
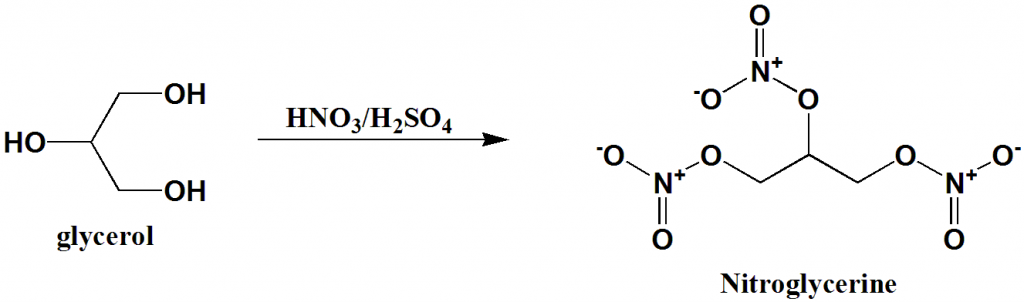
Nitroglycerin, also known as glyceryl trinitrate
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO⁻₃ and a molecular mass of 62.0049 u. Organic compounds that contain the nitrate ester as a functional group are also called nitrates.
What are the actions of nitroglycerin?
What are the actions of Nitroglycerin? Smooth muscle relaxant, vasodialation, venous pooling, increase coronary perfusion, reduce O2 consumption, relieve angina pain What are the indications of Nitroglycerin?
What is the proper name for nitroglycerin?
On p. 197, Sobrero names nitroglycerin "pyroglycerine": "Quelle gocciole costituiscono il corpo nuovo di cui descriverò ora le proprietà, e che chiamerò Piroglicerina ."
How does nitroglycerin treat angina pectoris?
People often use the drug nitroglycerin to relieve chest pain that angina causes. Most often, the reason for the decrease in blood flow is plaque formation and narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the heart. Nitroglycerin helps to open up the blood vessels and allow blood to flow.
How is nitroglycerin administered in the ICU?
There are intravenous (IV) routes of administration for nitroglycerin used most commonly in emergency rooms and intensive care units (ICU). It is administered as a 5% dextrose in drip and is indicated when sublingual nitroglycerin has failed to provide symptomatic relief or if rapid and continued relief of symptoms is necessary.
Why do doctors use nitroglycerin?
Uses. Doctors usually use nitroglycerin to treat the pain that angina causes. Narrowing of the arteries that supply the heart with blood is what causes unstable angina. Doctors call this condition coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is the most common type of heart disease. More than 370,000 people.
Why do people take nitroglycerin?
People often use the drug nitroglycerin to relieve chest pain that angina causes . Most often, the reason for the decrease in blood flow is plaque formation and narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the heart. Nitroglycerin helps to open up the blood vessels and allow blood to flow. People also use nitroglycerin to treat chronic anal fissures.
How much nitroglycerin is in a tablet?
Generic nitroglycerin comes in the form of a sublingual tablet. The strengths of these tablets are 0.3 mg, 0.4 mg, and 0.6 mg.
What is the best medicine for angina?
Doctors usually use nitroglycerin to treat the pain associated with angina.
How long before an activity can you take nitroglycerin?
People can also take fast-acting nitroglycerin formulations 5 to 10 minutes before doing an activity that may cause an angina attack.
What is the PDE-5 inhibitor?
PDE-5 inhibitors are drugs that doctors give to treat erectile dysfunction in males. Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra are PDE-5 inhibitors. As with nitroglycerin, these drugs also cause increased blood flow and can lower blood pressure.
Where to put nitroglycerin patch?
A person places the patch on their skin anywhere except the areas below the knee and elbow. Most people place the patch on their chest. The area should be clean, dry, and hairless to allow the nitroglycerin to absorb across the skin.
How long after nitroglycerin injection can you drive?
