popularity of nitrous oxide sedation are the very limited side effects. The most common side effect is nausea, but it can be easily controlled by lowering the percentage of the sedative gas in the N 2 O/O 2 mixture.
What happens if you take too much N20?
Chronic exposure to high concentrations of N20 may result in a condition resembling subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord. ‘Short-term exposures may result in megaloblastic anaemia and agranulocytosis.
Is nitrogen oxide oxidation irreversible?
Nitrous oxide metabolism is an irreversible oxidation. Vitamin B12 is a cofactor for methionine synthetase and is involved in the production of 5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate which is essential for DNA synthesis.