Do not drive yourself and call 911, if necessary. You may administer 1 or 2 sprays of Nitroglycerin oral spray at the onset of chest pain. If the pain continues after 5 minutes, a third spray may be used. You must wait 5 minutes after the first 1 or 2 sprays before using a third spray.
How long after taking Nitroglycerin can you spit?
Do not rinse or spit for 5 minutes after taking this medicine. Do not take more than 3 packets in 15 minutes. If you still have pain after you take a total of 3 packets, this is an emergency. Call 911. Do not drive yourself to the hospital. Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets should not be chewed, crushed, or swallowed.
How to treat angina in the chest?
Then place a sublingual powder or tablet in your mouth or under your tongue. If you use the oral spray, you should spray it on or under the tongue.
How does sublingual spray work?
The oral spray, sublingual powder, and sublingual tablets work quickly to stop an angina attack that has already started or they can be used to prevent angina if you plan to exercise or expect a stressful event.
How to store extended release capsules?
Store the extended-release capsules in a closed container at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light.
How long after taking a syringe can you take a second syringe?
However, if the pain is not relieved, you may use a second tablet 5 minutes after you take the first tablet. If the pain continues for another 5 minutes , a third tablet may be used. If you still have chest pain after a total of 3 tablets, contact your doctor or go to a hospital emergency room right away.
Can you chew nitroglycerin?
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets should not be chewed, crushed, or swallowed. They work much faster when absorbed through the lining of the mouth. Place the tablet under the tongue or between the cheek and gum, and let it dissolve. Do not eat, drink, smoke, or use chewing tobacco while a tablet is dissolving.
Who invented nitroglycerin?
Nitroglycerin was later adopted as a commercially useful explosive by Alfred Nobel, who experimented with safer ways to handle the dangerous compound after his younger brother, Emil Oskar Nobel, and several factory workers were killed in an explosion at the Nobels' armaments factory in 1864 in Heleneborg, Sweden.
How does nitroglycerin deflagrate?
Nitroglycerin and any diluents can certainly deflagrate (burn). The explosive power of nitroglycerin derives from detonation: energy from the initial decomposition causes a strong pressure wave that detonates the surrounding fuel. This is a self-sustained shock wave that propagates through the explosive medium at 30 times the speed of sound as a near-instantaneous pressure-induced decomposition of the fuel into a white-hot gas. Detonation of nitroglycerin generates gases that would occupy more than 1,200 times the original volume at ordinary room temperature and pressure. The heat liberated raises the temperature to about 5,000 °C (9,000 °F). This is entirely different from deflagration, which depends solely upon available fuel regardless of pressure or shock. The decomposition results in much higher ratio of energy to gas moles released compared to other explosives, making it one of the hottest detonating high explosives .
Why was nitroglycerin banned in California?
In April 1866, three crates of nitroglycerin were shipped to California for the Central Pacific Railroad, which planned to experiment with it as a blasting explosive to expedite the construction of the 1,659-foot-long (506 m) Summit Tunnel through the Sierra Nevada Mountains. One of the crates exploded, destroying a Wells Fargo company office in San Francisco and killing 15 people. This led to a complete ban on the transportation of liquid nitroglycerin in California. The on-site manufacture of nitroglycerin was thus required for the remaining hard-rock drilling and blasting required for the completion of the First Transcontinental Railroad in North America.
What happened to the nitroglycerin wagons?
In June 1869, two one-ton wagons loaded with nitroglycerin, then known locally as Powder-Oil, exploded in the road at the North Wales village of Cwm-y-glo. The explosion led to the loss of six lives, many injuries and much damage to the village. Little trace was found of the two horses. The UK Government was so alarmed at the damage caused and what could have happened in a city location (these two tons were part of a larger load coming from Germany via Liverpool) that they soon passed The Nitro-Glycerine Act of 1869. Liquid nitroglycerin was widely banned elsewhere, as well, and these legal restrictions led to Alfred Nobel and his company's developing dynamite in 1867. This was made by mixing nitroglycerin with diatomaceous earth (" Kieselguhr " in German) found in the Krümmel hills. Similar mixtures, such as "dualine" (1867), "lithofracteur" (1869), and " gelignite " (1875), were formed by mixing nitroglycerin with other inert absorbents, and many combinations were tried by other companies in attempts to get around Nobel's tightly held patents for dynamite.
What was the name of the chemical that was used to make dynamite?
Similar mixtures, such as "dualine" (1867), "lithofracteur" (1869), and " gelignite " (1875), were formed by mixing nitroglycerin with other inert absorbents, and many combinations were tried by other companies in attempts to get around Nobel's tightly held patents for dynamite.
How to desensitize nitroglycerin?
Early in its history, liquid nitroglycerin was found to be " desensitized " by freezing it, at a temperature below 45 to 55 °F (7 to 13 °C) depending on its purity. Its sensitivity to shock while frozen is somewhat unpredictable: "It is more insensitive to the shock from a fulminate cap or a rifle ball when in that condition but on the other hand it appears to be more liable to explode on breaking, crushing, tamping, etc." Frozen nitroglycerine is much less energetic than liquid, and so must be thawed before use. Thawing it out can be extremely sensitizing, especially if impurities are present or the warming is too rapid. Ethylene glycol dinitrate or another polynitrate may be added to lower the melting and thereby avoid the necessity of thawing frozen explosive.
How hot is nitroglycerin?
Early in its history, liquid nitroglycerin was found to be " desensitized " by freezing it, at a temperature below 45 to 55 °F (7 to 13 °C) depending on its purity.
What is nitroglycerin used for?
Earn continuing education credits (CME/CE) on this topic. Indications. Nitroglycerin is a vasodilatory drug used primarily to provide relief from anginal chest pain. Nitroglycerin has been FDA approved since 2000 and was first sold by Pfizer under the brand name Nitrostat. It is currently FDA approved for the acute relief ...
How long does nitroglycerin stay in the body?
Nitroglycerin is primarily eliminated via metabolism in the liver and has a mean half-life of approximately 2 to 3 minutes. There are intravenous (IV) routes of administration for nitroglycerin used most commonly in emergency rooms and intensive care units (ICU).
What are the contraindications for nitroglycerin?
The contraindications of nitroglycerine therapy include: 1 Allergic reactions to nitroglycerin are extremely rare, but reports do exist. Nitroglycerin is contraindicated in patients that have reported allergic symptoms to the medication. 2 Known history of increased intracranial pressure, severe anemia, right-sided myocardial infarction, or hypersensitivity to nitroglycerin are contraindications to nitroglycerin therapy. 3 Concurrent use of nitroglycerin with PDE-5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil citrate, vardenafil hydroxide, tadalafil) is absolutely contraindicated. PDE-5 inhibitors have proven to accentuate the hypotensive effects of nitrates and precipitate syncopal episodes.
How long does it take for nitroglycerin to absorb?
Absorption takes about 5 to 10 minutes for full effect.
What is the color of blood from a patient with methemoglobinemia?
Blood from patients with methemoglobinemia has the appearance of being "chocolate brown" in color, with no change in color upon exposure to air. The treatment for methemoglobinemia is an intravenous administration of methylene blue, dosed at 1 to 2 mg/kg of the patient's body weight.
Does nitroglycerin cause venodilation?
Although nitroglycer in has a vasodilatory effect in both arteries and veins, the profound desired effects caused by nitroglycerin are primarily due to venodilation.[2] Venodilation causes pooling of blood within the venous system, reducing preload to the heart, which causes a decrease in cardiac work, reducing anginal symptoms secondary to demand ischemia. Arterial vasodilation will still occur and contribute to the relief of anginal symptoms. [3][4] Vasodilation of the coronary arteries will cause increased blood flow to the heart, increasing perfusion, but this effect remains minimal compared to the effects of venodilation.
Is Nitrous Oxide a vasodilatory drug?
This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, methods of administration, important adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and toxicity of nitrous oxide, so providers can direct patient therapy successfully in instances where nitrous oxide provides a benefit to patient care. Nitroglycerin is a vasodilatory drug used primarily ...
What is nitroglycerin used for?
Nitroglycerin is used to treat angina (chest pain). Angina is a pain or discomfort that happens when part of your heart does not get enough blood. It feels like a pressing or squeezing pain. It can happen in your chest, neck, arms (usually the left one), and lower jaw.
How does nitroglycerin help with chest pain?
Nitroglycerin works by relaxing the smooth muscle and blood vessels in your body. This increases the amount of blood and oxygen that reaches your heart. In turn, your heart doesn’t work as hard. This reduces chest pain.
What is sublingual nitroglycerin?
A sublingual tablet is a tablet that you dissolve under your tongue or inside your cheek. Nitroglycerin also comes as a spray, aerosol solution, transdermal patch, and ointment. In addition, it comes in an injectable form that’s only given by a healthcare professional.
How to store nitroglycerin?
Store nitroglycerin at room temperature. Keep it between 59°F and 86°F (15°C and 30°C).
Can Nitroglycerin cause dizziness?
Nitroglycerin can cause dizziness during the first few hours after you take it. You shouldn’t drive or use machinery until you know how this medication affects you. This drug can also cause other side effects.
Can nitroglycerin cause allergic reactions?
Allergic reactions to nitroglycerin are extremely rare, but they do occur. Symptoms can include:
Can nitroglycerin interact with other medications?
Nitroglycerin sublingual tablet can interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs you may be taking. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well.
What is the purpose of amyl nitrite?
During the second half of the 19th century, several British scientists became interested in the newly discovered amyl nitrite, recognized as a powerful vasodilator. Lauder Brunton used the compound to relieve angina in 1867, and first reported the pharmacological resistance to repeated doses.16, 17Following Brunton’s work, scientists concentrated on recording the effects of nitrite-containing compounds on several pathological systems, which include angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, hypertension and heart failure.17–21Finally, GTN was established as a treatment for the relief of angina at the end of the 19th century. However, the mechanism of action of GTN-induced benefit was discovered only 80 years later.
What is the vasodilator action of GTN?
The vasodilator action of GTN was discovered as a process mediated by nitric oxide. 22, 24Subsequent studies discovered that a chemical reaction between GTN (or other nitro compounds) and a thiol generate an intermediate S-nitrosothiol, which resulted in further production of nitric oxide.23Nowadays, it is commonly assumed that GTN is converted in smooth muscle cells to nitric oxide which activates soluble guanylate cyclase to generate cyclic GMP which, in turn, results in vascular smooth muscle relaxation (Figure 1).26
How does organic nitrate affect mitochondria?
The deleterious effects of organic nitrate therapy on mitochondrial were first described 55 years ago, where acute GTN exposure was described to induce mitochondrial swelling, to stimulated oxygen consumption and to caused loss of respiratory control of rat liver and heart mitochondria. 58More recently, it was demonstrated that GTN infusion resulted in mitochondrial dysfunction-induced oxidative stress in both animal and human blood vessels.59–61An excessive reactive oxygen species production along with reduction of more than 50% in ALDH2 activity was observed in isolated mitochondria using the complex III inhibitor antimycin A.62, 63Mitochondrial-target antioxidants prevent complex I inhibition mediated by GTN treatment.54Therefore, accumulation of reactive aldehydes derived from oxidative stress may disrupt GTN bioactivation by negatively targeting ALDH2 function. Altogether, these findings suggest that GTN bioactivation requires functionally active mitochondria, since increased reactive oxygen species production due to mitochondrial dysfunction results in impaired ALDH2 activity and further GTN conversion.35, 44, 54
What is GTN used for?
GTN remains the treatment of choice for relieving angina; other organic esters and inorganic nitrates are also used, but the rapid action of GTN and its established efficacy make it the mainstay of angina pectoris relief.4. ALDH2 in nitroglycerin bioactivation.
Does GTN reduce nitrite?
The hypothesis that nitrite produced by GTN-reductase activity of mitochondrial ALDH2 is further reduced to generate nitric oxide, which activates soluble guanylate cyclase and promotes vasodilation is well accepted (Figure 1). However, the molecular mechanisms of nitrite conversion to nitric oxide remain controversial. Chen and collaborators demonstrated that incubation of isolated mitochondria from fibroblasts with different concentrations of GTN resulted in the dose-dependent generation of nitric oxide, where ALDH2 inhibition blocked this response.45It has been reported that mammalian mitochondria present a nitrite reductase activity, associated with complex III and IV of the mitochondrial respiratory chain.47, 48However, the mechanism for the three-electron reduction of GTN to generate nitric oxide remains unknown. Recent studies demonstrated that mitochondria respiratory chain is not involved in bioactivation of GTN-derived nitrite.41, 49
Does nitroglycerin increase blood flow?
Nitroglycerin achieves its benefit by giving rise to nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation and increases blood flow to the myocardium. However, continuous delivery of nitroglycerin results in tolerance, limiting the use of this drug.
Does nitroglycerin affect cardiomyocytes?
We have recently found that, in addition to nitroglycerin’s effect on the vasculature, sustained treatment with nitroglycerin negatively affects cardiomyocyte viability following ischemia, thus resulting in increased infarct size in a myocardial infarction model in animals.
Overview
Nitroglycerin, also known as glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), is a medication used for heart failure, high blood pressure, anal fissures, painful periods, and to treat and prevent chest pain caused by decreased blood flow to the heart (angina) or due to the recreational use of cocaine. This includes chest pain from a heart attack. It is taken by mouth, under the tongue, applied to the skin, or by injection into a vein.
Medical uses
Nitroglycerin is used for the treatment of angina, acute myocardial infarction, severe hypertension, and acute coronary artery spasms. It may be administered intravenously, as a sublingual spray, or as a patch applied to the skin.
GTN is useful in decreasing angina attacks, perhaps more so than reversing angina once started, by supplementing blood concentrations of NO, also called endothelium …
Adverse events
Glyceryl trinitrate can cause severe hypotension, reflex tachycardia, and severe headaches that necessitate analgesic intervention for pain relief, the painful nature of which can have a marked negative effect on patient compliance.
GTN also can cause severe hypotension, circulatory collapse, and death if used together with vasodilator drugs that are used for erectile dysfunction, such as sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil.
Mechanism of action
GTN is a prodrug which must be denitrated, with the nitrite anion or a related species further reduced to produce the active metabolite nitric oxide (NO). Organic nitrates that undergo these two steps within the body are called nitrovasodilators, and the denitration and reduction occur via a variety of mechanisms. The mechanism by which such nitrates produce NO is widely disputed. Some believe that organic nitrates produce NO by reacting with sulfhydryl groups, while others believe t…
History
It was known almost from the time of the first synthesis of GTN by Ascanio Sobrero in 1846 that handling and tasting of nitroglycerin could cause sudden intense headaches, which suggested a vasodilation effect (as suggested by Sobrero). Constantine Hering developed a form of nitroglycerin in 1847 and advocated for its dosing as a treatment of a number of diseases; however, its use as a specific treatment for blood pressure and chest pain was not among these…
Further reading
• Ferreira JC, Mochly-Rosen D (2012). "Nitroglycerin use in myocardial infarction patients". Circulation Journal. 76 (1): 15–21. doi:10.1253/circj.cj-11-1133. PMC 3527093. PMID 22040938.
• Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT (February 2008). "The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 7 (2): 156–67. doi:10.1038/nrd2466. PMID 18167491. S2CID 5141850.